Botox in ophtho - M.M.Joshi Eye Institute
... Sprouting of nerve fibers from the terminal axons Extra junctional Ach receptors ...
... Sprouting of nerve fibers from the terminal axons Extra junctional Ach receptors ...
Document
... brain during the reflex action, the primary response is "hard wired" through the spinal cord. ...
... brain during the reflex action, the primary response is "hard wired" through the spinal cord. ...
Principles of Biology II Lab Manual
... Nervous systems are unique to animals, and are critical for detecting and interpreting information, making decisions, and regulating body functions and movements. Nervous systems are constructed from neurons and glia. Neurons are the main functional cells, while glia play a variety of support roles. ...
... Nervous systems are unique to animals, and are critical for detecting and interpreting information, making decisions, and regulating body functions and movements. Nervous systems are constructed from neurons and glia. Neurons are the main functional cells, while glia play a variety of support roles. ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • Extrinsic or network mechanisms, which require the interaction of excitatory and inhibitory neurons within a population. • Intrinsic and network mechanisms can work alone (e.g., thalamic delta oscillations depend on the intrinsic properties of thalamic relay cells, cortical slow oscillation depend ...
... • Extrinsic or network mechanisms, which require the interaction of excitatory and inhibitory neurons within a population. • Intrinsic and network mechanisms can work alone (e.g., thalamic delta oscillations depend on the intrinsic properties of thalamic relay cells, cortical slow oscillation depend ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
The Science of Psychology
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce detailed images of the brain. ...
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce detailed images of the brain. ...
Module 3 - Psychology 40S with Susan Lawrie, M.Ed.
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
MINERALS summary - Akal College Of Nursing
... Maintains fluid level within the cell. Necessary for transmitting nerve impulses and muscle contractions. ...
... Maintains fluid level within the cell. Necessary for transmitting nerve impulses and muscle contractions. ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood press ...
... 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood press ...
Biology Standards Based Benchmark Assessment (5th
... 25. There are some diseases that cause paralysis due to the loss of the myelin sheath from spinal nerves. Why is the myelin sheath so important for the nervous system to function properly? a. The myelin sheath transmits impulses from one neuron to another. b. The myelin sheath insulates synapses bet ...
... 25. There are some diseases that cause paralysis due to the loss of the myelin sheath from spinal nerves. Why is the myelin sheath so important for the nervous system to function properly? a. The myelin sheath transmits impulses from one neuron to another. b. The myelin sheath insulates synapses bet ...
Diapositivo 1 - NEBM - Universidade de Lisboa
... the loss of retinal ganglion cells (specific cells from eye’s retina) and corresponding retinal nerve fibers that form the optic nerve. “Problem”: We were given the following task: study a small population of patients with this type of glaucoma and see their blood pressure (systolic, diastolic and m ...
... the loss of retinal ganglion cells (specific cells from eye’s retina) and corresponding retinal nerve fibers that form the optic nerve. “Problem”: We were given the following task: study a small population of patients with this type of glaucoma and see their blood pressure (systolic, diastolic and m ...
Exercise Physiology
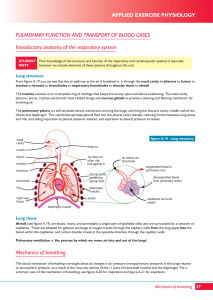
... Increased CO can be achieved by raising either stroke volume (SV) or heart rate (HR) steady-state HR rises essentially linearly with work rate over the whole range from rest to VO2max : increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic discharge to the cardiac pacemaker + catecholamines reflex sig ...
... Increased CO can be achieved by raising either stroke volume (SV) or heart rate (HR) steady-state HR rises essentially linearly with work rate over the whole range from rest to VO2max : increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic discharge to the cardiac pacemaker + catecholamines reflex sig ...
Addiction, Drugs, and the Endocrine System
... Alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream and starts to take effect within five to ten minutes. Effects GABA (inhibitory) and GLUTAMATE (excitatory) neurotransmitters. Activates the dopamine driven “pleasure pathway”. De-activates connections to the frontal lobe…causes disinhibition. alcohol affects ...
... Alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream and starts to take effect within five to ten minutes. Effects GABA (inhibitory) and GLUTAMATE (excitatory) neurotransmitters. Activates the dopamine driven “pleasure pathway”. De-activates connections to the frontal lobe…causes disinhibition. alcohol affects ...
AQAAS_ch2 Resp.system
... One of the short-term effects of physical activity is to cause a small increase in pulmonary blood pressure, which distorts red blood corpuscles within the alveolar capillary system, and this enables 10 times as much oxygen to be picked up as at rest. ...
