STAAR Biology EOC Practice Test #1
... bacteria and viruses in the lungs. B Immune system B-cells are produced in the bone marrow of the skeletal system and introduced into the blood stream. C The nervous system stimulates the digestive system to release toxins that kill invading microbes. D Hormones released by viruses increase both blo ...
... bacteria and viruses in the lungs. B Immune system B-cells are produced in the bone marrow of the skeletal system and introduced into the blood stream. C The nervous system stimulates the digestive system to release toxins that kill invading microbes. D Hormones released by viruses increase both blo ...
Science Study Guide
... 4. Critical Thinking: Between the trachea and the esophagus is a flap of skin called the epiglottis. What do you think its function is? ...
... 4. Critical Thinking: Between the trachea and the esophagus is a flap of skin called the epiglottis. What do you think its function is? ...
Cell Unit 9.26.16
... Diatoms – single celled organisms that are plant like. Diatoms have chloroplasts and make their own food. This type of algae produce a lot of Earth’s oxygen. ...
... Diatoms – single celled organisms that are plant like. Diatoms have chloroplasts and make their own food. This type of algae produce a lot of Earth’s oxygen. ...
Study guide packet part 1
... F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis happens. It contains a pigment called chlorophyll which keeps the plant green and captures light energy. G. Vacuole- Large vacuole only in plants. It stores food, water, enzyme, and waste. ...
... F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis happens. It contains a pigment called chlorophyll which keeps the plant green and captures light energy. G. Vacuole- Large vacuole only in plants. It stores food, water, enzyme, and waste. ...
Work Booklet Workstations Answers
... of the cells. Once you have answered all questions, use any of the material provided to construct correctly ONE prokaryotic cell and ONE eukaryotic cell with your partner. Use your creativity, but make sure all organelles for each type of cell are present!! 1. Which of the organelles is found in b ...
... of the cells. Once you have answered all questions, use any of the material provided to construct correctly ONE prokaryotic cell and ONE eukaryotic cell with your partner. Use your creativity, but make sure all organelles for each type of cell are present!! 1. Which of the organelles is found in b ...
Cells to Body Systems vocab and notes
... 4. Organelle: tiny structure within a cell that performs a particular function in a cell 5. Cell membrane: organelle that holds the parts of an animal or plant cell together and separates it from its surroundings 6. Nucleus: organelle that controls all of the animal or plant cell’s activities and co ...
... 4. Organelle: tiny structure within a cell that performs a particular function in a cell 5. Cell membrane: organelle that holds the parts of an animal or plant cell together and separates it from its surroundings 6. Nucleus: organelle that controls all of the animal or plant cell’s activities and co ...
1327004619.
... themselves. Such a change in the environment is termed as stimulus. Some of the signs of sensitivity include locomotion of animal, crying of a child on seeing a fierce looking dog, growing towards light by a plant shoot. Sensitivity is very essential in the survival of an organism. 4. Growth and dev ...
... themselves. Such a change in the environment is termed as stimulus. Some of the signs of sensitivity include locomotion of animal, crying of a child on seeing a fierce looking dog, growing towards light by a plant shoot. Sensitivity is very essential in the survival of an organism. 4. Growth and dev ...
Slide 1
... • Many-celled organisms are not just mixedup collections of different types of cells. • Cells are organized into systems that, together, perform functions that keep the organism healthy and alive. ...
... • Many-celled organisms are not just mixedup collections of different types of cells. • Cells are organized into systems that, together, perform functions that keep the organism healthy and alive. ...
In Figure 19-4, which disinfectant was the most effective at
... 100- plants Which of the following is NOT characteristic of all plants? A. They are eukaryotic B. They have cell walls C. They produce seeds D. They are multicellular ...
... 100- plants Which of the following is NOT characteristic of all plants? A. They are eukaryotic B. They have cell walls C. They produce seeds D. They are multicellular ...
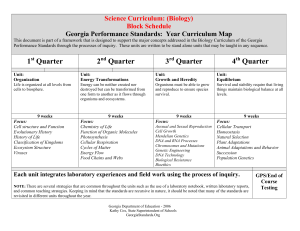
Curriculum Map - Biology
... This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may be taught in any sequence. ...
... This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may be taught in any sequence. ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... What does selectively permeable mean? What organelle doe this describe. Some molecules can pass, while others can not. The cell membrane. ...
... What does selectively permeable mean? What organelle doe this describe. Some molecules can pass, while others can not. The cell membrane. ...
