Slide ()
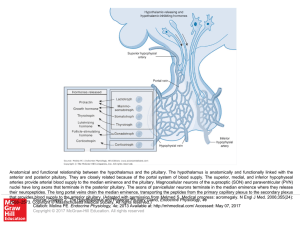
... Anatomical and functional relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The hypothalamus is anatomically and functionally linked with the anterior and posterior pituitary. They are closely related because of the portal system of blood supply. The superior, medial, and inferior hypophyseal ...
... Anatomical and functional relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The hypothalamus is anatomically and functionally linked with the anterior and posterior pituitary. They are closely related because of the portal system of blood supply. The superior, medial, and inferior hypophyseal ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... Recall that Hb can bind up to 4 molecules of O2 = 100% saturation At 75% saturation, Hb binds 3 molecules of O2 on average Sigmoidal (S) shape of curve indicates that the binding of one O2 makes it easier to bind the next O2 This curve tells us what the percent saturation of Hb will be at various pa ...
... Recall that Hb can bind up to 4 molecules of O2 = 100% saturation At 75% saturation, Hb binds 3 molecules of O2 on average Sigmoidal (S) shape of curve indicates that the binding of one O2 makes it easier to bind the next O2 This curve tells us what the percent saturation of Hb will be at various pa ...
Document
... Signals: From Postsynaptic Potentials to Neural Networks • One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons • Requires integration of signals – PSPs add up, balance out – Balance between IPSPs and EPSPs • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together o ...
... Signals: From Postsynaptic Potentials to Neural Networks • One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons • Requires integration of signals – PSPs add up, balance out – Balance between IPSPs and EPSPs • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together o ...
Objectives: 1. For normal neurons, understand structure and function
... appears semi-liquid as a result of dissolution of tissue by the action of hydrolytic enzymes released from lysosomes. 2. Apoptosis Apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, involves different cellular mechanisms than necrosis. Apoptosis is an energy-dependent process designed to switch cells off a ...
... appears semi-liquid as a result of dissolution of tissue by the action of hydrolytic enzymes released from lysosomes. 2. Apoptosis Apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, involves different cellular mechanisms than necrosis. Apoptosis is an energy-dependent process designed to switch cells off a ...
internal stimuli
... makes you aware of what is happening in the environment around you. • It lets you know that a ball is zooming toward you, your favorite song is on the radio and that the pizza in your hand is hot. • Your nervous system also checks conditions inside your body, like glucose levels in your blood. ...
... makes you aware of what is happening in the environment around you. • It lets you know that a ball is zooming toward you, your favorite song is on the radio and that the pizza in your hand is hot. • Your nervous system also checks conditions inside your body, like glucose levels in your blood. ...
nervous system
... • Presynaptic cell – transmitting cell • Postsynaptic cell – receiving cell • Two types of synapses – Electrical • Need gap junctions (channels between neurons) • No delays – Chemical • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Re ...
... • Presynaptic cell – transmitting cell • Postsynaptic cell – receiving cell • Two types of synapses – Electrical • Need gap junctions (channels between neurons) • No delays – Chemical • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Re ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...
Nervous System
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
Parts of the Brain - University of Peradeniya
... Nervous system and Brain Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
... Nervous system and Brain Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
Chapter 13- Central NS
... cerebellum by the transverse cerebral fissure. Grooves or furrows are called sulci and the twisted brain ridges are gyri. Deep sulci divide the brain into lobes. The central sulcus lies on the frontal plane between the precentral and postcentral gyrus; it separates the frontal and parietal lobes. Th ...
... cerebellum by the transverse cerebral fissure. Grooves or furrows are called sulci and the twisted brain ridges are gyri. Deep sulci divide the brain into lobes. The central sulcus lies on the frontal plane between the precentral and postcentral gyrus; it separates the frontal and parietal lobes. Th ...
Nervous System
... Motor Neurons – Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) Somatic motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) Visceral motor neurons – innervate all peripheral effectors ...
... Motor Neurons – Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) Somatic motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) Visceral motor neurons – innervate all peripheral effectors ...
Neurobiology of infectious diseases - HKU
... also called sleeping sickness – which is different from encephalitis lethargica, described by von Economo, whose etiology is still a mystery. The extracellular trypanosomes are transmitted by tsetse flies prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa. By localizing to basal meninges and circumventricular organs a ...
