Homeostasis – process by which an organisms
... Proteins pump molecules through membrane. Molecules move ______________________________ diffusion (from low to high concentration) OTHER WAYS CELLS GET MATERIALS... Vesicles – a membrane-bound sac that is used to transport materials inside of a cell Endocytosis - plasma membrane ____________ ...
... Proteins pump molecules through membrane. Molecules move ______________________________ diffusion (from low to high concentration) OTHER WAYS CELLS GET MATERIALS... Vesicles – a membrane-bound sac that is used to transport materials inside of a cell Endocytosis - plasma membrane ____________ ...
Keystone Biology Practice Questions copy.pages
... B. Translocation can cause duplication of certain sections of chromosomes.! C. Translocation can cause the exchange of genetic material between homologous! chromosomes.! D. Translocation can result in the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during! meiosis.! 38. Scientists have been able t ...
... B. Translocation can cause duplication of certain sections of chromosomes.! C. Translocation can cause the exchange of genetic material between homologous! chromosomes.! D. Translocation can result in the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during! meiosis.! 38. Scientists have been able t ...
Keystone Biology MC Review Questions 1. The diagram below
... A. Both cell types carry out transcription in the nucleus. B. Both cell types use ribosomes to carry out translation. C. Both cell types assemble amino acids to carry out transcription. D. Both cell types carry out translation in the endoplasmic reticulum. 26. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network ...
... A. Both cell types carry out transcription in the nucleus. B. Both cell types use ribosomes to carry out translation. C. Both cell types assemble amino acids to carry out transcription. D. Both cell types carry out translation in the endoplasmic reticulum. 26. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network ...
Answers to Biology Unit Handout
... bronchioles are the air sacs called the alveoli. Gas exchange happens at the site of the alveoli as they are held by capillaries. Capillaries allow for blood cells to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. When air is expired (exhaled) CO2 is removed from the blood cells and when we inspire (inhale) t ...
... bronchioles are the air sacs called the alveoli. Gas exchange happens at the site of the alveoli as they are held by capillaries. Capillaries allow for blood cells to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. When air is expired (exhaled) CO2 is removed from the blood cells and when we inspire (inhale) t ...
Objective 2 - Organization of Living Systems
... Carbon dioxide Plus Water Produces Glucose And Oxygen ...
... Carbon dioxide Plus Water Produces Glucose And Oxygen ...
Cells and tissues - Unpicking misconceptions
... “Cells are too small to see.” Because of the very small nature of cells and the difficulty in visualising them, students often have misconceptions regarding the actual sizes of cells or the relative sizes of different specialised cells (egg and sperm in particular). The use of scale models or scale ...
... “Cells are too small to see.” Because of the very small nature of cells and the difficulty in visualising them, students often have misconceptions regarding the actual sizes of cells or the relative sizes of different specialised cells (egg and sperm in particular). The use of scale models or scale ...
Introduction to Biology
... Cellular Organization • all living things are composed of cells – tiny compartments surrounded by a membrane ...
... Cellular Organization • all living things are composed of cells – tiny compartments surrounded by a membrane ...
Anatomical Terminology
... composed of DNA which directs the cell’s activities. They are the instructions for the building of all of your body’s proteins. ...
... composed of DNA which directs the cell’s activities. They are the instructions for the building of all of your body’s proteins. ...
Basic Biological Principles
... other cells, and they divide by mitosis or meiosis. Cells contain organelles and the genetic information of an organism. Tissues are composed of many cells that work together to perform a specific function. Tissue covers most parts of an organism. There are several types of tissues, such as connecti ...
... other cells, and they divide by mitosis or meiosis. Cells contain organelles and the genetic information of an organism. Tissues are composed of many cells that work together to perform a specific function. Tissue covers most parts of an organism. There are several types of tissues, such as connecti ...
Central Nervous System (CNS): the body`s main control center and
... system. Examples: dilation of pupils, peristalsis, blood vessels. Each muscle cell contains only one nucleus. Cardiac-Muscle-found only in the heart. Both striated and involuntary. Works slowly and constantly to beat for life. 4.5 Recognize that the sexual reproductive system allows organisms to pro ...
... system. Examples: dilation of pupils, peristalsis, blood vessels. Each muscle cell contains only one nucleus. Cardiac-Muscle-found only in the heart. Both striated and involuntary. Works slowly and constantly to beat for life. 4.5 Recognize that the sexual reproductive system allows organisms to pro ...
A study reveals how respiratory tubes and capillaries form
... A tube-cell image. In red, the tube; in blue, the cell nuclei; in green, cell shape. (electron microscopy). Credit: Copyright IRB Barcelona. J. Casanova Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and CSIC report on the formation of the small-diameter respiratory tubes of ...
... A tube-cell image. In red, the tube; in blue, the cell nuclei; in green, cell shape. (electron microscopy). Credit: Copyright IRB Barcelona. J. Casanova Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and CSIC report on the formation of the small-diameter respiratory tubes of ...
