Structure and Role of DNA Genetic and DNA Genetics
... Genetic information is contained in nucleic acids (large organic molecules made up or H, O, N, P) Nucleic acids are made up of smaller units called nucleotides o Nucleotide(5 carbon sugar bonded to Nitrogen base, phosphate group) 2 types of nucleic acids: o DNA- carries genetic information and conta ...
... Genetic information is contained in nucleic acids (large organic molecules made up or H, O, N, P) Nucleic acids are made up of smaller units called nucleotides o Nucleotide(5 carbon sugar bonded to Nitrogen base, phosphate group) 2 types of nucleic acids: o DNA- carries genetic information and conta ...
How Does DNA Control Traits? - 6thgrade
... mother . The other gene is inherited from the father. • Not every child in a family receives the same set of genes from the mother and father. Each egg cell of the mother contains a different combination of genes. Each sperm cell of the father also contains a different combination of genes. ...
... mother . The other gene is inherited from the father. • Not every child in a family receives the same set of genes from the mother and father. Each egg cell of the mother contains a different combination of genes. Each sperm cell of the father also contains a different combination of genes. ...
Study Guide for LS
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences can be readily aligned The biology of the gene (or other DNA sequence) must be understood to assure homology ...
... appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences can be readily aligned The biology of the gene (or other DNA sequence) must be understood to assure homology ...
DNA And Traits
... The process that determines which parts of the DNA are put into the sperm or egg cell is random. On top of that, it is random which egg and sperm come together to form the zygote. When you look at it this way, it’s not at all surprising that some people look different from their family members. This ...
... The process that determines which parts of the DNA are put into the sperm or egg cell is random. On top of that, it is random which egg and sperm come together to form the zygote. When you look at it this way, it’s not at all surprising that some people look different from their family members. This ...
Watermarking sexually reproducing diploid organisms
... derived from the original DNA-Crypt and can be used in combination with the DNA-Crypt algorithm. The binary file, which is thought to be encrypted into DNA is first modified by a mutation correction code, the Hamming-code, to correct mutations within the DNA sequences. A header, containing the lengt ...
... derived from the original DNA-Crypt and can be used in combination with the DNA-Crypt algorithm. The binary file, which is thought to be encrypted into DNA is first modified by a mutation correction code, the Hamming-code, to correct mutations within the DNA sequences. A header, containing the lengt ...
Lab Business - Memorial University
... SCOTUS in essence recognized that BRCA genes are ‘products of nature’ and thus on accepted principles not patentable. Such genes include expressed exon and intervening intron regions, as well as upstream and downstream promoters, enhancers, and other paraphernalia by which genes get things done. The ...
... SCOTUS in essence recognized that BRCA genes are ‘products of nature’ and thus on accepted principles not patentable. Such genes include expressed exon and intervening intron regions, as well as upstream and downstream promoters, enhancers, and other paraphernalia by which genes get things done. The ...
Atypical Patterns of Inheritance
... It is an inheritance process independent of the classical Mendelian inheritance. Imprinted alleles are silenced such that the genes are either expressed only from the non-imprinted allele inherited from the mother e.g. Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome, Silver– Russell syndrome, Angelman syndrome an ...
... It is an inheritance process independent of the classical Mendelian inheritance. Imprinted alleles are silenced such that the genes are either expressed only from the non-imprinted allele inherited from the mother e.g. Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome, Silver– Russell syndrome, Angelman syndrome an ...
Charles G. Kurland
... The endosymbionts that were the direct ancestors of mitochondria were in all probability descendents of free living ??proteobacteria. These must have had genome sizes sufficient to code 1000 to 2000 proteins if the facultative endocellular parasite Bartonella is a reliable guide. Where have all thes ...
... The endosymbionts that were the direct ancestors of mitochondria were in all probability descendents of free living ??proteobacteria. These must have had genome sizes sufficient to code 1000 to 2000 proteins if the facultative endocellular parasite Bartonella is a reliable guide. Where have all thes ...