UPcellprepro.10131154
... At the end of this unit you will be able to: 1. Describe each phase of the cell cycle 2. Describe the structure of a chromosome. 3. Compare prokaryotic chromosomes with eukaryotic chromosomes. 4. Explain the differences between sex chromosomes and autosomes. 5. Give examples of diploid and haploid c ...
... At the end of this unit you will be able to: 1. Describe each phase of the cell cycle 2. Describe the structure of a chromosome. 3. Compare prokaryotic chromosomes with eukaryotic chromosomes. 4. Explain the differences between sex chromosomes and autosomes. 5. Give examples of diploid and haploid c ...
Importance of Cell Division
... Asexual reproduction is the process of producing offspring from only one parent, this results in the production of offspring that are genetically identical. Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an o ...
... Asexual reproduction is the process of producing offspring from only one parent, this results in the production of offspring that are genetically identical. Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an o ...
2015 1st Semester Exam Review Key
... 1. Describe the difference between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. Give an example of each. Prokaryote- does not contain a nucleus or membranes bound organelles- example is bacteria Eukaryote- it has a nucleus and organelles such as mitochondria and golgi bodies- example is humans, fungi and pl ...
... 1. Describe the difference between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. Give an example of each. Prokaryote- does not contain a nucleus or membranes bound organelles- example is bacteria Eukaryote- it has a nucleus and organelles such as mitochondria and golgi bodies- example is humans, fungi and pl ...
Review Game - WordPress.com
... membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer with a channel protein. Each x represents the same type of molecule inside or outside the cell. Facilitated diffusion moves these molecules across the cell membrane. In what direction do these molecules move and through which structure? ...
... membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer with a channel protein. Each x represents the same type of molecule inside or outside the cell. Facilitated diffusion moves these molecules across the cell membrane. In what direction do these molecules move and through which structure? ...
Sample Questions for Exam One Multiple Choice. Choose the
... 16. Which of the following statements about the plasma membrane is TRUE? a. it plays a role regulating what can move into and out of the cell b. the plasma membrane contains a variety of proteins c. the plasma membrane helps maintain the shape of the cell d. it is a bilayer of lipid e. all of the ab ...
... 16. Which of the following statements about the plasma membrane is TRUE? a. it plays a role regulating what can move into and out of the cell b. the plasma membrane contains a variety of proteins c. the plasma membrane helps maintain the shape of the cell d. it is a bilayer of lipid e. all of the ab ...
Cells_and_Tissues_in_Health_and_Disease
... – Two types of nucleic acid combined with protein – Nuclear membrane: double-layered; with pores; separates nucleus from cytoplasm • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): in chromosomes in the nucleus, contains genetic information • Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in nucleoli; component of messenger, transfer, ribos ...
... – Two types of nucleic acid combined with protein – Nuclear membrane: double-layered; with pores; separates nucleus from cytoplasm • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): in chromosomes in the nucleus, contains genetic information • Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in nucleoli; component of messenger, transfer, ribos ...
Objective 2: demonstrate an understanding of the organization of
... homeostasis, permeability, energy production, transportation of molecules, disposal of wastes, function of cellular parts, and synthesis of new molecules. ...
... homeostasis, permeability, energy production, transportation of molecules, disposal of wastes, function of cellular parts, and synthesis of new molecules. ...
Biology Quiz Review – Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues
... 10. What is the Chloroplast? Organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that perform photosynthesis (take energy from the sun, water and carbon dioxide and make sugar and oxygen). 11. What is the Cytoplasm? A thick liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all organelles, ...
... 10. What is the Chloroplast? Organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that perform photosynthesis (take energy from the sun, water and carbon dioxide and make sugar and oxygen). 11. What is the Cytoplasm? A thick liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all organelles, ...
Cells, Genetics and Human Body Systems Unit Notes
... Nuclear envelope/membrane: determines what goes in and out of nucleus Cytoplasm: gel-like substance that holds organelles Cell membrane: determines what goes into and out of cell, provides shape and support Endoplasmic reticulum: passageways that transport materials (mostly proteins) throughout cell ...
... Nuclear envelope/membrane: determines what goes in and out of nucleus Cytoplasm: gel-like substance that holds organelles Cell membrane: determines what goes into and out of cell, provides shape and support Endoplasmic reticulum: passageways that transport materials (mostly proteins) throughout cell ...
Unit 3 Review Study Guide
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.