Biology Cell Labs - Oregon School District
... 1. What is the basic unit (or building block) of living organisms? 2. How are new cells made? Cell Structure All cells are enclosed by a cell membrane. Within the membrane are the nucleus and the cytoplasm, which consists of all the material outside the nucleus and inside the cell membrane. Within t ...
... 1. What is the basic unit (or building block) of living organisms? 2. How are new cells made? Cell Structure All cells are enclosed by a cell membrane. Within the membrane are the nucleus and the cytoplasm, which consists of all the material outside the nucleus and inside the cell membrane. Within t ...
Deterministic Global Parameter Estimation for a Budding
... Students: Nick Allen* Emery Conrad+ Ranjit Randhawa* Marc Vass* Jason Zwolak* ...
... Students: Nick Allen* Emery Conrad+ Ranjit Randhawa* Marc Vass* Jason Zwolak* ...
FOA 9-19-2011
... In what phase of mitosis does the nucleus break apart and the spindle fibers move to opposite ends of the cell? A. interphase C. telophase B. prophase D. metaphase ...
... In what phase of mitosis does the nucleus break apart and the spindle fibers move to opposite ends of the cell? A. interphase C. telophase B. prophase D. metaphase ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... Prokaryotic cells– like bacteria – very simple structure – nucleus not contained within a membranous boundary. Eukaryotic cells – everything else. Cells are much more complex – have a real nucleus within a nuclear envelope. You and I are eukaryotic!! Prokaryotic cells – primitive, rudimentary, primo ...
... Prokaryotic cells– like bacteria – very simple structure – nucleus not contained within a membranous boundary. Eukaryotic cells – everything else. Cells are much more complex – have a real nucleus within a nuclear envelope. You and I are eukaryotic!! Prokaryotic cells – primitive, rudimentary, primo ...
CELLS structure and function
... Highly specialized organelle that serves as the information processing and administrative center of the cell. This organelle has two major functions: ◦ it stores the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and ◦ it coordinates the cell's activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein ...
... Highly specialized organelle that serves as the information processing and administrative center of the cell. This organelle has two major functions: ◦ it stores the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and ◦ it coordinates the cell's activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein ...
Week 2 Lecture Summarys copy
... - cells continue to divide every 12-15hrs as it takes the 3 day trip down the fallopian tubes - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst) and the rapidly dividing cells form a ball of about 100 cells - implantation comes nex ...
... - cells continue to divide every 12-15hrs as it takes the 3 day trip down the fallopian tubes - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst) and the rapidly dividing cells form a ball of about 100 cells - implantation comes nex ...
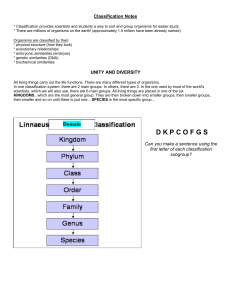
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... * There are millions of organisms on the earth! (approximately 1.5 million have been already named) Organisms are classified by their: * physical structure (how they look) * evolutionary relationships * embryonic similarities (embryos) * genetic similarities (DNA) * biochemical similarities ...
... * There are millions of organisms on the earth! (approximately 1.5 million have been already named) Organisms are classified by their: * physical structure (how they look) * evolutionary relationships * embryonic similarities (embryos) * genetic similarities (DNA) * biochemical similarities ...
Biology Review
... 54. Sample Sex-linked trait Question: Color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. A mother with normal color vision and a color blind father have a color blind daughter. Which of the following statements is ...
... 54. Sample Sex-linked trait Question: Color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. A mother with normal color vision and a color blind father have a color blind daughter. Which of the following statements is ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Cells Vocab Chart
... A temporary cytoplasmic protrusion in amoebas and other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
... A temporary cytoplasmic protrusion in amoebas and other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
cells! - Catawba County Schools
... Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi bodies ...
... Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi bodies ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... 19. In telophase, chromosomes begin to _________________________________ D. Cytoplasmic Division 1. Cytoplasmic division begins in ______________________________________ and ends in _______________________________________________________ . 2. ______________________ are responsible for pinching the c ...
... 19. In telophase, chromosomes begin to _________________________________ D. Cytoplasmic Division 1. Cytoplasmic division begins in ______________________________________ and ends in _______________________________________________________ . 2. ______________________ are responsible for pinching the c ...
Cells_and_Chemical_Changes_Background_Info_
... All plants and animals grow by reproducing cells. In large organisms such as people, the billions of cells perform many different roles. The cells combine to form body tissue and several different tissues also combine to form organs and to function as various parts of the body, from the brain to the ...
... All plants and animals grow by reproducing cells. In large organisms such as people, the billions of cells perform many different roles. The cells combine to form body tissue and several different tissues also combine to form organs and to function as various parts of the body, from the brain to the ...
class_objective_2 student
... • ______________ movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is diffusion. • The diffusion of water is called ____________. ...
... • ______________ movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is diffusion. • The diffusion of water is called ____________. ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.