DNA, Genes & Genomes
... All life forms rely on nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) for passing on their genetic information. DNA is a complex polymer of repeating nucleotides Each nucleotide = Deoxyribose Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogenous Base. ...
... All life forms rely on nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) for passing on their genetic information. DNA is a complex polymer of repeating nucleotides Each nucleotide = Deoxyribose Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogenous Base. ...
Human genome study reveals certain genes are less essential than
... “When we analysed the genomes of 2,500 people we were surprised to see over 200 genes that are missing entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished resear ...
... “When we analysed the genomes of 2,500 people we were surprised to see over 200 genes that are missing entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished resear ...
DNA notes File
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
Chapter 34 Study Guide File
... 26. What is the purpose of amniocentesis? Chorionic villus sampling? 27. What is the goal of gene replacement? How are the “therapeutic” genes carried to the cells ...
... 26. What is the purpose of amniocentesis? Chorionic villus sampling? 27. What is the goal of gene replacement? How are the “therapeutic” genes carried to the cells ...
genetics heredity test ANSWERS
... Calculate the average the number of codons (3 base sequences) per gene in the human genome. Hint: there are 3,000,000,000 base pairs and 26,000 genes in the human genome. You will need these 2 numbers and 2 others to make the calculation. (3,000,000,000 base pairs/genome) * (2 bases/pair) / (3 bases ...
... Calculate the average the number of codons (3 base sequences) per gene in the human genome. Hint: there are 3,000,000,000 base pairs and 26,000 genes in the human genome. You will need these 2 numbers and 2 others to make the calculation. (3,000,000,000 base pairs/genome) * (2 bases/pair) / (3 bases ...
mutations
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 15. Kanamycin can be used as a ___________________ marker ...
... 15. Kanamycin can be used as a ___________________ marker ...
EXAM 2
... 35. Any change in the chemical composition of DNA is a _mutation______________. 36. An alteration in the DNA composition that is not passed on to the subsequent genereation is referred to as _somatic______________, while those that can be passed on are referred to as _gametic___________. 37. An alte ...
... 35. Any change in the chemical composition of DNA is a _mutation______________. 36. An alteration in the DNA composition that is not passed on to the subsequent genereation is referred to as _somatic______________, while those that can be passed on are referred to as _gametic___________. 37. An alte ...
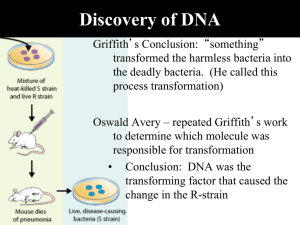
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
The Human Genome Project
... • detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food • match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs • determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds • authenicate consumables such as caviar and wine Agriculture and Livestock • disease-, insect-, and drought ...
... • detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food • match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs • determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds • authenicate consumables such as caviar and wine Agriculture and Livestock • disease-, insect-, and drought ...
energy exploration - Synergy Worldwide
... (thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid) and B7 (biotin) are known to be directly involved with cellular biochemical energy production and appear to influence mitochondrial function. L-carnitine and several of its derivatives, such as acetylcarnitine, are naturally occurring or ...
... (thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid) and B7 (biotin) are known to be directly involved with cellular biochemical energy production and appear to influence mitochondrial function. L-carnitine and several of its derivatives, such as acetylcarnitine, are naturally occurring or ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... polymorphisms in paternity, immigration, and murder cases. National Center for Human Genome Research created. $3 billion dollar effort to sequence human genome. 1990 Project launched ...
... polymorphisms in paternity, immigration, and murder cases. National Center for Human Genome Research created. $3 billion dollar effort to sequence human genome. 1990 Project launched ...
Changes in DNA can produce Variation
... by replacing defective genes with copies of a healthy one. ...
... by replacing defective genes with copies of a healthy one. ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.