Notes Module #1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... A part of the ENDOCRINE system. Releases the hormone MELOTONIN Works with the pons to regulate sleep/wake cycles. Controlled by LIGHT and DARK environments. How do your own sleep habits relate to the information you’ve learned about the pons and pineal gland? ...
... A part of the ENDOCRINE system. Releases the hormone MELOTONIN Works with the pons to regulate sleep/wake cycles. Controlled by LIGHT and DARK environments. How do your own sleep habits relate to the information you’ve learned about the pons and pineal gland? ...
How Does the Brain Learn Through Music?
... “ States should review their curriculum guidelines to ensure that they encourage adequate attention to and time for art and music, and should consider including measures of knowledge and skills in art and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
... “ States should review their curriculum guidelines to ensure that they encourage adequate attention to and time for art and music, and should consider including measures of knowledge and skills in art and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
Biology of Learning and Memory
... long-term declarative memories, although they can still recall events from before the damage and can still form new procedural memories. • The hippocampus is critical for consolidating some forms of memory but not all. It is especially important for declarative memory and spatial memory. ...
... long-term declarative memories, although they can still recall events from before the damage and can still form new procedural memories. • The hippocampus is critical for consolidating some forms of memory but not all. It is especially important for declarative memory and spatial memory. ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
... – Thalamus- relay info to cerebral cortex • Sorts data as to what goes to cerebrum and what comes out – Hypothalamus- regulates basics (body temp, BP, thirst, hunger) and biological clock- maintains daily biorhythms – Cerebrum- consists of hemispheres- site of memory, learning, emotion, speech, form ...
... – Thalamus- relay info to cerebral cortex • Sorts data as to what goes to cerebrum and what comes out – Hypothalamus- regulates basics (body temp, BP, thirst, hunger) and biological clock- maintains daily biorhythms – Cerebrum- consists of hemispheres- site of memory, learning, emotion, speech, form ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... topmost portion of the diencephalon. The structure has sensory and motor functions. Almost all sensory information enters this structure where neurons send that information to the overlying cortex. ...
... topmost portion of the diencephalon. The structure has sensory and motor functions. Almost all sensory information enters this structure where neurons send that information to the overlying cortex. ...
Slide 1
... proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory information before sending it to its proper area. Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. ...
... proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory information before sending it to its proper area. Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. ...
Emotions and Memory - Stanford Law School
... the nature of an attitude. The recall is then a construction, made largely on the basis of this attitude, and its general effect is that of a justification of the attitude,” where for Bartlett attitude is “very largely a matter of feeling, or affect.” Bartlett (1932/1995) ...
... the nature of an attitude. The recall is then a construction, made largely on the basis of this attitude, and its general effect is that of a justification of the attitude,” where for Bartlett attitude is “very largely a matter of feeling, or affect.” Bartlett (1932/1995) ...
heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... activates neurons, which then can turn on genes that enable structural changes to be made that strengthen the connections among activated neurons. Even the focus of attention is a form of experience that activates neurons, turns on genes, and makes structural changes to the connections among neurons ...
... activates neurons, which then can turn on genes that enable structural changes to be made that strengthen the connections among activated neurons. Even the focus of attention is a form of experience that activates neurons, turns on genes, and makes structural changes to the connections among neurons ...
The Biology of Trauma - BC Association of Social Workers
... HPA – Axis: Pituitary Secretes hormones to regulate homeostasis and stimulate additional endocrine glands. Under control of the hypothalamus ...
... HPA – Axis: Pituitary Secretes hormones to regulate homeostasis and stimulate additional endocrine glands. Under control of the hypothalamus ...
Learning and Memory, Part I: Brain Regions Involved in Two Types
... cortex, and tastes are consolidated in the insular cortex. Although the hippocampus is required for the consolidation of these declarative memories, it is thought that they are broken down into separate sensory components before their long-term storage in relevant cortical areas. Second, why were on ...
