B2 revision questions
... What is the function of the oesophagus in digestion? What is the function of the stomach in digestion? What is the function of the small intestine in digestion? What is the function of the large intestine in digestion? What is the function of the pancreas in digestion? What is the function of the li ...
... What is the function of the oesophagus in digestion? What is the function of the stomach in digestion? What is the function of the small intestine in digestion? What is the function of the large intestine in digestion? What is the function of the pancreas in digestion? What is the function of the li ...
Basis of Cell Structure and Function
... That is, the different cells within the body perform different jobs for functions. • Due to the differences in function of the cells we are can see great diversity in cell: • 1. Size • 2. Shape Of Cells • Cell Size • Cells vary in size from the smallest bacteria (1 micrometer) to the largest cell, a ...
... That is, the different cells within the body perform different jobs for functions. • Due to the differences in function of the cells we are can see great diversity in cell: • 1. Size • 2. Shape Of Cells • Cell Size • Cells vary in size from the smallest bacteria (1 micrometer) to the largest cell, a ...
1st 9 weeks Review KEY LIVING THINGS
... 7. What is an organism that makes its own food for energy called? PRODUCER 8. What is an example of a decomposer? FUNGUS 9. What is an example of a consumer? ANIMAL 10. What is an example of a producer? PLANT 11. What do a group of similar cells working together make? TISSUE 12. What do a group of s ...
... 7. What is an organism that makes its own food for energy called? PRODUCER 8. What is an example of a decomposer? FUNGUS 9. What is an example of a consumer? ANIMAL 10. What is an example of a producer? PLANT 11. What do a group of similar cells working together make? TISSUE 12. What do a group of s ...
Biology HSA Review Packet
... Cell parts you MUST know but don’t count out the others! Cell Membrane – plant and animal – regulates what enters and leaves Cell Wall – cellulose – supports plant cell, is rigid ...
... Cell parts you MUST know but don’t count out the others! Cell Membrane – plant and animal – regulates what enters and leaves Cell Wall – cellulose – supports plant cell, is rigid ...
Cells The cell theory: All living things are made up of cells. Cells are
... Eukaryotic cells have cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. However, there are many more organelles within eukaryotic cells. These include a nucleus to house the DNA, a nucleolus where ribosomes are made, rough endoplasmic reticulum for protein assembly, smooth endoplasmic reticulum for mak ...
... Eukaryotic cells have cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. However, there are many more organelles within eukaryotic cells. These include a nucleus to house the DNA, a nucleolus where ribosomes are made, rough endoplasmic reticulum for protein assembly, smooth endoplasmic reticulum for mak ...
Cell Biology - Faculty of Science
... Ultrastructure and function and their role in controlling cellular responses to cell matrix. Intracellular compartments: Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes and pearoxiyoms ultrastructure and functioum. Energy transformers: Mitochondria and chloroplasts. The course concentrates also on t ...
... Ultrastructure and function and their role in controlling cellular responses to cell matrix. Intracellular compartments: Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes and pearoxiyoms ultrastructure and functioum. Energy transformers: Mitochondria and chloroplasts. The course concentrates also on t ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review 2013
... 12. a) What are the functions of animal epithelial tissues? b) What are the functions of plant dermal tissues? c) What are the similarities and differences in these functions? 13. Compare the transport system in a plant with that in an animal. 14. Compare how a plant and an animal obtain nutrients. ...
... 12. a) What are the functions of animal epithelial tissues? b) What are the functions of plant dermal tissues? c) What are the similarities and differences in these functions? 13. Compare the transport system in a plant with that in an animal. 14. Compare how a plant and an animal obtain nutrients. ...
Student Packet 16 Plant Animal Cells L.14.3
... Activity 2 - Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells ............................................................9 ...
... Activity 2 - Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells ............................................................9 ...
bio eoc powerpoint study guide
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
Cells and Tissues - Lemon Bay High School
... A CELL is the smallest functioning unit of the human body. AN ORGANELLE is the tools that the cell uses TO FUNCTION. ...
... A CELL is the smallest functioning unit of the human body. AN ORGANELLE is the tools that the cell uses TO FUNCTION. ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Materials
... C. Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins are embedded & extend across the entire cell membrane. These are exposed to both the inside of the cell & the exterior environment. D. Other integral proteins extend only to the inside or only to the exterior surface. E. Cell membrane proteins help move ...
... C. Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins are embedded & extend across the entire cell membrane. These are exposed to both the inside of the cell & the exterior environment. D. Other integral proteins extend only to the inside or only to the exterior surface. E. Cell membrane proteins help move ...
Document
... _____an organism that absorbs nutrients from dead or decaying organisms. _____a filament of a fungus _____a rootlike structure that holds fungi in place and absorbs nutrients _____the mass of fungal filaments that forms the fungal body _____a sexual structure that contains zygotes. _____the microsco ...
