Historical Geology
... sediment from Rockies. Shallow Cretaceous sea way across Texas. Shallow limestones, shales. ...
... sediment from Rockies. Shallow Cretaceous sea way across Texas. Shallow limestones, shales. ...
Lab 2 Plate Tectonics and Ocean Geography OCE-3014L
... Your instructor has lithospheric plate/divergent boundary models. Working in groups of three or more, assemble a model so that Plate A (continental lithosphere) and Plate B (continental lithosphere) are joined as one continent—this configuration is the 15 million years ago when there was one contine ...
... Your instructor has lithospheric plate/divergent boundary models. Working in groups of three or more, assemble a model so that Plate A (continental lithosphere) and Plate B (continental lithosphere) are joined as one continent—this configuration is the 15 million years ago when there was one contine ...
CHAPTER 14
... 13. High-grade bituminous and anthracite coals have experienced greater metamorphism (through heat and/or pressure). It is logical that Paleozoic coals have experienced greater metamorphism because of their location along the eastern coast of North America. This was the site of continental-continent ...
... 13. High-grade bituminous and anthracite coals have experienced greater metamorphism (through heat and/or pressure). It is logical that Paleozoic coals have experienced greater metamorphism because of their location along the eastern coast of North America. This was the site of continental-continent ...
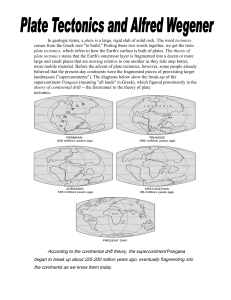
In geologic terms, a plate is a large, rigid slab of solid rock. The word
... the coastal parts of Africa and South America was the most compelling evidence that the two continents were once joined. In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on ...
... the coastal parts of Africa and South America was the most compelling evidence that the two continents were once joined. In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on ...
e-Science Teachers Pack - Faculty of Sciences
... Learning outcomes: The continents are situated upon an unstable, dynamic and always moving crust; this movement lead to the formation and destruction of the Pangea and Gondwana supercontinents The isotopes in zircon can be used as fingerprints to past geological processes; highlighting what the ...
... Learning outcomes: The continents are situated upon an unstable, dynamic and always moving crust; this movement lead to the formation and destruction of the Pangea and Gondwana supercontinents The isotopes in zircon can be used as fingerprints to past geological processes; highlighting what the ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 6, cont’d) What is the Theory of Continental Drift? • Continents appear to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. • Distribution of fossil remains over several continents. • Similar rock layers on different continents. • Glacial marks on different continents appear to line when the continents are moved ...
... 6, cont’d) What is the Theory of Continental Drift? • Continents appear to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. • Distribution of fossil remains over several continents. • Similar rock layers on different continents. • Glacial marks on different continents appear to line when the continents are moved ...
Divergent boundary
... East African Rift rift valley Example: _____________ Creates a __________. ...
... East African Rift rift valley Example: _____________ Creates a __________. ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that drive plate tectonics? 4. What happens at the boundaries between plates? 5. How do the different types of plate boundaries impact the regional geology and geomorphology? 6. How has continental drift affected ...
... Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that drive plate tectonics? 4. What happens at the boundaries between plates? 5. How do the different types of plate boundaries impact the regional geology and geomorphology? 6. How has continental drift affected ...
Chapter 6
... • What is the evidence for Gondwanaland? • How does paleomagnetism demonstrate that continents have moved in the course of time? • How was paleomagnetism used to show that lithosphere forms at mid-ocean ridges and then ...
... • What is the evidence for Gondwanaland? • How does paleomagnetism demonstrate that continents have moved in the course of time? • How was paleomagnetism used to show that lithosphere forms at mid-ocean ridges and then ...
plate tectonics
... Diverge (Go away from each other), slide past each other, go on top/ below one another ...
... Diverge (Go away from each other), slide past each other, go on top/ below one another ...
CHAPTER 3
... - Wegener was a meteorologist by training. - Wegener believed that there was once a super continent called Pangaea that contained all landmass (see fig. 3.4 in your text). Pangaea later broke apart into two masses: Laurasia (North America and Eurasia) and Gondwanaland (Africa, South America, India, ...
... - Wegener was a meteorologist by training. - Wegener believed that there was once a super continent called Pangaea that contained all landmass (see fig. 3.4 in your text). Pangaea later broke apart into two masses: Laurasia (North America and Eurasia) and Gondwanaland (Africa, South America, India, ...
Plate Tectonics PowerPoint
... – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. ...
... – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. ...
