Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... thalamus—relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness -switchboard that sends incoming info where it needs to go in the brain hypothalamus—links the nervous and endocrine systems via the pituitary ...
... thalamus—relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness -switchboard that sends incoming info where it needs to go in the brain hypothalamus—links the nervous and endocrine systems via the pituitary ...
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain
... • Serotonin – affects mood, sleep, sensory perception, and other functions, may play a role in psychological disorders like depression • Acetylcholine – involved in memory, muscle action, sleep, emotions, those w/ Alzheimer’s have lower levels • Dopamine – affects movement, attention, memory, learni ...
... • Serotonin – affects mood, sleep, sensory perception, and other functions, may play a role in psychological disorders like depression • Acetylcholine – involved in memory, muscle action, sleep, emotions, those w/ Alzheimer’s have lower levels • Dopamine – affects movement, attention, memory, learni ...
Resetting the Fear Switch in PTSD
... unique in my 44 years of clinical practice. As a neuropsychologist, I naturally had questions about the neural mechanism of action that could cause such profound changes so quickly. I contacted Richard Bruursema who has trained and supported BAUD therapists for the last 9 years, and whose research i ...
... unique in my 44 years of clinical practice. As a neuropsychologist, I naturally had questions about the neural mechanism of action that could cause such profound changes so quickly. I contacted Richard Bruursema who has trained and supported BAUD therapists for the last 9 years, and whose research i ...
Clinical Research Center for Brain Sciences, Herzog Hospital
... Natural age-related decay in prefrontal executive attention functioning: significant inverse association between WM accuracy scores and age throughout the entire adult-life span (r = -.693, p < .001) ...
... Natural age-related decay in prefrontal executive attention functioning: significant inverse association between WM accuracy scores and age throughout the entire adult-life span (r = -.693, p < .001) ...
Chapter Four
... visual cortex. Sensory association cortex – receives information from the primary sensory areas. Motor association cortex – those regions of the cerebral cortex that control the primary motor cortex; involved in planning and executing behaviors. Occipital ...
... visual cortex. Sensory association cortex – receives information from the primary sensory areas. Motor association cortex – those regions of the cerebral cortex that control the primary motor cortex; involved in planning and executing behaviors. Occipital ...
Central Nervous System Part 2
... • Parietal lobe: somatic sensory area : impulses from sensory receptors are localized and interpreted; path are X’d, able to interpret characteristics of objects feel with hand and to comprehend spoken and written language • Occipital lobe: visual cortex, receives visual info via thalamus (primary v ...
... • Parietal lobe: somatic sensory area : impulses from sensory receptors are localized and interpreted; path are X’d, able to interpret characteristics of objects feel with hand and to comprehend spoken and written language • Occipital lobe: visual cortex, receives visual info via thalamus (primary v ...
THE PREFRONTAL CORTEX Connections Dorsolateral
... are involved, in this way, past experience can be brought ‘on-line’ and may play a role in guiding complex behavioral processes. Second, the reciprocal relationships with the hypothalamic and autonomic systems would provide the OPFC with information about the bioregulatory responses that take place ...
... are involved, in this way, past experience can be brought ‘on-line’ and may play a role in guiding complex behavioral processes. Second, the reciprocal relationships with the hypothalamic and autonomic systems would provide the OPFC with information about the bioregulatory responses that take place ...
BRAIN REPAIR YOURSELF SUMMARY
... The birth of a new brain cell is a process, not an event. Multipotent neural stem cells divide periodically in the brain, in two main areas: the ventricles and the hippocampus. In order to develop, either into a neuron or a glia cell, a given stem cell migrates out from the area of influence of the ...
... The birth of a new brain cell is a process, not an event. Multipotent neural stem cells divide periodically in the brain, in two main areas: the ventricles and the hippocampus. In order to develop, either into a neuron or a glia cell, a given stem cell migrates out from the area of influence of the ...
Chapter 2 – Biology of the Mind
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) brainstem medulla reticular formation thalamus cerebellum limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) brainstem medulla reticular formation thalamus cerebellum limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association ...
