DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
nervous system B
... • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influence “brain”; as cognitive therapy for depression can physically change the brain. • Neur ...
... • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influence “brain”; as cognitive therapy for depression can physically change the brain. • Neur ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... LIMBIC SYSTEM - A group of brain structures — including the amygdala, hippocampus, septum, basal ganglia, and others — that help regulate the expression of emotion and emotional memory. MIDBRAIN - The most anterior segment of the brainstem. With the pons and medulla, the midbrain is involved in man ...
... LIMBIC SYSTEM - A group of brain structures — including the amygdala, hippocampus, septum, basal ganglia, and others — that help regulate the expression of emotion and emotional memory. MIDBRAIN - The most anterior segment of the brainstem. With the pons and medulla, the midbrain is involved in man ...
CHAPTER 12 Learning and Memory Basic Outline with notes I. The
... behavior. We refer to these changes as memory. Experiences change the way we perceive, perform, think and plan. A. Learning can take 4 basic forms: 1. Perceptual Learning – The identification of objects and things. Changes in the perceptual systems that make it possible for us to recognize stimuli s ...
... behavior. We refer to these changes as memory. Experiences change the way we perceive, perform, think and plan. A. Learning can take 4 basic forms: 1. Perceptual Learning – The identification of objects and things. Changes in the perceptual systems that make it possible for us to recognize stimuli s ...
Unit 03B
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Outline
... Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with schizophrenia o Schizophrenia Symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought proc ...
... Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with schizophrenia o Schizophrenia Symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought proc ...
Grant Clay
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
Psych 2 Practice Test - b
... 32.Between the oldest and newest brain areas lies the limbic system. This system includes all of the following except: a. hippocampus b. hypothalamus c. cerebellum d. amygdala 33.Which structure is known for processing memory? a. hippocampus b. hypothalamus c. amygdala d. none of the above 33.Which ...
... 32.Between the oldest and newest brain areas lies the limbic system. This system includes all of the following except: a. hippocampus b. hypothalamus c. cerebellum d. amygdala 33.Which structure is known for processing memory? a. hippocampus b. hypothalamus c. amygdala d. none of the above 33.Which ...
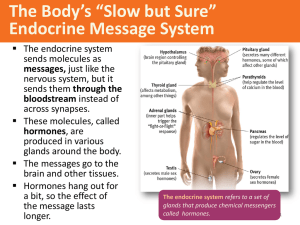
Endocrine System
... – Various structures in the brain that regulate our emotions and motivations (includes: amygdala, hippocampus) ...
... – Various structures in the brain that regulate our emotions and motivations (includes: amygdala, hippocampus) ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... = areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... = areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
Learning & Memory
... and Long-term Memory Machinery Patient E.E. has damage to the left angular gyrus causing a deficit in shortterm, but not long term memory Patient H.M. had damage to the medial temporal lobe causing a deficit in longterm, but not short-term memory ...
... and Long-term Memory Machinery Patient E.E. has damage to the left angular gyrus causing a deficit in shortterm, but not long term memory Patient H.M. had damage to the medial temporal lobe causing a deficit in longterm, but not short-term memory ...
HP Authorized Customer
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
LeDoux outlines his theory of emotions and memory
... oncoming car and the impact of the crash, but he also “feels” the memory—his heart starts to race, he begins to sweat and his muscles tense. The factual and “feeling” components of this memory may seem inseparable, but in reality, they come from two distinct areas of the brain, said Joseph LeDoux, P ...
... oncoming car and the impact of the crash, but he also “feels” the memory—his heart starts to race, he begins to sweat and his muscles tense. The factual and “feeling” components of this memory may seem inseparable, but in reality, they come from two distinct areas of the brain, said Joseph LeDoux, P ...
unit 3b brain
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
... that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal de ...
General PLTW Document - Buncombe County Schools
... Long-term memory hippocampus, frontal lobes, thalamus, and hypothalamus Movement ...
... Long-term memory hippocampus, frontal lobes, thalamus, and hypothalamus Movement ...
Functional neuroanatomy of pain
... levels of the neuraxis: the medullary dorsal horn, thalamus, and primary somatosensory cortex. In nine subjects, noxious thermal stimuli (46°C) were applied to the facial skin at sites within the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2, and V3) and also to the ipsilateral thumb. Anatomical a ...
... levels of the neuraxis: the medullary dorsal horn, thalamus, and primary somatosensory cortex. In nine subjects, noxious thermal stimuli (46°C) were applied to the facial skin at sites within the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2, and V3) and also to the ipsilateral thumb. Anatomical a ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The limbic system is a complex network of tracts and nuclei that incorporates portions of the cerebral lobes, the basal nuclei, and the diencephalon. The hippocampus communicates with the prefrontal area of the brain, which is involved in learning and memory. The amygdala allows us to respond to and ...
... The limbic system is a complex network of tracts and nuclei that incorporates portions of the cerebral lobes, the basal nuclei, and the diencephalon. The hippocampus communicates with the prefrontal area of the brain, which is involved in learning and memory. The amygdala allows us to respond to and ...
General PLTW Document
... The brain is a complex organ composed of lobes, ventricles, and systems that are organized into specialized regions. These regions are responsible for functions such as speech, emotion, and memory as well as vision, hearing, and taste. Other regions of the brain control involuntary functions such as ...
... The brain is a complex organ composed of lobes, ventricles, and systems that are organized into specialized regions. These regions are responsible for functions such as speech, emotion, and memory as well as vision, hearing, and taste. Other regions of the brain control involuntary functions such as ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
CNS - Misericordia University
... • Coma is a severe loss in mental function due to brain damage; sustained loss of arousal (even with heavy stimuli), behavior response is lost, no sleep/wake cycles • Persistent Vegetative State –sleep/wake cycles are present; no sign of external awareness ...
... • Coma is a severe loss in mental function due to brain damage; sustained loss of arousal (even with heavy stimuli), behavior response is lost, no sleep/wake cycles • Persistent Vegetative State –sleep/wake cycles are present; no sign of external awareness ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... The limbic system coordinates: emotions such as fear and aggression. basic drives such as hunger and sex. the formation of episodic memories. The hippocampus (“seahorse”) processes conscious, episodic memories. works with the amygdala to form emotionally charged memories. one of the few ...
... The limbic system coordinates: emotions such as fear and aggression. basic drives such as hunger and sex. the formation of episodic memories. The hippocampus (“seahorse”) processes conscious, episodic memories. works with the amygdala to form emotionally charged memories. one of the few ...
Biopsychology and Perception
... • The cell body, which contains the nucleus, is called the soma--it is the living part of the neuron • The axon is the long fiber over which outgoing messages travel The axon terminal buttons are the transmitters, sending information on to the next neuron • The space between neurons is the synaptic ...
... • The cell body, which contains the nucleus, is called the soma--it is the living part of the neuron • The axon is the long fiber over which outgoing messages travel The axon terminal buttons are the transmitters, sending information on to the next neuron • The space between neurons is the synaptic ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.