Assignment 4: The mutation
... The scientists located a normal allele of the candidate gene in the database. The DNA sequence of the normal allele is known. What do you think the next step should be? What question will the researchers ask? At this stage, the scientists must find the difference between the allele that is considere ...
... The scientists located a normal allele of the candidate gene in the database. The DNA sequence of the normal allele is known. What do you think the next step should be? What question will the researchers ask? At this stage, the scientists must find the difference between the allele that is considere ...
Using Yeast to study Eukaryotic Gene Function From Recombinant
... Homolgous recombination is a relative frequent event in yeast ...
... Homolgous recombination is a relative frequent event in yeast ...
Chapter 20 – DNA Technology - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 5. One feature of “engineered” plasmids that is helpful in the isolation and analysis of cloned DNA is: a) they can only handle DNA fragments of up to 120 kb b) that they are an integral part of all eukaryotic cells c) they contain no genetic material of their own so that the cloned fragment is trul ...
... 5. One feature of “engineered” plasmids that is helpful in the isolation and analysis of cloned DNA is: a) they can only handle DNA fragments of up to 120 kb b) that they are an integral part of all eukaryotic cells c) they contain no genetic material of their own so that the cloned fragment is trul ...
Notes
... IQ domain that block calmodulin binding also block the activation of CRE-dependent gene transcription while retaining normal calcium influx. These mutations selectively inhibit the ability of calcium entering through the L-VGCC to activate the Ras–MAPK pathway, and the activation of channels with IQ ...
... IQ domain that block calmodulin binding also block the activation of CRE-dependent gene transcription while retaining normal calcium influx. These mutations selectively inhibit the ability of calcium entering through the L-VGCC to activate the Ras–MAPK pathway, and the activation of channels with IQ ...
Lecture 15 - Psychology
... If marker and trait gene are far away from one another, independent assortment occurs This pedigree demonstrates a random association with the A allele and the disorder, which indicates that A and D are not linked ...
... If marker and trait gene are far away from one another, independent assortment occurs This pedigree demonstrates a random association with the A allele and the disorder, which indicates that A and D are not linked ...
PDF
... [6-9]. No protein gene sequence information has been available from any plant-pathogenic MLO, and thus their codon usage was unknown. In order to obtain comparable data for the MLOs, we cloned and sequenced a segment of an operon containing several ribosomal protein genes. Since ribosomal protein ge ...
... [6-9]. No protein gene sequence information has been available from any plant-pathogenic MLO, and thus their codon usage was unknown. In order to obtain comparable data for the MLOs, we cloned and sequenced a segment of an operon containing several ribosomal protein genes. Since ribosomal protein ge ...
The DNA Connection
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
LLog4 - CH 4
... female mating preferences could lead to the evolution of elaborate patterns in males. Human observation is flawed though, since we can’t see UV colors, unlike most birds. However some can’t see UV as well (birds with the amino acid serine see violet, while those with cysteine see the UV range). Star ...
... female mating preferences could lead to the evolution of elaborate patterns in males. Human observation is flawed though, since we can’t see UV colors, unlike most birds. However some can’t see UV as well (birds with the amino acid serine see violet, while those with cysteine see the UV range). Star ...
Overview Discontinuous variation Genetic methodology Continuous
... Genes are segments of DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Hereditary variation is caused by variant forms of genes known as alleles. Alleles can be studied at many levels. Each species has its own distinctive pool of genes. Evolution is a consequence of genetic changes in a popula ...
... Genes are segments of DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Hereditary variation is caused by variant forms of genes known as alleles. Alleles can be studied at many levels. Each species has its own distinctive pool of genes. Evolution is a consequence of genetic changes in a popula ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... DNA, functioning as the hereditary material, ultimately determines the traits of an individual. The idea that this one type of molecule can play such a singular role in determining our characteristics is remarkable. What is still more amazing is the manner in which DNA affects these traits. DNA func ...
... DNA, functioning as the hereditary material, ultimately determines the traits of an individual. The idea that this one type of molecule can play such a singular role in determining our characteristics is remarkable. What is still more amazing is the manner in which DNA affects these traits. DNA func ...
PowerPoint file
... processing algorithms and methods are used to study functional structures in the DNA. An appropriate mapping of the DNA sequence into one or more numerical sequences, enables the use of many digital signal processing tools. DNA Segment ...
