Geologic History of Central Pennsylvania
... ash clouds, now seen as thick beds of volcanic ash interbedded with the limestones. For a while, the configuration of Laurentia's southeastern margin resembled the volcanic island complexes around the Pacific, such as Japan or the Aleutians, but after a few tens of millions of years, plate convergen ...
... ash clouds, now seen as thick beds of volcanic ash interbedded with the limestones. For a while, the configuration of Laurentia's southeastern margin resembled the volcanic island complexes around the Pacific, such as Japan or the Aleutians, but after a few tens of millions of years, plate convergen ...
Ocean Regions Day 2
... Key Points • The three major regions of the ocean floor are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor and the mid-ocean ridges. • The gently sloping submerged surface extending from the shoreline toward the deep ocean is called the continental shelf. • At the continental margin in the Pacific ...
... Key Points • The three major regions of the ocean floor are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor and the mid-ocean ridges. • The gently sloping submerged surface extending from the shoreline toward the deep ocean is called the continental shelf. • At the continental margin in the Pacific ...
File
... of India was attached to Africa. Then it broke off and drifted on its own, heading northeast for about 100 million years until it crashed into the Eurasian landmass. India also had to push the oceanic crust out of the way by forcing it under the Eurasian plate. As the Indian plate slid underneath Eu ...
... of India was attached to Africa. Then it broke off and drifted on its own, heading northeast for about 100 million years until it crashed into the Eurasian landmass. India also had to push the oceanic crust out of the way by forcing it under the Eurasian plate. As the Indian plate slid underneath Eu ...
Geología Norteamerica
... In this phase, the continent started to expand basinward (westward) by accretion. All the events are recorded in the rock and structural features of the terranes and by continental arcs. Glimpses of the pre-Cretaceous plate tectonics within the Proto-Pacific Ocean come the tectonostratigraphic recor ...
... In this phase, the continent started to expand basinward (westward) by accretion. All the events are recorded in the rock and structural features of the terranes and by continental arcs. Glimpses of the pre-Cretaceous plate tectonics within the Proto-Pacific Ocean come the tectonostratigraphic recor ...
Work Package 3 Drifting Apart Story
... Although continental drift was first pondered as early as the 15th century, it wasn’t until 1912, that a German meteorologist and geologist called Alfred Wegener first proposed the theory. His theory was based on the observation that the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America would ...
... Although continental drift was first pondered as early as the 15th century, it wasn’t until 1912, that a German meteorologist and geologist called Alfred Wegener first proposed the theory. His theory was based on the observation that the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America would ...
CHAPTER 13 THE OCEAN FLOOR
... Later studies gave credibility to this idea, and geologist established such concept of seafloor spreading that occurs along narrow zones called rift zones (regions of Earth’s crust along which divergence is taking place) that are located at the crests of ocean ridges. As plates move apart, magma ris ...
... Later studies gave credibility to this idea, and geologist established such concept of seafloor spreading that occurs along narrow zones called rift zones (regions of Earth’s crust along which divergence is taking place) that are located at the crests of ocean ridges. As plates move apart, magma ris ...
Development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics
... (1880-1930) noticed the same thing and proposed that the continents were once compressed into a single protocontinent which he called Pangaea (meaning "all lands"), and over time they have drifted apart into their current distribution. He believed that Pangaea was intact until the late Carboniferous ...
... (1880-1930) noticed the same thing and proposed that the continents were once compressed into a single protocontinent which he called Pangaea (meaning "all lands"), and over time they have drifted apart into their current distribution. He believed that Pangaea was intact until the late Carboniferous ...
"Dynamic Earth Guided Notes" (Plate Tectonics)
... ~ Subduction Zone: A zone where one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate at a convergent plate boundary. The denser plate always moves under the less dense plate. ...
... ~ Subduction Zone: A zone where one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate at a convergent plate boundary. The denser plate always moves under the less dense plate. ...
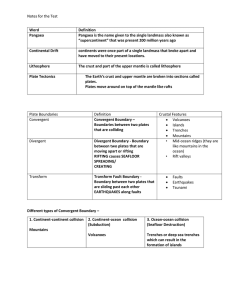
Notes for the Test Word Definition Pangaea Pangaea is the name
... Contour lines: tell us the elevation, or height from sea level. Contour interval: the distance represented between each contour ...
... Contour lines: tell us the elevation, or height from sea level. Contour interval: the distance represented between each contour ...
ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT
... For more information about what the continents looked like throughout the Earth’s History go to: ...
... For more information about what the continents looked like throughout the Earth’s History go to: ...
Chapter 19 - Heritage Collegiate
... matched those on other continents. For example, the mountain belt that contains the Appalachians extends through the eastern US and ends in Newfoundland. However, rocks of similar type and age reappear in the British Isles and extend through Scandinavia (see Figure 19.6 p. 518 text). When current la ...
