Sodium dodecyl sulfate (L3771)
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
emboj7600663-sup
... monomer) in the cell with 180 seconds between two consecutive injections, while the sample was stirred at 316 rpm. In experiments for studying the effect of the L2 domain on nucleotide binding, the L2 was added into both the cell and the injection syringe to the final concentration of 30 M. For L2 ...
... monomer) in the cell with 180 seconds between two consecutive injections, while the sample was stirred at 316 rpm. In experiments for studying the effect of the L2 domain on nucleotide binding, the L2 was added into both the cell and the injection syringe to the final concentration of 30 M. For L2 ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis (pp 300 – 306)
... • There is one codon AUG that can either specify the amino acid methionine or serve as a “start” codon for protein synthesis • There are three “stop” codons that do not code for any amino acids • These “stop” codons signify the end of a polypeptide ...
... • There is one codon AUG that can either specify the amino acid methionine or serve as a “start” codon for protein synthesis • There are three “stop” codons that do not code for any amino acids • These “stop” codons signify the end of a polypeptide ...
Title Gene Synthesis, Expression, and Mutagenesis of Zucchini
... with the expected molecular weight on an agarose gel (data not shown), being inserted into the linearized pET-15b to yield pMAV1-1 (6.0 kbp). The insert of pMAV1-1 had the correct nucleotide sequence over the entire length of the synthetic gene. Protein expression, purification, and reconstitution. ...
... with the expected molecular weight on an agarose gel (data not shown), being inserted into the linearized pET-15b to yield pMAV1-1 (6.0 kbp). The insert of pMAV1-1 had the correct nucleotide sequence over the entire length of the synthetic gene. Protein expression, purification, and reconstitution. ...
Enzymes: Regulatory - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Regulatory - Allosteric enzyme Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) Feedback control by production of end product of pathway Allosteric inhibition - CTP inhibits aspartate transcarbamoylase by binding to a regulatory site (not an active site) ...
... Regulatory - Allosteric enzyme Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) Feedback control by production of end product of pathway Allosteric inhibition - CTP inhibits aspartate transcarbamoylase by binding to a regulatory site (not an active site) ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • During translation, the codons are read in the 5’->3’ direction along the mRNA. • Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated at the corresponding position along a polypeptide. • Because codons are base triplets, the number of nucleotides making up a genetic message ...
... • During translation, the codons are read in the 5’->3’ direction along the mRNA. • Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated at the corresponding position along a polypeptide. • Because codons are base triplets, the number of nucleotides making up a genetic message ...
biochem ch 37 [2-9
... o Patients suffer muscle wasting and decreased concentration of plasma proteins, particularly albumin o Result is increase in interstitial fluid that causes edema and distended abdomen o Muscle wasting caused by lack of essential AAs in diet; existing proteins must be broken down to produce AAs for ...
... o Patients suffer muscle wasting and decreased concentration of plasma proteins, particularly albumin o Result is increase in interstitial fluid that causes edema and distended abdomen o Muscle wasting caused by lack of essential AAs in diet; existing proteins must be broken down to produce AAs for ...
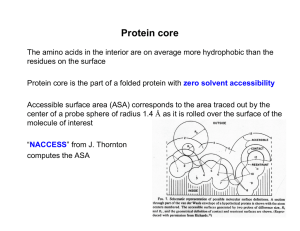
Protein core - Acsu.buffalo.edu
... Simple hydrophobic interaction can contribute more to stability than buried salt bridges, while offering conformational specificity required for function However, internal salt bridges may confer specificity by discriminating against alternate conformations ...
... Simple hydrophobic interaction can contribute more to stability than buried salt bridges, while offering conformational specificity required for function However, internal salt bridges may confer specificity by discriminating against alternate conformations ...
Notes Protein Synthesis
... • The first 20 amino acids of the polypeptide serve as a signal peptide and act as a cellular zip code, directing the polypeptide to its final ...
... • The first 20 amino acids of the polypeptide serve as a signal peptide and act as a cellular zip code, directing the polypeptide to its final ...
Protein Function and Classification
... • Curators manually inspect the matches before integrating the signatures into InterPro ...
... • Curators manually inspect the matches before integrating the signatures into InterPro ...
L. helveticus - NC State University
... The Lactobacillus acidophilus complex is a clade of homologous Gram-positive, lactic acid bacteria including L. acidophilus, L. helveticus, L. crispatus, L. amylovorus, L. gallinarum, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, L. gasseri, and L. johnsonii. Although these bacteria are closely related, they ha ...
... The Lactobacillus acidophilus complex is a clade of homologous Gram-positive, lactic acid bacteria including L. acidophilus, L. helveticus, L. crispatus, L. amylovorus, L. gallinarum, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, L. gasseri, and L. johnsonii. Although these bacteria are closely related, they ha ...