... processing algorithms and methods are used to study functional structures in the DNA. An appropriate mapping of the DNA sequence into one or more numerical sequences, enables the use of many digital signal processing tools. DNA Segment ...
Chapter 3 PPT 3 - Blair Community Schools
... • Furrow deepens until it pinches into two daughter cells • Each daughter cell is smaller and has less cytoplasm than mother cell but is genetically identical ...
... • Furrow deepens until it pinches into two daughter cells • Each daughter cell is smaller and has less cytoplasm than mother cell but is genetically identical ...
Microbial diversity
... Sequence of 16 S rRNA gene often used to compare organisms 16 S rRNA gene amplified by PCR PCR product sequenced and sequence compared with that of known organism New development: comparative genomics ...
... Sequence of 16 S rRNA gene often used to compare organisms 16 S rRNA gene amplified by PCR PCR product sequenced and sequence compared with that of known organism New development: comparative genomics ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... analyze the impact of genotype/phenotype interactions on gene expression. 4. Explain the genetic basis of heterogeneous traits, quantitative traits, and cancer (multiple-hit hypothesis). Explain the various techniques of genetic testing, the current state of gene therapy, and the future potential of ...
... analyze the impact of genotype/phenotype interactions on gene expression. 4. Explain the genetic basis of heterogeneous traits, quantitative traits, and cancer (multiple-hit hypothesis). Explain the various techniques of genetic testing, the current state of gene therapy, and the future potential of ...
DNA – RNA – PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
... Watson and Crick’s model of DNA was called a ____________________________________, in which two strands were wound around each other, like a twisted ladder or spiral ...
... Watson and Crick’s model of DNA was called a ____________________________________, in which two strands were wound around each other, like a twisted ladder or spiral ...
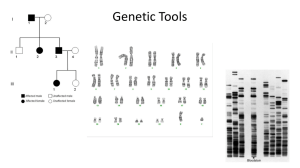
Genetic Tools
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
Molecular Evolution
... • The differences in the rates of evolution are usually due to functional constraints • mutations that remove or reduce the function of a gene are removed by negative selection • very important genes tend to evolve slowly • proteins (gene products) that interact with other proteins etc. also evo ...
... • The differences in the rates of evolution are usually due to functional constraints • mutations that remove or reduce the function of a gene are removed by negative selection • very important genes tend to evolve slowly • proteins (gene products) that interact with other proteins etc. also evo ...
4-2 Sources of DNA
... Characteristics of Mammalian Cells • Require stringent environment, very shear sensitive • Many are attachment dependent • In addition to typical metabolic requirements, cells need growth factors and other proteins • Mammalian cells grow at a much slower rate than bacteria and yeast, doubling every ...
... Characteristics of Mammalian Cells • Require stringent environment, very shear sensitive • Many are attachment dependent • In addition to typical metabolic requirements, cells need growth factors and other proteins • Mammalian cells grow at a much slower rate than bacteria and yeast, doubling every ...
myPresentation
... Is there any way to rank these and then list only the ‘best’? Also, be careful to explain what the red text is highlighting Convert the underxpressed fold change as follows: -1/foldchange - that will make 0.1 = -10 fold change for example ...
... Is there any way to rank these and then list only the ‘best’? Also, be careful to explain what the red text is highlighting Convert the underxpressed fold change as follows: -1/foldchange - that will make 0.1 = -10 fold change for example ...
Multiple choice questions BIO1130FF
... b. a disease-causing group of proteins X c. an entity composed of proteins and nucleic acids d. an entity composed of proteins, nucleic acids, and ribosomes FF.13 The habitat overpasses along the transCanada highway in the Canadian Rockies are trying to solve a problem created by this. (Choose the m ...
... b. a disease-causing group of proteins X c. an entity composed of proteins and nucleic acids d. an entity composed of proteins, nucleic acids, and ribosomes FF.13 The habitat overpasses along the transCanada highway in the Canadian Rockies are trying to solve a problem created by this. (Choose the m ...
DNA 101 intro
... forms – an allele that can produce blue eyes (b), and an allele that produces brown eyes (B). In a plant that occurs in tall and short forms, there may be an allele that tends to produce tall plants (T) and an alternative allele that produces short plants (t). • The individual genes that form a pair ...
... forms – an allele that can produce blue eyes (b), and an allele that produces brown eyes (B). In a plant that occurs in tall and short forms, there may be an allele that tends to produce tall plants (T) and an alternative allele that produces short plants (t). • The individual genes that form a pair ...