Outline Doc
... the parasite can contribute to biodiversity by controlling the size of specific species populations. 2. Mutually beneficial interactions also exist in ecological environments. 3. Mutualism is a relationship that benefits both species; these benefits can be in dispersing pollen and seeds for reproduc ...
... the parasite can contribute to biodiversity by controlling the size of specific species populations. 2. Mutually beneficial interactions also exist in ecological environments. 3. Mutualism is a relationship that benefits both species; these benefits can be in dispersing pollen and seeds for reproduc ...
137202_Interactions
... Individuals whose characteristics are best suited for their environment tend to survive and produce offspring. The offspring inherit those characteristics and also live to reproduce. Individuals that are poorly suited to the environment are less likely to survive and reproduce. The poorly suited cha ...
... Individuals whose characteristics are best suited for their environment tend to survive and produce offspring. The offspring inherit those characteristics and also live to reproduce. Individuals that are poorly suited to the environment are less likely to survive and reproduce. The poorly suited cha ...
population - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • Limiting factors that depend on population size • Density-dependent factors become limiting only when population density reaches a certain level • So as a population’s density increases, these are mechanisms that slow or stop growth by decreasing birth rates or increasing death rates. ...
... • Limiting factors that depend on population size • Density-dependent factors become limiting only when population density reaches a certain level • So as a population’s density increases, these are mechanisms that slow or stop growth by decreasing birth rates or increasing death rates. ...
Hantavirus- Yosemite
... When organisms try to obtain food, water, space, sunlight, and other resources in the same place at the same time, competition occurs. Competition in nature drives biological evolution. The ability to compete for resources is dependent upon whether an organism has adaptations that enable it to thr ...
... When organisms try to obtain food, water, space, sunlight, and other resources in the same place at the same time, competition occurs. Competition in nature drives biological evolution. The ability to compete for resources is dependent upon whether an organism has adaptations that enable it to thr ...
Population Ecology
... ´2. Growth slows down – In reality, population growth slows down, can’t be sustained at an exponential rate ´3. Growth stops – Size of the population levels off, no more growth, will remain at this size indefinitely ...
... ´2. Growth slows down – In reality, population growth slows down, can’t be sustained at an exponential rate ´3. Growth stops – Size of the population levels off, no more growth, will remain at this size indefinitely ...
ch29_lecture
... structure • Removal of a keystone species can cause drastic changes in a community; can increase or decrease diversity ...
... structure • Removal of a keystone species can cause drastic changes in a community; can increase or decrease diversity ...
ch29_lecture
... structure • Removal of a keystone species can cause drastic changes in a community; can increase or decrease diversity ...
... structure • Removal of a keystone species can cause drastic changes in a community; can increase or decrease diversity ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... and decay, nutrients accumulate. The dune gets bigger and larger plants like sand couch grass colonise it. Sand couch grass has long underground stems that helps to stabilise the sand. With more stability and more nutrients, Marram grass starts to grow. Marram grass has an extensive vertical root sy ...
... and decay, nutrients accumulate. The dune gets bigger and larger plants like sand couch grass colonise it. Sand couch grass has long underground stems that helps to stabilise the sand. With more stability and more nutrients, Marram grass starts to grow. Marram grass has an extensive vertical root sy ...
PhD position - timing in ecological interaction networks Department
... and its functional consequences”. Temporal variability of species interactions has long been recognized, but we still lack a mechanistic understanding of its drivers and consequences, e.g. for interpretation of network structure, for conclusions about biodiversity-functioning relationships and for r ...
... and its functional consequences”. Temporal variability of species interactions has long been recognized, but we still lack a mechanistic understanding of its drivers and consequences, e.g. for interpretation of network structure, for conclusions about biodiversity-functioning relationships and for r ...
Community Ecology: Structure, Species Interactions, Succession
... 39. What “descriptors” or labels have gradually come in to use in place of or to be used in conjunction with “climax community”? 40. What is stability, in terms of an organism, a population, a community, or the biosphere? 41. Define each of the following: Inertia, or Persistence; Constancy; Resilien ...
... 39. What “descriptors” or labels have gradually come in to use in place of or to be used in conjunction with “climax community”? 40. What is stability, in terms of an organism, a population, a community, or the biosphere? 41. Define each of the following: Inertia, or Persistence; Constancy; Resilien ...
MS - LS2 - 2 Construct an explanation that predicts
... 5.________________ Remora fish are small fish that make their niche by picking up the scraps that sharks leave behind while feeding. The shark makes no attempt to prey on the remora fish. 6.________________ The Monarch butterfly is a well-known type of butterfly found commonly in the North American ...
... 5.________________ Remora fish are small fish that make their niche by picking up the scraps that sharks leave behind while feeding. The shark makes no attempt to prey on the remora fish. 6.________________ The Monarch butterfly is a well-known type of butterfly found commonly in the North American ...
