Group presentations guide 10-4
... Virtually every single cell in the body contains a complete copy of the approximately 3 billion DNA base pairs, or letters, that make up the human genome. With its four-letter language, DNA contains the information needed to build the entire human body. A gene traditionally refers to the unit of DNA ...
... Virtually every single cell in the body contains a complete copy of the approximately 3 billion DNA base pairs, or letters, that make up the human genome. With its four-letter language, DNA contains the information needed to build the entire human body. A gene traditionally refers to the unit of DNA ...
Human Heredity and Birth Defects
... Course Description: This course covers topics including: DNA and genes; cell structure and control; what causes genetic disease, including single trait disorders, multifactorial inheritance, chromosomal abnormalities and mitochondrial disorders; autosomal and sex-linked inheritance; genetics of beha ...
... Course Description: This course covers topics including: DNA and genes; cell structure and control; what causes genetic disease, including single trait disorders, multifactorial inheritance, chromosomal abnormalities and mitochondrial disorders; autosomal and sex-linked inheritance; genetics of beha ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... specifically engineered to an individuals needs. It may also give new insights into the origins, evolution and migrations of humans. 65. Because genetic code is universal, when genes are transferred between species, these genes will produce the same polypeptides. This occurs when the gene that codes ...
... specifically engineered to an individuals needs. It may also give new insights into the origins, evolution and migrations of humans. 65. Because genetic code is universal, when genes are transferred between species, these genes will produce the same polypeptides. This occurs when the gene that codes ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... C. Its nucleus is fused with the nucleus of the differentiated cell. D. Its nucleus is exchanged with the nucleus of the sperm. ...
... C. Its nucleus is fused with the nucleus of the differentiated cell. D. Its nucleus is exchanged with the nucleus of the sperm. ...
Genetic Technology
... • Transgenic animals – scientists can create animals with human diseases and animals that can produce human materials. ...
... • Transgenic animals – scientists can create animals with human diseases and animals that can produce human materials. ...
[ the current understanding of DNA has changed dramatically from
... out of one location and reinserting in ...
... out of one location and reinserting in ...
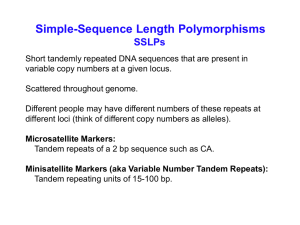
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... The metaphase chromosome is an adaption for mitosis and meiosis. The fibre must be less condensed for transcription to occur during interphase. Condensing controls if the genes are transcribed or not. ...
... The metaphase chromosome is an adaption for mitosis and meiosis. The fibre must be less condensed for transcription to occur during interphase. Condensing controls if the genes are transcribed or not. ...
Ess | Rebekah Ess Biology Lab November 2, 2012 “Genomic DNA
... mastodon, who would be the closest out-group to elephants and mammoths, are to this day extinct which makes it considerably harder to find material for genetic analysis. Rohland et al. used “a combination of modern DNA sequencing and targeted PCR amplification to obtain a large data set for comparin ...
... mastodon, who would be the closest out-group to elephants and mammoths, are to this day extinct which makes it considerably harder to find material for genetic analysis. Rohland et al. used “a combination of modern DNA sequencing and targeted PCR amplification to obtain a large data set for comparin ...
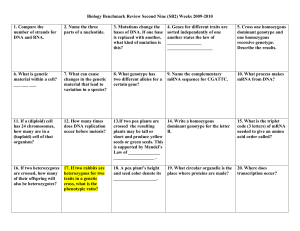
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 13.If two pea plants are 14. Write a homozygous crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or ...
... 13.If two pea plants are 14. Write a homozygous crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... DNA Tech for 400 What is the major functional difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells? ASCs are pluripotent. They can divide to produce a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
... DNA Tech for 400 What is the major functional difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells? ASCs are pluripotent. They can divide to produce a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
Document
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
Practice Question for Replication, Genetics and Biotechnology
... 10. Enzymes that join two fragments of DNA together are called? ...
... 10. Enzymes that join two fragments of DNA together are called? ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Example - UBC Pathology
... We all accumulate mutations within our mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) which encodes proteins necessary for our energy production. The more mutations we accumulate, the less we can produce energy, the less we can maintain the health of our tissues. This mitochondrial aging is believed to be one of the mai ...
... We all accumulate mutations within our mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) which encodes proteins necessary for our energy production. The more mutations we accumulate, the less we can produce energy, the less we can maintain the health of our tissues. This mitochondrial aging is believed to be one of the mai ...
Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. ...
... DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
... 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
3-10
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
Chapter 27 How Humans Evolved Visual Understanding 1. Figure
... discoveries of ancestral species need to be found and classified to allow a complete mapping of the evolution of our species. ...
... discoveries of ancestral species need to be found and classified to allow a complete mapping of the evolution of our species. ...
Slide 1
... expressed • Can be transferred to other cells • DNA is universal, so bacteria will produce plasmids even if DNA is not theirs originally • Used as a “vector” ...
... expressed • Can be transferred to other cells • DNA is universal, so bacteria will produce plasmids even if DNA is not theirs originally • Used as a “vector” ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickl ...
... 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickl ...
CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS
... • A PEDIGREE (diagram of family relationships that include 2 or more generations) can show how the sickle cell allele is passed on through generations of a family. ...
... • A PEDIGREE (diagram of family relationships that include 2 or more generations) can show how the sickle cell allele is passed on through generations of a family. ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.