... cortex, and tastes are consolidated in the insular cortex. Although the hippocampus is required for the consolidation of these declarative memories, it is thought that they are broken down into separate sensory components before their long-term storage in relevant cortical areas. Second, why were on ...
The Brain
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
emotion_08
... because we strike, afraid because we tremble ... Without the bodily states following on the perception, the latter would be purely cognitive in form, pale, colorless, destitute of emotional warmth. We might then see the bear, and judge it best to run, receive the insult and deem it right to strike, ...
... because we strike, afraid because we tremble ... Without the bodily states following on the perception, the latter would be purely cognitive in form, pale, colorless, destitute of emotional warmth. We might then see the bear, and judge it best to run, receive the insult and deem it right to strike, ...
Brain Structures and their Functions
... higher frontal lobe centers to generally fit socially acceptable norms (see executive functions above). The frontal lobes have rich neuronal input from both the alert centers in the brain-stem, and from the limbic regions. Psychological tests that measure frontal lobe function include Finger tapping ...
... higher frontal lobe centers to generally fit socially acceptable norms (see executive functions above). The frontal lobes have rich neuronal input from both the alert centers in the brain-stem, and from the limbic regions. Psychological tests that measure frontal lobe function include Finger tapping ...
Wilson Language Training 10th Annual Conference Providence
... • No executive center or grandmother cell (BC) ...
... • No executive center or grandmother cell (BC) ...
SKZ Hx Ebefrenia Catatonia Demenza paranoide Demenza precox
... disorder (last 20 years) Not to dismiss environmental stressors, but rather to put these in the perspective of a brain disorder in evolution ...
... disorder (last 20 years) Not to dismiss environmental stressors, but rather to put these in the perspective of a brain disorder in evolution ...
Brain Plasticity
... musicians, and lowest in non-musicians in several brain areas involved in playing music: motor regions, anterior superior parietal areas and inferior temporal areas. Finally, Draganski and colleagues (2006) recently showed that extensive learning of abstract information can also trigger some plastic ...
... musicians, and lowest in non-musicians in several brain areas involved in playing music: motor regions, anterior superior parietal areas and inferior temporal areas. Finally, Draganski and colleagues (2006) recently showed that extensive learning of abstract information can also trigger some plastic ...
Declarative Memory
... example, when birds or squirrels store seeds for the winter they must remember the arbitrary locations and their contents (episode) even if they have just been to the particular places just once and several months earlier. In humans it would mean remembering a particular person and what they said (a ...
... example, when birds or squirrels store seeds for the winter they must remember the arbitrary locations and their contents (episode) even if they have just been to the particular places just once and several months earlier. In humans it would mean remembering a particular person and what they said (a ...
Brain Functional Organization
... In the ventricular walls neural stem cells are developed to produce new neurons. ...
... In the ventricular walls neural stem cells are developed to produce new neurons. ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
... the limbic system? 1. Establishing emotional states 2. Linking the conscious, intellectual function of the cerebral cortex with unconscious, autonomic functions of the brain stem 3. Facilitating memory storage and retrieval 4. Directing somatic motor patterns associated with rage, pleasure, and pain ...
... the limbic system? 1. Establishing emotional states 2. Linking the conscious, intellectual function of the cerebral cortex with unconscious, autonomic functions of the brain stem 3. Facilitating memory storage and retrieval 4. Directing somatic motor patterns associated with rage, pleasure, and pain ...
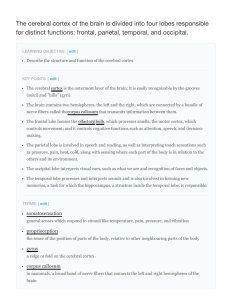
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain. It is primarily involved in vision: seeing, recognizing, and identifying the visual world. The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by the ears. It is primarily involved in processing and interpreting sounds. It also contains the h ...
... The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain. It is primarily involved in vision: seeing, recognizing, and identifying the visual world. The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by the ears. It is primarily involved in processing and interpreting sounds. It also contains the h ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.