I. Introduction to NMR spectroscopy
... What are some useful ranges to remember? H's on C next to C=O H's on C with N H's on C with O or X OH or NH in alcohols or amines H's on C=C H's on aromatic ring H's on amides H's on C=O OH in carboxylic acids ...
... What are some useful ranges to remember? H's on C next to C=O H's on C with N H's on C with O or X OH or NH in alcohols or amines H's on C=C H's on aromatic ring H's on amides H's on C=O OH in carboxylic acids ...
C–H Bond Functionalization in Complex Organic Synthesis REVIEW
... These reactions are frequently applied to the synthesis of advanced intermediates and natural products (12). Several features make them attractive in this respect, including neutral reaction conditions, good functional group tolerance, and a high degree of stereoselectivity. They provide a unique an ...
... These reactions are frequently applied to the synthesis of advanced intermediates and natural products (12). Several features make them attractive in this respect, including neutral reaction conditions, good functional group tolerance, and a high degree of stereoselectivity. They provide a unique an ...
Chem 30CL - Lecture 1c - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Chiral pool: optically active compounds that can be isolated from natural sources (i.e., amino acids, monosaccharides, terpenes, etc.) and can be used as reactants or as part of a chiral catalyst or a chiral auxiliary • The TADDOL, DIOP and the Chiraphos ligand have tartaric acid as ...
... • Chiral pool: optically active compounds that can be isolated from natural sources (i.e., amino acids, monosaccharides, terpenes, etc.) and can be used as reactants or as part of a chiral catalyst or a chiral auxiliary • The TADDOL, DIOP and the Chiraphos ligand have tartaric acid as ...
Origin of the Diastereoselection in the Indium
... obtained in 55% and 62% yields under refluxing EtOH and H2O, respectively. The yields were improved in a mixed solvent of H2O and an organic solvent at reflux temperatures. The best result was obtained in a 4:1 volumetric mixture of H2O and THF at reflux for 2.5 h, in which the homoallylic alcohol 3 ...
... obtained in 55% and 62% yields under refluxing EtOH and H2O, respectively. The yields were improved in a mixed solvent of H2O and an organic solvent at reflux temperatures. The best result was obtained in a 4:1 volumetric mixture of H2O and THF at reflux for 2.5 h, in which the homoallylic alcohol 3 ...
Dicyanomethylenedihydrofuran photorefractive materials
... Scheme 3. Synthesis of 12, 13 and 14 with the acceptor ring attached directly to the benzene ring. ...
... Scheme 3. Synthesis of 12, 13 and 14 with the acceptor ring attached directly to the benzene ring. ...
Modulation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Protease
... Mature, fully active human immunodeficiency virus protease (PR) is liberated from the Gag-Pol precursor via regulated autoprocessing. A chimeric protease precursor, glutathione S-transferase–transframe region (TFR)–PR–FLAG, also undergoes N-terminal autocatalytic maturation when it is expressed in E ...
... Mature, fully active human immunodeficiency virus protease (PR) is liberated from the Gag-Pol precursor via regulated autoprocessing. A chimeric protease precursor, glutathione S-transferase–transframe region (TFR)–PR–FLAG, also undergoes N-terminal autocatalytic maturation when it is expressed in E ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Synthesis of monoazo disperse dyes, their dyeing performance on polyester fibers and ….. Preparation of 2-chloro-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide(2) 4-nitro aniline (2.76 g, 0.02 mole) and 15 ml glacial acetic acid was added to a 250 ml R.B.F. then cooled to 0-5 ◦ C. Chloroacetyl chloride (3.39ml, 0.02 m ...
... Synthesis of monoazo disperse dyes, their dyeing performance on polyester fibers and ….. Preparation of 2-chloro-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide(2) 4-nitro aniline (2.76 g, 0.02 mole) and 15 ml glacial acetic acid was added to a 250 ml R.B.F. then cooled to 0-5 ◦ C. Chloroacetyl chloride (3.39ml, 0.02 m ...
Lecture 16 Aromatic Diazonium Salts
... Aromatic azo-compounds are coloured. Several of those compounds synthesized by the diazo-coupling are employed as dye-stuffs. These compounds can be classified into three groups. ...