... _____an organism that absorbs nutrients from dead or decaying organisms. _____a filament of a fungus _____a rootlike structure that holds fungi in place and absorbs nutrients _____the mass of fungal filaments that forms the fungal body _____a sexual structure that contains zygotes. _____the microsco ...
Sex - Plantsbrook Science
... lining (implantation). The woman is now pregnant. Once it has developed all its organs (after about 10 weeks) it is called a fetus. It takes about 40 weeks (9 months) for a fertilised egg cell to grow into a baby ready to be born. This time is called the gestation period. ...
... lining (implantation). The woman is now pregnant. Once it has developed all its organs (after about 10 weeks) it is called a fetus. It takes about 40 weeks (9 months) for a fertilised egg cell to grow into a baby ready to be born. This time is called the gestation period. ...
62.1E6 INVESTIGATOR Name Thomas M. Jessell and
... Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., Roelink, H., and Jessell, T.M. (1995). Dorsal differentiation of neural plate cells induced by BMP-mediated signals from epidermal ectoderm. Cell 82, 969-979. Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., and Jessell, T.M. (1997). A role for the roof plate and its resident TGFß-related p ...
... Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., Roelink, H., and Jessell, T.M. (1995). Dorsal differentiation of neural plate cells induced by BMP-mediated signals from epidermal ectoderm. Cell 82, 969-979. Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., and Jessell, T.M. (1997). A role for the roof plate and its resident TGFß-related p ...
Chapter 19 – Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life
... Like kingdoms, there are much broader groups called domains. There are three such domains. They are eukarya, archae, and bacteria. Eukarya is the newest group. The Domain Bacteria Characteristics and Kinds of Bacteria The first domain is bacteria. All organisms of the bacteria domain are prokaryotes ...
... Like kingdoms, there are much broader groups called domains. There are three such domains. They are eukarya, archae, and bacteria. Eukarya is the newest group. The Domain Bacteria Characteristics and Kinds of Bacteria The first domain is bacteria. All organisms of the bacteria domain are prokaryotes ...
Development and Apoptosis
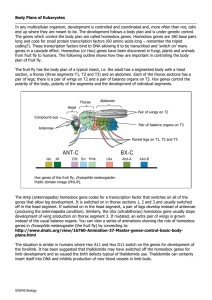
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
biology xi - Dehradun Public School
... described as antiparallel? Q.49.What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins? Q.50.Explain the structure of DNA. Write three major differences between DNA and RNA? Q.51.Enlist the important properties of enzymes. Chapter-10:Cell cycle and Cell division Q.52.What is the significance of meiosis? Q. ...
... described as antiparallel? Q.49.What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins? Q.50.Explain the structure of DNA. Write three major differences between DNA and RNA? Q.51.Enlist the important properties of enzymes. Chapter-10:Cell cycle and Cell division Q.52.What is the significance of meiosis? Q. ...
Cell Transport graphic organizer
... When do red blood cells become wrinkled? Does Passive transport require energy? The door to the ice rink is compared to what? What is it called when water diffuses across a cell membrane? How does anything diffuse? Does Active Transport require energy? Can molecules move from low concentration to hi ...
... When do red blood cells become wrinkled? Does Passive transport require energy? The door to the ice rink is compared to what? What is it called when water diffuses across a cell membrane? How does anything diffuse? Does Active Transport require energy? Can molecules move from low concentration to hi ...
Transport Phenomena in Cell Biology - Thermal
... • Background and Societal Impact – Cells are the basic organizing unit of life • A cell is a membrane-bound soup of water, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids that grows, reproduces and interacts with its environment ...
... • Background and Societal Impact – Cells are the basic organizing unit of life • A cell is a membrane-bound soup of water, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids that grows, reproduces and interacts with its environment ...
Level Of Organisation
... • Exchange of martial between tissue and their environment has the potential to be far more efficient if the tissue is made up of many small cells rather than fewer larger cells. ...
... • Exchange of martial between tissue and their environment has the potential to be far more efficient if the tissue is made up of many small cells rather than fewer larger cells. ...
Unit 2 Test
... 2. What is the primary (main) difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? a. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles that eukaryotic cells lack b. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles that prokaryotic cells lack c. Prokaryotic cells make ...
... 2. What is the primary (main) difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? a. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles that eukaryotic cells lack b. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles that prokaryotic cells lack c. Prokaryotic cells make ...
Chapter 2, section 2
... • Some consumers get food by breaking down dead organisms or waste. They are • Decomposers ...
... • Some consumers get food by breaking down dead organisms or waste. They are • Decomposers ...
Cell Physiology
... Synthesis of RNA • During synthesis of RNA, two strands of DNA molecules separate temporarily; one of these strands is used as a template for synthesis of the RNA molecules. • The code triplets in the DNA cause the formation of complementary code triplets (called codons) in the RNA; these codons in ...
... Synthesis of RNA • During synthesis of RNA, two strands of DNA molecules separate temporarily; one of these strands is used as a template for synthesis of the RNA molecules. • The code triplets in the DNA cause the formation of complementary code triplets (called codons) in the RNA; these codons in ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.