Lec. No.10 Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome is an
... In cells with a flagellum, e.g. sperm, the flagellum develops from a single basal body. (While sperm cells have a basal body, eggs have none. So the sperm's basal body is absolutely essential for forming a centrosome which will form a spindle enabling the first division of the zygote to take place. ...
... In cells with a flagellum, e.g. sperm, the flagellum develops from a single basal body. (While sperm cells have a basal body, eggs have none. So the sperm's basal body is absolutely essential for forming a centrosome which will form a spindle enabling the first division of the zygote to take place. ...
Control of Cell Division
... workers (ribosomes) on the assembly line are in the factory (cytosol) who receive orders for production from the boss’s messanger (mRNA). The raw materials are the amino acids. When things are sent to the mailroom for outside delivery (golgi apparatus), they are eventually shuttled to the gates of t ...
... workers (ribosomes) on the assembly line are in the factory (cytosol) who receive orders for production from the boss’s messanger (mRNA). The raw materials are the amino acids. When things are sent to the mailroom for outside delivery (golgi apparatus), they are eventually shuttled to the gates of t ...
SURFIN` THROUGH STAAR Session 2: Cellular Processes
... Lysosome- digests worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed bacteria & viruses (like a janitor/clean up crew) Ribosome- site of protein synthesis (think of meat-has protein in it) Cell membrane- controls what enter and leaves the cell, “semi or selectively permeable” (like a bouncer) ...
... Lysosome- digests worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed bacteria & viruses (like a janitor/clean up crew) Ribosome- site of protein synthesis (think of meat-has protein in it) Cell membrane- controls what enter and leaves the cell, “semi or selectively permeable” (like a bouncer) ...
Energy in the Cell
... 1.1a All of the cells in your body come from a single cell that differentiates into many different cells, but they all essentially have the same genetic instructions. • 1.11 All organisms begin their life cycles as a single cell, and in multicellular organisms, new generations of embryonic cells fo ...
... 1.1a All of the cells in your body come from a single cell that differentiates into many different cells, but they all essentially have the same genetic instructions. • 1.11 All organisms begin their life cycles as a single cell, and in multicellular organisms, new generations of embryonic cells fo ...
March 21,200O Food and Drug Administration
... j ..‘ cell ),) repair in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection ...
... j ..‘ cell ),) repair in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection ...
A Journey Through the Cell: Part Two— Cells Functions: A Closer
... mitosis: The process in cell division by which the nucleus divides, typically consisting of five stages—interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—and normally resulting in two new nuclei, each of which contains a scomplete copy of the parental chromosomes. Also called karyokinesis. nu ...
... mitosis: The process in cell division by which the nucleus divides, typically consisting of five stages—interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—and normally resulting in two new nuclei, each of which contains a scomplete copy of the parental chromosomes. Also called karyokinesis. nu ...
Cells and Systems UNIT Test Unit 2 1. Growth and development
... 3. Body Systems interact in many ways. Identify the ...
... 3. Body Systems interact in many ways. Identify the ...
cells?
... know re: cells? 11/2/15 Animal cells are different from plant cells Cells are alive, so they can die Many different types of cells All eukaryotic cells have a nucleus Animal cells are not connected to each other like plant cells Cells are basic building block of life Plant cells are a ...
... know re: cells? 11/2/15 Animal cells are different from plant cells Cells are alive, so they can die Many different types of cells All eukaryotic cells have a nucleus Animal cells are not connected to each other like plant cells Cells are basic building block of life Plant cells are a ...
Fertilization
... the first series of cell divisions by mitosis after fertilization Cell division is rapid, new cells do not take time for the growth phase G1 cell growth does not occur so cells decrease in size with each cleavage division ...
... the first series of cell divisions by mitosis after fertilization Cell division is rapid, new cells do not take time for the growth phase G1 cell growth does not occur so cells decrease in size with each cleavage division ...
big
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
Lecture 19
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
Review for Final Exam - 2015
... 5. List the generation and the numbers that have straight hair. I – 1, II – 1,5,8, III – 1,6,8 6. What numbers may have the genotype PP? 7. How many females have the recessive trait? 4 8. How many males have the dominant trait? 5 ...
... 5. List the generation and the numbers that have straight hair. I – 1, II – 1,5,8, III – 1,6,8 6. What numbers may have the genotype PP? 7. How many females have the recessive trait? 4 8. How many males have the dominant trait? 5 ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4 Study Guide
... 14. Base: supports the upper part of the microscope Know how to calculate the magnification of an object viewed under the microscope. (Page 393)—Extra Question The eyepiece has a power of 10x. Each objective lens on the revolving nosepiece has its ...
... 14. Base: supports the upper part of the microscope Know how to calculate the magnification of an object viewed under the microscope. (Page 393)—Extra Question The eyepiece has a power of 10x. Each objective lens on the revolving nosepiece has its ...
