Introduction to Nucleic Acids
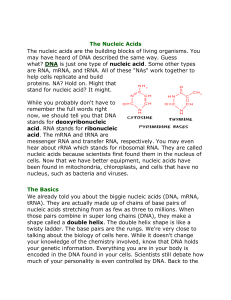
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
Multiple choice questions BIO1130MM
... c. a group of biotically produced innorganic molecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure. d. a group of biotically produced organic molecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure. MM.5 In modern terminology, diversity is understood to be a result of genetic variation. Sources of variation f ...
... c. a group of biotically produced innorganic molecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure. d. a group of biotically produced organic molecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure. MM.5 In modern terminology, diversity is understood to be a result of genetic variation. Sources of variation f ...
DNAAlias - UBC Let`s Talk Science
... The kids write down their own name. On the worksheet is a code giving the nucleotides for each letter in the alphabet. The kids figure out the 3 letter code for each letter in their name. Each of the four nucleotides is represented by a different colour. The kids put a white bead on the string ...
... The kids write down their own name. On the worksheet is a code giving the nucleotides for each letter in the alphabet. The kids figure out the 3 letter code for each letter in their name. Each of the four nucleotides is represented by a different colour. The kids put a white bead on the string ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 24
... D. Metastasis Tumor cells travel through lymphatic and/or blood vessels to new sites Blood flow patterns influence sites of metastasis Growth factor production by “target” organs can influence success of tumor metastasis E. Immune system response to cancer cells III. Causes of Cancer A. Epidemiologi ...
... D. Metastasis Tumor cells travel through lymphatic and/or blood vessels to new sites Blood flow patterns influence sites of metastasis Growth factor production by “target” organs can influence success of tumor metastasis E. Immune system response to cancer cells III. Causes of Cancer A. Epidemiologi ...
Knowledge-based Analysis of Microarray Gene Expression Data
... Most current methods employ unsupervised learning methods (at the time of the publication) ...
... Most current methods employ unsupervised learning methods (at the time of the publication) ...
The plant cell that is responsible for asexual reproduction is called
... chromosomes, how many would each the sperm and the egg have? ...
... chromosomes, how many would each the sperm and the egg have? ...
Genetics Notes
... f. 6th basic principle is that some genes are neither dominant nor recessive, they show incomplete dominance or codominance. 6. Genes are units of heredity or characteristics of an organism. 7. Dominant genes are “stronger” genes and always show up when 2 different genes are crossed. They are always ...
... f. 6th basic principle is that some genes are neither dominant nor recessive, they show incomplete dominance or codominance. 6. Genes are units of heredity or characteristics of an organism. 7. Dominant genes are “stronger” genes and always show up when 2 different genes are crossed. They are always ...
Facts about the Worm C. elegans
... o About 20 000 genes (humans: 30 000) About 6 000 C. elegans genes have human homologues o Entire genome of C. elegans has been sequenced, and so has that of 4 other similar worms, with another 5-10 on the way Laboratory Experiments o Knock out one gene at a time to see what the effect is o Insert ...
... o About 20 000 genes (humans: 30 000) About 6 000 C. elegans genes have human homologues o Entire genome of C. elegans has been sequenced, and so has that of 4 other similar worms, with another 5-10 on the way Laboratory Experiments o Knock out one gene at a time to see what the effect is o Insert ...
Exp DAV Spike protein
... Summary • DAV-spike gene was amplified by PCR using primers flanking the coding sequence • The PCR product was successfully cloned into TOPO vector • Re-cloning the DAV-spike gene into the expression vector result is pending • After successfully ligating into the expression vector, Purify the vecto ...
... Summary • DAV-spike gene was amplified by PCR using primers flanking the coding sequence • The PCR product was successfully cloned into TOPO vector • Re-cloning the DAV-spike gene into the expression vector result is pending • After successfully ligating into the expression vector, Purify the vecto ...
Document
... C8. These drugs would diminish the amount of negative supercoiling. Negative supercoiling is needed to compact the chromosomal DNA, and it also aids in strand separation. Bacteria might not be able to survive and/or transmit their chromosomes to daughter cells if their DNA was not compacted properly ...
... C8. These drugs would diminish the amount of negative supercoiling. Negative supercoiling is needed to compact the chromosomal DNA, and it also aids in strand separation. Bacteria might not be able to survive and/or transmit their chromosomes to daughter cells if their DNA was not compacted properly ...