... also called sleeping sickness – which is different from encephalitis lethargica, described by von Economo, whose etiology is still a mystery. The extracellular trypanosomes are transmitted by tsetse flies prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa. By localizing to basal meninges and circumventricular organs a ...
Review for Medical Physiology
... 13. List the factors that affect heart pumping and the effect of each. (1) Preload – Frank-Starling mechanism; (2) Afterload; (3) Myocardial contractility; (4) Heart rate. 14. Describe the structure and function of the conduction system of the heart, and compare the action potentials in each part of ...
... 13. List the factors that affect heart pumping and the effect of each. (1) Preload – Frank-Starling mechanism; (2) Afterload; (3) Myocardial contractility; (4) Heart rate. 14. Describe the structure and function of the conduction system of the heart, and compare the action potentials in each part of ...
Stochastic Modeling the Tripartite Synapse and Applications
... Motivations: Similarly to a network of electronic communication devices, neurons are able to gather inputs coming from other cells, process these inputs according to its own physiological characteristics and produce a response which is forwarded to adjacent neurons in the network. In this respect, t ...
... Motivations: Similarly to a network of electronic communication devices, neurons are able to gather inputs coming from other cells, process these inputs according to its own physiological characteristics and produce a response which is forwarded to adjacent neurons in the network. In this respect, t ...
institute for translational neuroscience at northwestern medicine
... aging can impair brain function and deprive us of the ability to lead a happy and productive life. The challenge we face is to find ways of stopping and reversing the effects of disease and injury. As our population ages and becomes more vulnerable, this challenge takes on a growing sense of urgency ...
... aging can impair brain function and deprive us of the ability to lead a happy and productive life. The challenge we face is to find ways of stopping and reversing the effects of disease and injury. As our population ages and becomes more vulnerable, this challenge takes on a growing sense of urgency ...
LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
... The sweeping band (commissure) of white matter that provides a connection between the two halves of the cerebrum in the brain. It enables the transfer of information from one cerebral hemisphere to the other. Cingulate Gyrus A gyrus within the longitudinal fissure above and almost surrounding the co ...
... The sweeping band (commissure) of white matter that provides a connection between the two halves of the cerebrum in the brain. It enables the transfer of information from one cerebral hemisphere to the other. Cingulate Gyrus A gyrus within the longitudinal fissure above and almost surrounding the co ...
Body Systems - Nervous System
... c. There are gaps between many of the nerve cells in your body d. The somatic nervous system allows you to feel hot and cold sensations 7. If an area of your body is particularly sensitive, what can you conclude about that area? a. It contains more skin cells than other areas of your body b. It cont ...
... c. There are gaps between many of the nerve cells in your body d. The somatic nervous system allows you to feel hot and cold sensations 7. If an area of your body is particularly sensitive, what can you conclude about that area? a. It contains more skin cells than other areas of your body b. It cont ...
1 Pathophysiology of Alzheimer`s Disease Alzheimer`s disease (AD
... degenerated axonal or dendritic processes, glial cells, and astrocytes an amyloid core. These plaques disrupt nerve impulse transmission. Neurofibrillary tangles consist of insoluble helical filaments which developed from Tau proteins which once were attached to microtubules and in the normal settin ...
... degenerated axonal or dendritic processes, glial cells, and astrocytes an amyloid core. These plaques disrupt nerve impulse transmission. Neurofibrillary tangles consist of insoluble helical filaments which developed from Tau proteins which once were attached to microtubules and in the normal settin ...
NMSI - 4 Central Nervous System
... of the brain are hollow and filled with cerebrospinal fluid • The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
... of the brain are hollow and filled with cerebrospinal fluid • The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
آلفا با دامنهي زياد
... It is based on anatomical location and on percentage of distance among these points giving the 10 or 20% in the system name. The original 10-20 system has only nineteen electrodes but has been extended to accommodate more than 200 electrodes. ...
... It is based on anatomical location and on percentage of distance among these points giving the 10 or 20% in the system name. The original 10-20 system has only nineteen electrodes but has been extended to accommodate more than 200 electrodes. ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.