Metabolism
... inorganic substances such as including water, vitamins and minerals (Na, Fe, etc.) The USDA has made major revision in its nutritional ...
... inorganic substances such as including water, vitamins and minerals (Na, Fe, etc.) The USDA has made major revision in its nutritional ...
PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE
... Changes in Protein Structure Upon Heating Proteins are complex molecules made from long, amino acid chains which are also branched. The chains are held together by intermolecular bonding between the side chains of the constituent amino acids. Hydrogen bonds occur between the amide links and between ...
... Changes in Protein Structure Upon Heating Proteins are complex molecules made from long, amino acid chains which are also branched. The chains are held together by intermolecular bonding between the side chains of the constituent amino acids. Hydrogen bonds occur between the amide links and between ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... in the transport of the amino acids or that mare than one “hit” is necessary to inactivate the transport system. If the straight line portion of the curve is extrapolated back to the zero dosage, the intercept values for phenylalanine, tryptophon and leucine are near two. This would indicate that pr ...
... in the transport of the amino acids or that mare than one “hit” is necessary to inactivate the transport system. If the straight line portion of the curve is extrapolated back to the zero dosage, the intercept values for phenylalanine, tryptophon and leucine are near two. This would indicate that pr ...
Transient transfection (Oprian, Molday et al. 1987) was carried with
... have acidic motifs that binds Ca2+, such as calmodulin and calsequestrin (Campbell, MacLennan et al. 1983). CaBPs stain blue with Stains-all, whereas other proteins stain pink and the color fades away quickly in the light. Sharma and Balasubramanian (1991) reported that CaBPs could be separated into ...
... have acidic motifs that binds Ca2+, such as calmodulin and calsequestrin (Campbell, MacLennan et al. 1983). CaBPs stain blue with Stains-all, whereas other proteins stain pink and the color fades away quickly in the light. Sharma and Balasubramanian (1991) reported that CaBPs could be separated into ...
Chapeville
... This key concept in the tRNA adapter hypothesis was subject to a direct test. In 1962, Chapeville and his colleagues, under the auspices of Seymour Benzer, switched the contents of such a tRNA “letter” to see if it made any difference in where it was delivered (figure 15.1). What they did was charge ...
... This key concept in the tRNA adapter hypothesis was subject to a direct test. In 1962, Chapeville and his colleagues, under the auspices of Seymour Benzer, switched the contents of such a tRNA “letter” to see if it made any difference in where it was delivered (figure 15.1). What they did was charge ...
Test 1
... exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Both peptides will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide A will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide B will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide A will bind to an anion exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide B will bind to ...
... exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Both peptides will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide A will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide B will bind to a cation exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide A will bind to an anion exchange resin at pH 7. ____ Peptide B will bind to ...
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 1. In DNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 2. In RNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 3. Transcription takes place in the ________________; translation takes place in the _______________. 4. The building blocks of nucleic ac ...
... 1. In DNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 2. In RNA, adenine binds with ____________ and guanine binds with _____________. 3. Transcription takes place in the ________________; translation takes place in the _______________. 4. The building blocks of nucleic ac ...
Single TMS Receptors
... globular domains. On the extracellular side is the binding site for the hormone, on the cystolic side of the membrane there is a catalytic domain, typically a tyrosine kinase or guanylate cyclase. For our first example consider the human growth hormone and its receptor. The human growth hormone is a ...
... globular domains. On the extracellular side is the binding site for the hormone, on the cystolic side of the membrane there is a catalytic domain, typically a tyrosine kinase or guanylate cyclase. For our first example consider the human growth hormone and its receptor. The human growth hormone is a ...
1 Proteins: Workshop I Amino Acids
... c. Intermolecular forces are an important aspect of the interaction between a pharmaceutical and its receptor site. Experimental evidence indicates that drugs interact with receptor sites which have protein-like properties. Hydrophobic bonds (London dispersion forces) are formed between non-polar hy ...
... c. Intermolecular forces are an important aspect of the interaction between a pharmaceutical and its receptor site. Experimental evidence indicates that drugs interact with receptor sites which have protein-like properties. Hydrophobic bonds (London dispersion forces) are formed between non-polar hy ...
(CH14) Translation (Slides)
... Ribosomes are the protein synthesis machinery • Assemble in the nucleolus of the cell and are exported to the cytoplasm. • Decode the genetic code in the mRNA. ...
... Ribosomes are the protein synthesis machinery • Assemble in the nucleolus of the cell and are exported to the cytoplasm. • Decode the genetic code in the mRNA. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.