Midterm Review Cover page
... potassium ion concentration is higher inside many cells than it is outside these cells. This condition is mainly a result of the process of (a) passive transport (b) active transport (c) osmosis (d) pinocytosis 3. Chemical analysis indicates that the cell membrane is composed mainly of (a) proteins ...
... potassium ion concentration is higher inside many cells than it is outside these cells. This condition is mainly a result of the process of (a) passive transport (b) active transport (c) osmosis (d) pinocytosis 3. Chemical analysis indicates that the cell membrane is composed mainly of (a) proteins ...
File - Once Upon A Cell
... Lysosome- digests worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed bacteria & viruses (like a janitor/clean up crew) Ribosome- site of protein synthesis (think of meat-has protein in it) ...
... Lysosome- digests worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed bacteria & viruses (like a janitor/clean up crew) Ribosome- site of protein synthesis (think of meat-has protein in it) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 01. Define prokaryotic cell. 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is ...
... 01. Define prokaryotic cell. 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is ...
Biology STAAR Review
... Cell Theory – 1.) All living things are composed of cells. 2.) Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.) All cells come from preexisting cells. Cell Size: small to maximize surface area to volume ratio (SA/V) for regulating internal cell environment. As a cell’s volumes increases, the SA/V decreases. Ce ...
... Cell Theory – 1.) All living things are composed of cells. 2.) Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.) All cells come from preexisting cells. Cell Size: small to maximize surface area to volume ratio (SA/V) for regulating internal cell environment. As a cell’s volumes increases, the SA/V decreases. Ce ...
1. What feature is similar among all organisms? A. They can
... Structure 3 is the nucleus, which serves as the control center of the cell. Structure 3 is the cell membrane, which controls what enters and leaves the cell. Structure 3 is the cytoplasm, which contains organelles and is the site of many cell processes. Structure 3 is a chloroplast, which is the s ...
... Structure 3 is the nucleus, which serves as the control center of the cell. Structure 3 is the cell membrane, which controls what enters and leaves the cell. Structure 3 is the cytoplasm, which contains organelles and is the site of many cell processes. Structure 3 is a chloroplast, which is the s ...
Additional Biology
... ability to differentiate throughout life. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement Cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow, called stem cells, can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, e.g. nerve cells Human stem cells have the abi ...
... ability to differentiate throughout life. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement Cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow, called stem cells, can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, e.g. nerve cells Human stem cells have the abi ...
GHSGT BIOLOGY REVIEW
... better suited to their environments will live longer and reproduce more offspring, thus passing on the traits that made them better suited to more of the next generation. This theory is also called survival of the fittest. Fossils (traces of previously living organisms) are the most convincing evide ...
... better suited to their environments will live longer and reproduce more offspring, thus passing on the traits that made them better suited to more of the next generation. This theory is also called survival of the fittest. Fossils (traces of previously living organisms) are the most convincing evide ...
Sickle Cell Anemia - Woodcliff Lake School
... because of the wrong DNA sequence make an abnormal protein, causing there red blood cells to become sickle shaped. These crescent moon shaped cells get clogged in small blood vessels and often fail to reach the cells they are trying to deliver oxygen too. This leaves the person with many serious sym ...
... because of the wrong DNA sequence make an abnormal protein, causing there red blood cells to become sickle shaped. These crescent moon shaped cells get clogged in small blood vessels and often fail to reach the cells they are trying to deliver oxygen too. This leaves the person with many serious sym ...
Unit 1 - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... the cell membrane allow ions and other molecules to diffuse into and out of a cell o Where have we seen facilitate diffusion in action? o Neuron’s gated Na+ and K+ channels o Ca+ channels in nerve and muscle ...
... the cell membrane allow ions and other molecules to diffuse into and out of a cell o Where have we seen facilitate diffusion in action? o Neuron’s gated Na+ and K+ channels o Ca+ channels in nerve and muscle ...
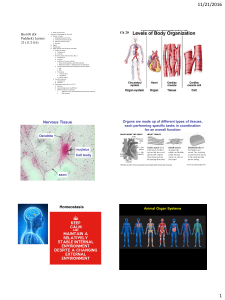
Nervous Tissue Homeostasis
... Echinoderms (seastars, urchins, etc) have? 10. Bilateral symmetry allows cephalization, as well as distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is involved in each step: sensory input, integration, motor output. ...
... Echinoderms (seastars, urchins, etc) have? 10. Bilateral symmetry allows cephalization, as well as distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is involved in each step: sensory input, integration, motor output. ...
REVIEW
... a.allows all substances to pass into c. is composed mainly of a protein and out of the cell. bilayer. b. prevents all substances from d. is composed mainly of a lipid passing into and out of the cell. bilayer. _____ 2. Substances produced in a cell and exported outside of the cell would pass through ...
... a.allows all substances to pass into c. is composed mainly of a protein and out of the cell. bilayer. b. prevents all substances from d. is composed mainly of a lipid passing into and out of the cell. bilayer. _____ 2. Substances produced in a cell and exported outside of the cell would pass through ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.