STUDY GUIDE for MICROBIAL GENETICS 1. Define the following
... Compare and contrast replication of the leading and lagging strands. f. Why is DNA replication said to be semi-conservative? g. What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and transl ...
... Compare and contrast replication of the leading and lagging strands. f. Why is DNA replication said to be semi-conservative? g. What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and transl ...
DNA, RNA, Genetic Engineering
... Codon (triplet) matches to anticodon on tRNA tRNA brings AA to ribosome to build peptide chain Start codon= Met (yes, codes for AA & can be inside sequence) Stop codon= stop (no AA & terminates sequence) ...
... Codon (triplet) matches to anticodon on tRNA tRNA brings AA to ribosome to build peptide chain Start codon= Met (yes, codes for AA & can be inside sequence) Stop codon= stop (no AA & terminates sequence) ...
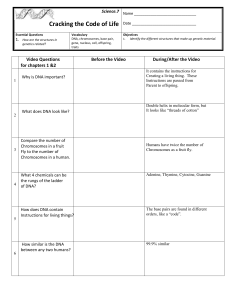
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
Gene Technology
... Gene cloning – many copies of the gene of interest are made by the vector copying its DNA with the gene in it Screening – cells that have the gene you want are separated from those that don’t ...
... Gene cloning – many copies of the gene of interest are made by the vector copying its DNA with the gene in it Screening – cells that have the gene you want are separated from those that don’t ...
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
HSLS4-1
... 7. Explain why sex-linked traits are expressed more frequently in males. 8. Recognize that any environmental factor that influences gene expression or alteration in hormonal balance may have an impact on development. 9. Describe early embryonic development and distinguish each: oogenesis, fertilizat ...
... 7. Explain why sex-linked traits are expressed more frequently in males. 8. Recognize that any environmental factor that influences gene expression or alteration in hormonal balance may have an impact on development. 9. Describe early embryonic development and distinguish each: oogenesis, fertilizat ...
Ch. 13 SOL - Groupfusion.net
... variety of strawberry is resistant to a bk One damaging fungus but produces small fruit. Another strawberry variety produces large fruit but is not resistant to the fungus. How might the desirable qualities of the two varieties be combined? A cloning B asexual reproduction C direct harvesting D sele ...
... variety of strawberry is resistant to a bk One damaging fungus but produces small fruit. Another strawberry variety produces large fruit but is not resistant to the fungus. How might the desirable qualities of the two varieties be combined? A cloning B asexual reproduction C direct harvesting D sele ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... effort to sequence all 3 billion base pairs of human DNA. • Other important goals included sequencing the genomes of model organisms to compare to human DNA, developing technology to support the research, exploring gene functions, studying human variation, and training future scientists. • Today, mu ...
... effort to sequence all 3 billion base pairs of human DNA. • Other important goals included sequencing the genomes of model organisms to compare to human DNA, developing technology to support the research, exploring gene functions, studying human variation, and training future scientists. • Today, mu ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... To prepare for the test, go back and review: Chapter 12.1-12.3 Notes Chapter 13.1-13.3 Labs Class handouts Other 1. Identify the three main experiments leading to our acceptance of DNA as the molecule of inheritance. Include: a. Scientist(s) b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experime ...
... To prepare for the test, go back and review: Chapter 12.1-12.3 Notes Chapter 13.1-13.3 Labs Class handouts Other 1. Identify the three main experiments leading to our acceptance of DNA as the molecule of inheritance. Include: a. Scientist(s) b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experime ...
Lecture 6: Genome variation File
... • mtDNA is inherited only from the mother only a single haplotype – Inferring haplotype for nuclear DNA is a computational problem known as phasing – Suppose we have 2 polymorphisms in a nuclear gene of an individual, i.e., there are 2 differences between the maternal and paternal versions of the ...
... • mtDNA is inherited only from the mother only a single haplotype – Inferring haplotype for nuclear DNA is a computational problem known as phasing – Suppose we have 2 polymorphisms in a nuclear gene of an individual, i.e., there are 2 differences between the maternal and paternal versions of the ...
Andrews 1999 Corrected CRS.NatGen
... sequence, which is actually a single cytosine residue. The other errors are mistakes in the identification of single base pairs and typically involve the incorrect assignment of a guanine residue. Errors at nt 14,272 and 14,365 result from the use of the bovine mtDNA sequence at ambiguous sites1. Th ...
... sequence, which is actually a single cytosine residue. The other errors are mistakes in the identification of single base pairs and typically involve the incorrect assignment of a guanine residue. Errors at nt 14,272 and 14,365 result from the use of the bovine mtDNA sequence at ambiguous sites1. Th ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Allow the bacteria to reproduce itself and the plasmid. Harvest and purify the protein made in the bacterial cell Cloning the Organism “Dolly” 1. An udder cell was isolated from a sheep and grown in culture (replicated) 2. An egg was taken from another sheep and its nucleus (DNA) was removed 3. ...
... Allow the bacteria to reproduce itself and the plasmid. Harvest and purify the protein made in the bacterial cell Cloning the Organism “Dolly” 1. An udder cell was isolated from a sheep and grown in culture (replicated) 2. An egg was taken from another sheep and its nucleus (DNA) was removed 3. ...
2nd problem set
... 1. Imagine you are sequencing the DNA molecule shown above. Assume the primer 5’ GATGCCT 3’ is used to initiate DNA synthesis. You have a tube containing template, primer, millions of ACGT nucleotides and millions of dideoxyC nucleotides. (p. 387-393 of your textbook has a good review if you are hav ...
... 1. Imagine you are sequencing the DNA molecule shown above. Assume the primer 5’ GATGCCT 3’ is used to initiate DNA synthesis. You have a tube containing template, primer, millions of ACGT nucleotides and millions of dideoxyC nucleotides. (p. 387-393 of your textbook has a good review if you are hav ...
Sources of DNA
... called plasmids. They contain a few nonessential genes. These genes code for extra traits that help bacteria survive some extraordinary circumstances, such as antibiotics or extreme ...
... called plasmids. They contain a few nonessential genes. These genes code for extra traits that help bacteria survive some extraordinary circumstances, such as antibiotics or extreme ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of ...
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.