... One of the short-term effects of physical activity is to cause a small increase in pulmonary blood pressure, which distorts red blood corpuscles within the alveolar capillary system, and this enables 10 times as much oxygen to be picked up as at rest. ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... activated. The UPR involves increased synthesis of proteins involved in protein folding and degradation along with decreased synthesis of most other proteins. If the UPR fails to relieve ER stress, apoptosis is triggered. Any factor that interferes with protein processing in the ER can activate the ...
... activated. The UPR involves increased synthesis of proteins involved in protein folding and degradation along with decreased synthesis of most other proteins. If the UPR fails to relieve ER stress, apoptosis is triggered. Any factor that interferes with protein processing in the ER can activate the ...
Bio211 Lecture 19
... • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning!) ...
... • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning!) ...
Outline for CNS, PNS, and ANS
... transverse fissure – divides cerebrum from cerebellum J. lateral sulcus – divides parietal lobe from temporal lobe K. central sulcus – divides parietal lobe from frontal lobe L. parieto-occipital sulcus – divides parietal lobe from occipital lobe M. precentral gyrus – convolution anterior to central ...
... transverse fissure – divides cerebrum from cerebellum J. lateral sulcus – divides parietal lobe from temporal lobe K. central sulcus – divides parietal lobe from frontal lobe L. parieto-occipital sulcus – divides parietal lobe from occipital lobe M. precentral gyrus – convolution anterior to central ...
Chapter 2
... formation, migration, and differentiation of neurons, and experience “fine-tuned” the brain. Now there is a greater emphasis on postnatal experience. ...
... formation, migration, and differentiation of neurons, and experience “fine-tuned” the brain. Now there is a greater emphasis on postnatal experience. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System - Ashland Independent Schools
... Active under normal, restful conditions Prepares body for normal activities Maintains homeostasis ...
... Active under normal, restful conditions Prepares body for normal activities Maintains homeostasis ...
Fatigue
... b. What areas of the neuron generate signals that open these voltage-gated channels? __________________________________________ c. Opening of these channels causes the membrane to __________________ (voltage change). ...
... b. What areas of the neuron generate signals that open these voltage-gated channels? __________________________________________ c. Opening of these channels causes the membrane to __________________ (voltage change). ...
Body and Behavior - Miami East Local Schools
... hemispheres are connected by a band of fibers called the corpus callosum. lobes: the different regions Each cerebral hemisphere has deep grooves, some of which mark regions, into which the cerebral cortex or lobes (see Figure 6.6). The occipital lobe is where the visual signals are is divided proces ...
... hemispheres are connected by a band of fibers called the corpus callosum. lobes: the different regions Each cerebral hemisphere has deep grooves, some of which mark regions, into which the cerebral cortex or lobes (see Figure 6.6). The occipital lobe is where the visual signals are is divided proces ...
ch. 6 pdf - TeacherWeb
... hemispheres are connected by a band of fibers called the corpus callosum. lobes: the different regions Each cerebral hemisphere has deep grooves, some of which mark regions, into which the cerebral cortex or lobes (see Figure 6.6). The occipital lobe is where the visual signals are is divided proces ...
... hemispheres are connected by a band of fibers called the corpus callosum. lobes: the different regions Each cerebral hemisphere has deep grooves, some of which mark regions, into which the cerebral cortex or lobes (see Figure 6.6). The occipital lobe is where the visual signals are is divided proces ...
PROJECT FIRST STEP®
... For 90% of right handed learners, looking up and to the left allows your to access stored pictures (visual recall). Looking up and to the right is where your eyes usually go to create new pictures. Looking ahead, eyes to the left best accesses stored sounds (what was said or heard) and to the right, ...
... For 90% of right handed learners, looking up and to the left allows your to access stored pictures (visual recall). Looking up and to the right is where your eyes usually go to create new pictures. Looking ahead, eyes to the left best accesses stored sounds (what was said or heard) and to the right, ...
Summary Ch - Dr. Allan N. Schore
... From another perspective, Schore starts this section of the paper with a central tenet of dynamic systems theory concerning critical moments in complex self-organizing systems. Times at which small additional flows of energy cause the system to become increasingly interconnected and causes the syste ...
... From another perspective, Schore starts this section of the paper with a central tenet of dynamic systems theory concerning critical moments in complex self-organizing systems. Times at which small additional flows of energy cause the system to become increasingly interconnected and causes the syste ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.