
(Extrinsic) Proteins
... From left to right are (a) a protein whose polypeptide chain traverses the membrane once as an a helix, (b) a protein that forms several transmembrane helices connected by hydrophilic loop regions, (c) a protein with several b strands that form a channel through the membrane, and (d) a protein tha ...
... From left to right are (a) a protein whose polypeptide chain traverses the membrane once as an a helix, (b) a protein that forms several transmembrane helices connected by hydrophilic loop regions, (c) a protein with several b strands that form a channel through the membrane, and (d) a protein tha ...
Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
... group being modified. The sorbents are, therefore, generally subjected to further silanization with a small reactive silane to produce an end-capped packing material. The type of n-alkyl ligand significantly influences the retention of peptides and proteins and can therefore be used to manipulate th ...
... group being modified. The sorbents are, therefore, generally subjected to further silanization with a small reactive silane to produce an end-capped packing material. The type of n-alkyl ligand significantly influences the retention of peptides and proteins and can therefore be used to manipulate th ...
protein expression after nacl treatment in two tomato cultivars
... degradation can be used as an indicator of a plant's tolerance threshold after which the plant needs to provide essential amino acids to maintain protein synthesis at stressed sites (Feller et al., 2008). The second protein in band A was identified as a structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) pr ...
... degradation can be used as an indicator of a plant's tolerance threshold after which the plant needs to provide essential amino acids to maintain protein synthesis at stressed sites (Feller et al., 2008). The second protein in band A was identified as a structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) pr ...
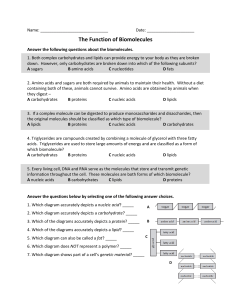
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
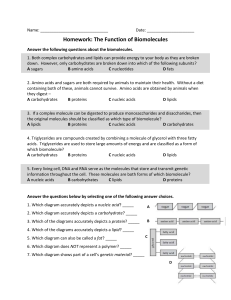
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
Chapter 10.1
... mRNA “start” codon AUG, signals beginning of protein chain, is oriented in ribosome in the P ...
... mRNA “start” codon AUG, signals beginning of protein chain, is oriented in ribosome in the P ...
Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid
... group being modified. The sorbents are, therefore, generally subjected to further silanization with a small reactive silane to produce an end-capped packing material. The type of n-alkyl ligand significantly influences the retention of peptides and proteins and can therefore be used to manipulate th ...
... group being modified. The sorbents are, therefore, generally subjected to further silanization with a small reactive silane to produce an end-capped packing material. The type of n-alkyl ligand significantly influences the retention of peptides and proteins and can therefore be used to manipulate th ...
TRANSLATION
... Stop Codon A special codon called a STOP CODON marks the end of the gene and protein synthesis. STOP ...
... Stop Codon A special codon called a STOP CODON marks the end of the gene and protein synthesis. STOP ...
Lipids and Membranes, Fall 12—Worksheet - KEY
... influenced by extracellular signals (like the chemical cues from bacteria!) causing them to group in on region of the membrane. So the reality is more complex. ...
... influenced by extracellular signals (like the chemical cues from bacteria!) causing them to group in on region of the membrane. So the reality is more complex. ...
12010_2017_2424_MOESM1_ESM
... Supplementary Fig. 1. Homology model of RT-460 generated by using 1V04 as a template. Panel A shows a ribbon diagram representing the modelled structure of RT-460 enzyme, viewed along the axis with the catalytic and the structural calcium (yellow spheres). Mutated amino acid residues (H115W, R192K, ...
... Supplementary Fig. 1. Homology model of RT-460 generated by using 1V04 as a template. Panel A shows a ribbon diagram representing the modelled structure of RT-460 enzyme, viewed along the axis with the catalytic and the structural calcium (yellow spheres). Mutated amino acid residues (H115W, R192K, ...
I will henceforth cover the importance of eating simpler meals versus
... examples of disaccharides. 3) Polysaccharides (“poly” means multiple or many), also known as complex carbohydrates or starches, are composed of 3 or more monosaccharides. No organism can use this kind of sugar in its complex form. Like disaccharides, these sugars must be broken down into simple suga ...
... examples of disaccharides. 3) Polysaccharides (“poly” means multiple or many), also known as complex carbohydrates or starches, are composed of 3 or more monosaccharides. No organism can use this kind of sugar in its complex form. Like disaccharides, these sugars must be broken down into simple suga ...
NUTRITION
... Plant protein foods contain: Less saturated fat More fibre Cheaper to produce ...
... Plant protein foods contain: Less saturated fat More fibre Cheaper to produce ...
Protein and amino acids
... acids (AAs), which can be regarded as the building blocks for the formation of skin, muscle tissue, feathers, eggs, etc. Body proteins are in a dynamic state with synthesis and degradation occurring continuously; therefore, a constant, adequate intake of dietary AAs is required. An inadequate intake ...
... acids (AAs), which can be regarded as the building blocks for the formation of skin, muscle tissue, feathers, eggs, etc. Body proteins are in a dynamic state with synthesis and degradation occurring continuously; therefore, a constant, adequate intake of dietary AAs is required. An inadequate intake ...