C1. Self-assembly occurs spontaneously, without the aid of other
... C8. These drugs would diminish the amount of negative supercoiling. Negative supercoiling is needed to compact the chromosomal DNA, and it also aids in strand separation. Bacteria might not be able to survive and/or transmit their chromosomes to daughter cells if their DNA was not compacted properly ...
... C8. These drugs would diminish the amount of negative supercoiling. Negative supercoiling is needed to compact the chromosomal DNA, and it also aids in strand separation. Bacteria might not be able to survive and/or transmit their chromosomes to daughter cells if their DNA was not compacted properly ...
Dissection of a DNA-damage-induced transcriptional network using
... knocked-down for Rel-A, p53 and ATM), each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
... knocked-down for Rel-A, p53 and ATM), each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... RNA (a genetic blueprint for a single DNA strand) Translation: Definition: Used with the ribosome the mRNA(messenger RNA) is then used to create a protein, which is the building block for most organisms. The mRNA carries specific codes each form certain types of proteins. Codon Definition: A sequenc ...
... RNA (a genetic blueprint for a single DNA strand) Translation: Definition: Used with the ribosome the mRNA(messenger RNA) is then used to create a protein, which is the building block for most organisms. The mRNA carries specific codes each form certain types of proteins. Codon Definition: A sequenc ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 1 Notes, Part 3 – The Importance of
... 12. According to the information given in Section A, there are four mechanisms that can create new gene sequences or new combinations of genes to increase genetic variation within a population of organisms: mutation during DNA replication, crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilizat ...
... 12. According to the information given in Section A, there are four mechanisms that can create new gene sequences or new combinations of genes to increase genetic variation within a population of organisms: mutation during DNA replication, crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilizat ...
Modelling Gene Regulatory Networks Using Computational
... while a simple organism such as Drosophila melanogaster, also known as the fruit fly has about 14,000 genes. Therefore, the complexity may be due to a phenomena such as regulation of expression of genes in both temporal and spatial manners. A prerequisite for cellular behaviour is that the correct g ...
... while a simple organism such as Drosophila melanogaster, also known as the fruit fly has about 14,000 genes. Therefore, the complexity may be due to a phenomena such as regulation of expression of genes in both temporal and spatial manners. A prerequisite for cellular behaviour is that the correct g ...
An Introduction to Affymetrix Microarrays
... cDNAs have different hybridization properties due to their biochemistry Oligos may be chosen to have similar hybridization properties - and to represent maximally unique parts of genes - or to represent common domains ...
... cDNAs have different hybridization properties due to their biochemistry Oligos may be chosen to have similar hybridization properties - and to represent maximally unique parts of genes - or to represent common domains ...
DNA and RNA
... just enough force to hold the two strands together H-bonds form only between given pairs A-T and C-G This is known as base pairing Adenine-Thiamine, Cytosine-Guanine ...
... just enough force to hold the two strands together H-bonds form only between given pairs A-T and C-G This is known as base pairing Adenine-Thiamine, Cytosine-Guanine ...
Exam 2 Full v4A Bio200 Sum12
... creative where necessary. You should do this in less than one sentence for each mutation (If necessary, you can use two short sentences). Research outside of Bio200 lectures and labs is not necessary, but is allowed if you want to find specific examples of parts of this question. Show the diversity ...
... creative where necessary. You should do this in less than one sentence for each mutation (If necessary, you can use two short sentences). Research outside of Bio200 lectures and labs is not necessary, but is allowed if you want to find specific examples of parts of this question. Show the diversity ...
12 Units of Heredity
... • May suffer for a range of Developmental issues – Severity varies with the size of the inversion ...
... • May suffer for a range of Developmental issues – Severity varies with the size of the inversion ...
View/Open - JEWLScholar@MTSU
... 20mM of H2O2 showed only one fragment at approximately 49 bp. • The splicing of the domain TyrKc was significantly different under different environmental conditions. • We can conclude that, under different environmental conditions, the domain TyrKc of DAF-2 mRNA is spliced alternatively. • This wou ...
... 20mM of H2O2 showed only one fragment at approximately 49 bp. • The splicing of the domain TyrKc was significantly different under different environmental conditions. • We can conclude that, under different environmental conditions, the domain TyrKc of DAF-2 mRNA is spliced alternatively. • This wou ...
long - David Pollock
... structural comparison and prediction, biochemical adaptation, evolution of protein complexes, probabilistic methods for detecting patterns of sequence evolution, effects of population structure on ...
... structural comparison and prediction, biochemical adaptation, evolution of protein complexes, probabilistic methods for detecting patterns of sequence evolution, effects of population structure on ...