... Aromatic azo-compounds are coloured. Several of those compounds synthesized by the diazo-coupling are employed as dye-stuffs. These compounds can be classified into three groups. ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... Synthesis of carboxylic acids using malonic ester via the decarboxylation of malonic acid The malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide into a ...
... Synthesis of carboxylic acids using malonic ester via the decarboxylation of malonic acid The malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide into a ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
1 THE BARTON-McCOMBIE REACTION STUART W. McCOMBIE 28
... Deoxygenations of alcohols, i.e. processes that replace a hydroxyl group with hydrogen at a saturated carbon, find applications in both total synthesis and the systematic modification of natural products. They may also be employed to introduce deuterium or tritium in a site-specific manner. Reductiv ...
... Deoxygenations of alcohols, i.e. processes that replace a hydroxyl group with hydrogen at a saturated carbon, find applications in both total synthesis and the systematic modification of natural products. They may also be employed to introduce deuterium or tritium in a site-specific manner. Reductiv ...
- Wiley Online Library
... used, optically pure @-aminoalcohols were obtained. This inspired us to investigate the use of LiBH,/Me,SiCI as a reducing agent for other functional groups. Thus, simple carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols (No. 5), while primary, secondary and tertiary amides (Nos. 6-8) and nitriles (Nos. 10-1 ...
... used, optically pure @-aminoalcohols were obtained. This inspired us to investigate the use of LiBH,/Me,SiCI as a reducing agent for other functional groups. Thus, simple carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols (No. 5), while primary, secondary and tertiary amides (Nos. 6-8) and nitriles (Nos. 10-1 ...
Microbiology (MIC)
... biogeochemical cycling of elements, interactions of microorganisms with other aquatic biota, the role of microorganisms in pollution problems, and applications of microbial ecology to biotechnology. Laboratory emphasis is on experimental design and sampling techniques, quantification of microbial bi ...
... biogeochemical cycling of elements, interactions of microorganisms with other aquatic biota, the role of microorganisms in pollution problems, and applications of microbial ecology to biotechnology. Laboratory emphasis is on experimental design and sampling techniques, quantification of microbial bi ...
Methods in Molecular Biology 1297: RNA Nanotechnology and
... only biopolymer that has the ability to serve as a repository of genetic information, an architectural building block, and a catalyst for chemical reactions. The diversity of RNA biological functions relies on complex architectures that fold from single strands into a hierarchical sequence of second ...
... only biopolymer that has the ability to serve as a repository of genetic information, an architectural building block, and a catalyst for chemical reactions. The diversity of RNA biological functions relies on complex architectures that fold from single strands into a hierarchical sequence of second ...
5 end
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins ...
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins ...
- Iranian Chemical Communication
... phase-transfer catalyst and in the presence of potassium carbonate (K2CO3). A wide range of esters and thioesters was prepared in high yields and suitable times by the treatment of alcohols, phenols and thiols with acetic anhydride. Acylation reactions of a number of alcohols, phenols and thiols wit ...
... phase-transfer catalyst and in the presence of potassium carbonate (K2CO3). A wide range of esters and thioesters was prepared in high yields and suitable times by the treatment of alcohols, phenols and thiols with acetic anhydride. Acylation reactions of a number of alcohols, phenols and thiols wit ...
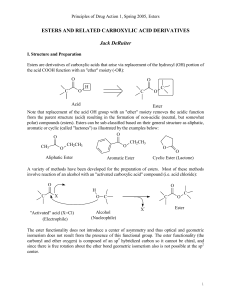
esters and related carboxylic acid derivatives
... In the introduction of this section it was noted that esters are derivatives of carboxylic acids which arise via replacement of the -OH portion of the acid COOH function with an "ether" moiety (-OR) and that this replacement removes the acidic function from the parent structure (acid) resulting in t ...
... In the introduction of this section it was noted that esters are derivatives of carboxylic acids which arise via replacement of the -OH portion of the acid COOH function with an "ether" moiety (-OR) and that this replacement removes the acidic function from the parent structure (acid) resulting in t ...
RIBOSWITCHES - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Structural studies of aptamer-ligand complexes have provided a wealth of information regarding RNA structure and ligand interaction ...
... Structural studies of aptamer-ligand complexes have provided a wealth of information regarding RNA structure and ligand interaction ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.