Appendix
... following the procedure described by Burns and Zydney (2000). Typical experimental data obtained using a 1 mM Bis-Tris buffer with 10 mM NaCl at pH 7 are shown in Figure A1 for an unmodified 300 kDa UltracelTM membrane and a negatively-charged version that was charged for 24 hr. The apparent zeta po ...
... following the procedure described by Burns and Zydney (2000). Typical experimental data obtained using a 1 mM Bis-Tris buffer with 10 mM NaCl at pH 7 are shown in Figure A1 for an unmodified 300 kDa UltracelTM membrane and a negatively-charged version that was charged for 24 hr. The apparent zeta po ...
Chapter 2 : The Chemistry of Life Section 3 : Carbon
... Four Major Groups of Macromolecules (found in living things) ...
... Four Major Groups of Macromolecules (found in living things) ...
Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
Efficacy of fungicide treatments on the winter wheat senescence
... winter wheat cv. ‛Zentos’. The efficacy of F use on the parameters tested depended on the weather conditions of the harvest year and on the F applied. F use prolonged retention of green canopy of wheat plants in 2003–2004. Chlorophyll concentrations in flag leaves at the end of plant vegetation, i. ...
... winter wheat cv. ‛Zentos’. The efficacy of F use on the parameters tested depended on the weather conditions of the harvest year and on the F applied. F use prolonged retention of green canopy of wheat plants in 2003–2004. Chlorophyll concentrations in flag leaves at the end of plant vegetation, i. ...
Bioinformatics in Brief This week: DB for structures Structure
... Many unexpected links: • Histon and heat-shock protein ...
... Many unexpected links: • Histon and heat-shock protein ...
Liver Function - Wk 1-2
... Like all other biological molecules, proteins have a limited life span and must be broken down and replaced before they begin to deteriorate. As proteins are broken down, their amino acids are recycled and used in building new proteins or modified to form a different N-containing compound. Newly ing ...
... Like all other biological molecules, proteins have a limited life span and must be broken down and replaced before they begin to deteriorate. As proteins are broken down, their amino acids are recycled and used in building new proteins or modified to form a different N-containing compound. Newly ing ...
The 14-3-3 proteins in regulation of cellular metabolism - BORA
... and interactomic studies clearly illustrate the diverse biological functions associated with this protein family. The extensive interactome of the 14-3-3 proteins and its regulation by protein phosphorylation events suggest a fundamental function of these proteins in signaling related to cellular me ...
... and interactomic studies clearly illustrate the diverse biological functions associated with this protein family. The extensive interactome of the 14-3-3 proteins and its regulation by protein phosphorylation events suggest a fundamental function of these proteins in signaling related to cellular me ...
HydF as a scaffold protein in [FeFe] hydrogenase H
... HydADEFG, demonstrating an essential role for HydE and HydG in forming the activation-competent form of HydF. These results, which demonstrate the ability of purified HydFEG to activate HydADEFG in the absence of any other proteins or small molecules, support our hypothesis that HydF serves as a scaff ...
... HydADEFG, demonstrating an essential role for HydE and HydG in forming the activation-competent form of HydF. These results, which demonstrate the ability of purified HydFEG to activate HydADEFG in the absence of any other proteins or small molecules, support our hypothesis that HydF serves as a scaff ...
5.1 How Is the Structure of the Cell Membrane Related to Its Function?
... – Water-soluble substances such as salts, amino acids, and sugars cannot easily cross phospholipid bilayers ...
... – Water-soluble substances such as salts, amino acids, and sugars cannot easily cross phospholipid bilayers ...
Enzymes - TeacherWeb
... • The substrate – Is the reactant an enzyme acts on • The enzyme – binds to its substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate complex ...
... • The substrate – Is the reactant an enzyme acts on • The enzyme – binds to its substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate complex ...
28P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... to yield a first-order velocity constant for the rate of approach to pH equilibrium. Between pH6 and pH7 mitochondria in distilled water increased the rate constant for the approach to equilibrium from the alkaline side (002 hydration predominating). At pH6.4 the rate constant was doubled by 1.2mg o ...
... to yield a first-order velocity constant for the rate of approach to pH equilibrium. Between pH6 and pH7 mitochondria in distilled water increased the rate constant for the approach to equilibrium from the alkaline side (002 hydration predominating). At pH6.4 the rate constant was doubled by 1.2mg o ...
Lecture 13
... Fundamental points about conformational studies • While exciting, these are often very difficult experiments, requiring a lot of time and good control experiments • The data one gets is often ambiguous, but no more so than solid state structures obtained in X-Ray crystallography • It’s crucial to d ...
... Fundamental points about conformational studies • While exciting, these are often very difficult experiments, requiring a lot of time and good control experiments • The data one gets is often ambiguous, but no more so than solid state structures obtained in X-Ray crystallography • It’s crucial to d ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.

















![HydF as a scaffold protein in [FeFe] hydrogenase H](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022194833_1-d80dffc73c0d81a42175e12a27187746-300x300.png)