... matched those on other continents. For example, the mountain belt that contains the Appalachians extends through the eastern US and ends in Newfoundland. However, rocks of similar type and age reappear in the British Isles and extend through Scandinavia (see Figure 19.6 p. 518 text). When current la ...
Ocean Basin Physiography
... shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here because they serve as major conduits which funnel turbidity currents and sediments f ...
... shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here because they serve as major conduits which funnel turbidity currents and sediments f ...
Ocean Floor Answers
... Construct a small foldable that demonstrates the ocean floor by folding a piece of plain paper in half using the hot dog fold. Using a combination of information found in your notes and in the other graphics of the ocean floor in the graphics review section, draw the ocean floor. Your drawing on ...
... Construct a small foldable that demonstrates the ocean floor by folding a piece of plain paper in half using the hot dog fold. Using a combination of information found in your notes and in the other graphics of the ocean floor in the graphics review section, draw the ocean floor. Your drawing on ...
Chapter 3: Marine Provinces
... Amount of Earth’s surface (%) at different elevations and depths 70.8% of Earth covered by oceans Average depth ocean 3729 m Average elevation land 840 m Uneven distribution of areas of different depths/elevations ...
... Amount of Earth’s surface (%) at different elevations and depths 70.8% of Earth covered by oceans Average depth ocean 3729 m Average elevation land 840 m Uneven distribution of areas of different depths/elevations ...
The Ocean Floor Bethany Ostlund 4th Grade The Ocean Floor
... The green colors are the spreading ridges, older crust, that moves away from the ridge as new crust is formed. The blue colors are the oldest regions of the seafloor. They are either next to continents, or are near areas on Earth where seduction is taking place. ...
... The green colors are the spreading ridges, older crust, that moves away from the ridge as new crust is formed. The blue colors are the oldest regions of the seafloor. They are either next to continents, or are near areas on Earth where seduction is taking place. ...
Chapter 2, Section 4
... Figure 1. They noticed alternating belts of higher and lower-than-average magnetic field strength. The belts with the higher polarity were of normal polarity. The bands with lower polarity were reversed. In 1963, F. J. Vine and D. H. Matthews proposed the theory of seafloor spreading to explain this ...
... Figure 1. They noticed alternating belts of higher and lower-than-average magnetic field strength. The belts with the higher polarity were of normal polarity. The bands with lower polarity were reversed. In 1963, F. J. Vine and D. H. Matthews proposed the theory of seafloor spreading to explain this ...
Plate Tectonics
... shorelines of the continents seemed to ‘fit together’ like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. Wegener’s theory was ...
... shorelines of the continents seemed to ‘fit together’ like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. Wegener’s theory was ...
Plate Tectonics PPT
... shorelines of the continents seemed to ‘fit together’ like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. Wegener’s theory was ...
... shorelines of the continents seemed to ‘fit together’ like the pieces of a giant jig saw puzzle. Wegener’s theory stated: 1) The continents were once all together in one place forming a supercontinent, Pangea. 2) The continents broke apart and drifted to their present locations. Wegener’s theory was ...
Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide
... How does a covalent bond work? How does an ionic bond work? Why do we say water has polar molecules? What remarkable attributes does water owe to its polar nature? What is the difference between temperature and heat? What does adding heat to an object or fluid do? What is meant by heat capacity (aka ...
... How does a covalent bond work? How does an ionic bond work? Why do we say water has polar molecules? What remarkable attributes does water owe to its polar nature? What is the difference between temperature and heat? What does adding heat to an object or fluid do? What is meant by heat capacity (aka ...
Geology Library Notes Wk8.cwk (WP)
... Islands created as the Pacific plate moved over the hot spot which periodically burned through the plate. ...
... Islands created as the Pacific plate moved over the hot spot which periodically burned through the plate. ...
Chapter 23 The Geology of the Mesozoic Era
... Jurassic, Cretaceous – breakup of Pangaea was the major geologic event – tectonism and sedimentation are used to classify the Mesozoic in N. America – Note the overlap in three styles of Cordilleran Orogeny ...
... Jurassic, Cretaceous – breakup of Pangaea was the major geologic event – tectonism and sedimentation are used to classify the Mesozoic in N. America – Note the overlap in three styles of Cordilleran Orogeny ...
The Pacific Ring of Fire
... A geologic ______________________ has been going on for the past ________ billion years or so. Stresses and strains inside the Earth have been heaving up _____________________. Meanwhile, the forces of _______________ keep wearing them down. The Earth in Motion If you cut out the ___________________ ...
... A geologic ______________________ has been going on for the past ________ billion years or so. Stresses and strains inside the Earth have been heaving up _____________________. Meanwhile, the forces of _______________ keep wearing them down. The Earth in Motion If you cut out the ___________________ ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiːə/) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from earlier continental units approximately 300 million years ago, and it began to break apart about 175 million years ago. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, much of Pangaea was in the southern hemisphere and surrounded by a super ocean, Panthalassa. Pangaea was the last supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.