Bi 101 (Summer 2006) Ecology
... _________________________, has such a strong effect on the species involved that each evolves ways to reduce any overlap in needs In other words, each species specializes within the community, developing its own well-defined, ________________________ ________________________ Adaptations Reduce the O ...
... _________________________, has such a strong effect on the species involved that each evolves ways to reduce any overlap in needs In other words, each species specializes within the community, developing its own well-defined, ________________________ ________________________ Adaptations Reduce the O ...
Community Structure, Population Control, and Competition
... the producers are resource-limited will be the most persistent. The development of this pattern is less likely where high producer mortalities are inevitable. In lakes, forexample, algal populations are prone to crash whether grazed or not. In the same environment,grazing depletion is much more' com ...
... the producers are resource-limited will be the most persistent. The development of this pattern is less likely where high producer mortalities are inevitable. In lakes, forexample, algal populations are prone to crash whether grazed or not. In the same environment,grazing depletion is much more' com ...
Competition
... This means that when species 1 is at its carrying capacity, its impact on species 2 (measured by K1 times a21) is greater than the impact of K2 individuals of species 2.! Thus, species 1 is affecting species 2 more negatively than species 2 ...
... This means that when species 1 is at its carrying capacity, its impact on species 2 (measured by K1 times a21) is greater than the impact of K2 individuals of species 2.! Thus, species 1 is affecting species 2 more negatively than species 2 ...
Chapter 6: Populations and Community Ecology
... The different growth models used to explain changes in population size are exponential and logistic. Some populations experience cycles of overshoots and die-offs that oscillate around the carrying capacity. Predators play an important role in limiting population growth. The two reproductive strateg ...
... The different growth models used to explain changes in population size are exponential and logistic. Some populations experience cycles of overshoots and die-offs that oscillate around the carrying capacity. Predators play an important role in limiting population growth. The two reproductive strateg ...
Ecology review assignment
... 28. Few populations are capable of exponential growth. 29.Exponential growth is slow at first and then speeds up. 30.Populations change only through births and deaths. 31.Limiting factors increase population growth rates. 32.Light may be a density-dependent limiting factor. 33.K-selected species’ po ...
... 28. Few populations are capable of exponential growth. 29.Exponential growth is slow at first and then speeds up. 30.Populations change only through births and deaths. 31.Limiting factors increase population growth rates. 32.Light may be a density-dependent limiting factor. 33.K-selected species’ po ...
Chapter 9 Activity 5 Competition Among Organisms
... • Gardeners of course are familiar with many of these parameters. When you buy plants or seeds you buy them with your garden in mind; some plants cannot live in wet soils, others require shade, still others need acid soils. Animals likewise have similar requirements; a tropical lizard like the iguan ...
... • Gardeners of course are familiar with many of these parameters. When you buy plants or seeds you buy them with your garden in mind; some plants cannot live in wet soils, others require shade, still others need acid soils. Animals likewise have similar requirements; a tropical lizard like the iguan ...
Populations
... species living in the same place at the same time. • Populations are described in terms of: – Size, density and dispersion – Density – the number of individuals per unit of area or volume – Dispersion – describes the arrangement of its individuals in space • Clumped, even or random ...
... species living in the same place at the same time. • Populations are described in terms of: – Size, density and dispersion – Density – the number of individuals per unit of area or volume – Dispersion – describes the arrangement of its individuals in space • Clumped, even or random ...
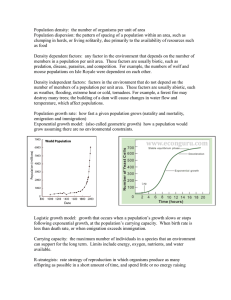
Population density: the number of organisms per unit of area
... less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species that an environment can support for the long term. Limits include energy, oxygen, nutrients, and water available. R-strategists: rate strategy of reproduction in which orga ...
... less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species that an environment can support for the long term. Limits include energy, oxygen, nutrients, and water available. R-strategists: rate strategy of reproduction in which orga ...
Name: - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... because we tend to keep a cell phone for only one year, and do not always dispose of the cell phone responsibly, so that chemicals leak into the earth. However, a practice that does promote sustainable development, because it attempts to ensure there are adequate resources for future generations, is ...
... because we tend to keep a cell phone for only one year, and do not always dispose of the cell phone responsibly, so that chemicals leak into the earth. However, a practice that does promote sustainable development, because it attempts to ensure there are adequate resources for future generations, is ...
Ecology
... – Exclusion: “out-compete”--force a species out of a niche--Asian carp in Mississippi R. and our fish, humans and every other species on Earth. – Character displacement: make a species modify or change it’s niche-- raccoons in your garbage. • Niches can be fundamental (preferred--what you want), or ...
... – Exclusion: “out-compete”--force a species out of a niche--Asian carp in Mississippi R. and our fish, humans and every other species on Earth. – Character displacement: make a species modify or change it’s niche-- raccoons in your garbage. • Niches can be fundamental (preferred--what you want), or ...