multiple choice
... C) elicits repetitive chewing movements. D) inhibits food intake. E) produces eating and drinking. 6) Aggressive behaviors A) need not be an actual attack. B) include actual attacks against another organism. C) include those involved in predation. D) are often associated with reproduction. E) All of ...
... C) elicits repetitive chewing movements. D) inhibits food intake. E) produces eating and drinking. 6) Aggressive behaviors A) need not be an actual attack. B) include actual attacks against another organism. C) include those involved in predation. D) are often associated with reproduction. E) All of ...
copyright 2004 scientific american, inc.
... along separately tuned fibers of the auditory nerve as trains of neural discharges. Eventually these trains reach the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Different cells in the auditory system of the brain respond best to certain frequencies; neighboring cells have overlapping tuning curves so tha ...
... along separately tuned fibers of the auditory nerve as trains of neural discharges. Eventually these trains reach the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Different cells in the auditory system of the brain respond best to certain frequencies; neighboring cells have overlapping tuning curves so tha ...
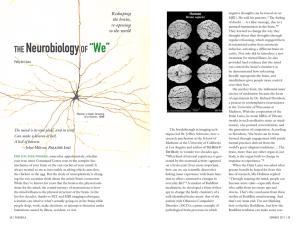
THE NeurobiologyOF “We”
... this little tiny piece of us (the last joint of the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” h ...
... this little tiny piece of us (the last joint of the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” h ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
The Nervous System
... Somatic nerves transmit signals from the outer parts of the body to the brain. Autonomic nerves help to control the functions of internal organs, like the heart and stomach. ...
... Somatic nerves transmit signals from the outer parts of the body to the brain. Autonomic nerves help to control the functions of internal organs, like the heart and stomach. ...
neurons
... Electroencephalogram (EEG) An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
... Electroencephalogram (EEG) An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
File
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
Unit II Practice Exam – Answer Key
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Steady-state p35 mRNA induced in monocytes is approximately 0.2 kb shorter than constitutive or enhanced mRNA in EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cells (Northern analysis). ...
... Steady-state p35 mRNA induced in monocytes is approximately 0.2 kb shorter than constitutive or enhanced mRNA in EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cells (Northern analysis). ...
Neurons
... This transmission of an electrochemical impulse is called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
... This transmission of an electrochemical impulse is called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
Development of the Brain
... • Excess positve ions in the neuron block metabolism in the mitochondria and kill the ...
... • Excess positve ions in the neuron block metabolism in the mitochondria and kill the ...
cardiac muscle
... Spindle shaped cells with a single central nuclei Walls of hollow organs (blood vessels, GI tract, bladder) Involuntary and nonstriated ...
... Spindle shaped cells with a single central nuclei Walls of hollow organs (blood vessels, GI tract, bladder) Involuntary and nonstriated ...
Lecture notes for Chapter 12
... 52 original areas duplicated in hemispheres Subsequently subdivided areas as more refined techniques developed. Functional separation of parts of the cortex grossly matches cytoarchitectural differences ...
... 52 original areas duplicated in hemispheres Subsequently subdivided areas as more refined techniques developed. Functional separation of parts of the cortex grossly matches cytoarchitectural differences ...
Physiology Lec.(2) Dr. Abeer mansoor
... decrease ordinarily increases the rate of red blood cell production. Thus, when a person becomes extremelyanemic as a result of hemorrhage or any other condition, the bone marrow immediately begins to producelarge quantities of red blood cells.Also, destruction of major portions of the bone marrow b ...
... decrease ordinarily increases the rate of red blood cell production. Thus, when a person becomes extremelyanemic as a result of hemorrhage or any other condition, the bone marrow immediately begins to producelarge quantities of red blood cells.Also, destruction of major portions of the bone marrow b ...
DOC
... Narration (Narrator’s voice in almost the only voice in the program; also hear ambient voices) (ALT Narration; may be cut) Character NAME; BRAIN region/part; SCENE heading [Description of Action or Notes from Sarah] ...
... Narration (Narrator’s voice in almost the only voice in the program; also hear ambient voices) (ALT Narration; may be cut) Character NAME; BRAIN region/part; SCENE heading [Description of Action or Notes from Sarah] ...
neuro_pathology
... Acute Injury o Red neuron: anoxia, ischemia, pyknosis of nucleus Atrophy and Degeneration o Loss of neurons without other change = slowly progressive or systemic dz ...
... Acute Injury o Red neuron: anoxia, ischemia, pyknosis of nucleus Atrophy and Degeneration o Loss of neurons without other change = slowly progressive or systemic dz ...
Lab07 Brain - Tacoma Community College
... cerebrum. The visible part of the cerebrum is the neocortex. Interior to the cortex is the midbrain. Underneath the cerebrum lies the brainstem, resembling handle underneath the main portion of ...
... cerebrum. The visible part of the cerebrum is the neocortex. Interior to the cortex is the midbrain. Underneath the cerebrum lies the brainstem, resembling handle underneath the main portion of ...
Understanding the Brain and Mental Illness
... Research indicates that some people with schizophrenia appear to have larger ventricles. Research also indicates that some people experiencing schizophrenia seem to have a loss of tissue in the anterior hippocampus, which may account for memory problems and irrationality. Recent research carried out ...
... Research indicates that some people with schizophrenia appear to have larger ventricles. Research also indicates that some people experiencing schizophrenia seem to have a loss of tissue in the anterior hippocampus, which may account for memory problems and irrationality. Recent research carried out ...
Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
... Imaginary training in rehabilitation? • Paralysis due to stroke may prevent early participation in a rehabilitation program • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements ...
... Imaginary training in rehabilitation? • Paralysis due to stroke may prevent early participation in a rehabilitation program • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.