Plate Tectonics Part 1
... Theory of Plate tectonics • Earth’s surface is divided into large sections called plates. • Plates are bordered by ridge systems, trenches and faults. • Fault – break in Earth’s crust ...
... Theory of Plate tectonics • Earth’s surface is divided into large sections called plates. • Plates are bordered by ridge systems, trenches and faults. • Fault – break in Earth’s crust ...
The two major areas of the ocean floor are the and the
... 17. Rocks from the ocean floor were found to be no older than _____ ___________ years. 18. Harry Hess proposed an idea called _______________ ________________. 19. When lava cools it acts like a _________________. 20. The earth’s magnetic field switched to the ____________ almost a million years ago ...
... 17. Rocks from the ocean floor were found to be no older than _____ ___________ years. 18. Harry Hess proposed an idea called _______________ ________________. 19. When lava cools it acts like a _________________. 20. The earth’s magnetic field switched to the ____________ almost a million years ago ...
LAB 4-3: Seafloor Spreading
... hidden from direct view making it difficult for scientists to study. Recent advances in technology along with underwater research vessels have allowed scientists to create detailed maps of the ocean floor and make many new discoveries about the deep ocean. These maps and discoveries have led to a be ...
... hidden from direct view making it difficult for scientists to study. Recent advances in technology along with underwater research vessels have allowed scientists to create detailed maps of the ocean floor and make many new discoveries about the deep ocean. These maps and discoveries have led to a be ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... underwater mountain range of the Atlantic Ocean, which runs from Iceland to Antarctica; this is the longest mountain range on Earth. ...
... underwater mountain range of the Atlantic Ocean, which runs from Iceland to Antarctica; this is the longest mountain range on Earth. ...
Plate Tectonics - NewPath Learning
... to the continental drift theory, all of the continents were together as a large, single landmass. This landmass was given the name Pangaea. About 180 million years ago, the super-continent Pangaea began to split into two smaller continents. Geologists call these two continents Laurasia and Gondwana. ...
... to the continental drift theory, all of the continents were together as a large, single landmass. This landmass was given the name Pangaea. About 180 million years ago, the super-continent Pangaea began to split into two smaller continents. Geologists call these two continents Laurasia and Gondwana. ...
Ocean Basin
... 2.The mid-ocean ridge is a continuous chain of mountains that runs from the central Arctic Ocean down through the Atlantic, through the Indian Ocean and northward through the eastern Pacific. 3.The mid-ocean ridge is approximately 1000 km wide and rises 1000 to 3000 m above the adjacent seafloor. 4. ...
... 2.The mid-ocean ridge is a continuous chain of mountains that runs from the central Arctic Ocean down through the Atlantic, through the Indian Ocean and northward through the eastern Pacific. 3.The mid-ocean ridge is approximately 1000 km wide and rises 1000 to 3000 m above the adjacent seafloor. 4. ...
Document
... oceanic crust between a spreading mid-ocean ridge and the trench it disappears into. These make up 30% of the ...
... oceanic crust between a spreading mid-ocean ridge and the trench it disappears into. These make up 30% of the ...
Warm- up Question Summarize: What you know about Continental
... continents Match of mountain belts, rock types ...
... continents Match of mountain belts, rock types ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Madison County Schools
... • Using a submarine named Alvin, scientists were able to look into a rift valley and examine something called pillow lava, which is a special type of solid rock that only forms on the ocean floor when magma cools very rapidly. This proved that new molten material was being added to the ocean floor a ...
... • Using a submarine named Alvin, scientists were able to look into a rift valley and examine something called pillow lava, which is a special type of solid rock that only forms on the ocean floor when magma cools very rapidly. This proved that new molten material was being added to the ocean floor a ...
plate tectonics 2009..
... Alfred Wegener (German scientist) All the continents were jointed together “Pangaea” The single ocean “Panthalassa Ocean” - For reasons yet unclear: 200 m.y.a. Cracks began to divide Pangaea into 2 supercontinents, north: Laurasia south: Gondwanaland They then began to be broken apart by additional ...
... Alfred Wegener (German scientist) All the continents were jointed together “Pangaea” The single ocean “Panthalassa Ocean” - For reasons yet unclear: 200 m.y.a. Cracks began to divide Pangaea into 2 supercontinents, north: Laurasia south: Gondwanaland They then began to be broken apart by additional ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiːə/) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from earlier continental units approximately 300 million years ago, and it began to break apart about 175 million years ago. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, much of Pangaea was in the southern hemisphere and surrounded by a super ocean, Panthalassa. Pangaea was the last supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.