Scientists study Pavlovian conditioning in neural
... March 22, also reveal that the neurons never returned to their original state, even after the training was undone. Although this was not the main focus of the study, this research could have wide-ranging implications for studying emotional Mouse brain image with neurons in the amygdala stained so th ...
... March 22, also reveal that the neurons never returned to their original state, even after the training was undone. Although this was not the main focus of the study, this research could have wide-ranging implications for studying emotional Mouse brain image with neurons in the amygdala stained so th ...
physiological psychology
... 67. An area in the left temporal lobe, known to play an important role in language comprehension is called ___________________ area. a. Wernicke's ...
... 67. An area in the left temporal lobe, known to play an important role in language comprehension is called ___________________ area. a. Wernicke's ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... the left side of the brain will show bodily symptoms on the right side. We also must keep in mind that while each side of the brain may be responsible for certain actions and abilities, the two areas work cooperatively on most tasks. ...
... the left side of the brain will show bodily symptoms on the right side. We also must keep in mind that while each side of the brain may be responsible for certain actions and abilities, the two areas work cooperatively on most tasks. ...
Understanding Trauma, Its Impact on brain and body and its Treatment
... access and process bodily memories and help the brain to return to the same state of consciousness as when the memory was initiated. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), is currently one of the most popular and well-researched methods of trauma treatment developed in the 1980s. EMDR ...
... access and process bodily memories and help the brain to return to the same state of consciousness as when the memory was initiated. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), is currently one of the most popular and well-researched methods of trauma treatment developed in the 1980s. EMDR ...
F - Journals
... Limbic circle: emotions Basal ganglia: motor control, movement initiation Cortex of large hemispheres: “higher” functions, motor ...
... Limbic circle: emotions Basal ganglia: motor control, movement initiation Cortex of large hemispheres: “higher” functions, motor ...
long-term memory
... Damage limited to the hippocampus, or to its major connections through the fornix, produces only a modest impairment. In contrast, damage that includes the ...
... Damage limited to the hippocampus, or to its major connections through the fornix, produces only a modest impairment. In contrast, damage that includes the ...
Slide 1
... • Signals from proprioceptors and visual and equilibrium pathways continuously “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s position and momentum • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to smoothly coordinate a muscle contraction • A “blueprint” of coordinated movement is sent to the cerebral motor cor ...
... • Signals from proprioceptors and visual and equilibrium pathways continuously “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s position and momentum • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to smoothly coordinate a muscle contraction • A “blueprint” of coordinated movement is sent to the cerebral motor cor ...
Serial model Amnesia Amnesia HM
... • reads newspapers repeatedly • doesn’t remember own physician • see on formal tests or everyday life • word lists • faces and objects • recall or recognition ...
... • reads newspapers repeatedly • doesn’t remember own physician • see on formal tests or everyday life • word lists • faces and objects • recall or recognition ...
The left hemisphere
... The limbic lobe: Also called the limbic system. This is the ancient cortex, sometimes called the paleocortex. The neocortex has taken over most of the limbic system's original functions. Now, the limbic system primarily controls emotional behaviors and memories. ...
... The limbic lobe: Also called the limbic system. This is the ancient cortex, sometimes called the paleocortex. The neocortex has taken over most of the limbic system's original functions. Now, the limbic system primarily controls emotional behaviors and memories. ...
music and the brain - College of Natural Sciences
... the brain when an individual listens, performs, composes, or reads music. This interest would include studies of cognitive neuroscience, along with neuroanatomy and psychology. Music’s role in human experience has been a widely studied topic dating back to Plato, Socrates, and Aristotle. These philo ...
... the brain when an individual listens, performs, composes, or reads music. This interest would include studies of cognitive neuroscience, along with neuroanatomy and psychology. Music’s role in human experience has been a widely studied topic dating back to Plato, Socrates, and Aristotle. These philo ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... that lie between the cortex and the rest of the brain Influences emotions, motivation, and memory Sometimes called the “emotional brain” Includes the hypothalamus and other parts • Amygdala – aggression and fear responses • Hippocampus – converts short-term memory to longterm memory • Olfactory bulb ...
... that lie between the cortex and the rest of the brain Influences emotions, motivation, and memory Sometimes called the “emotional brain” Includes the hypothalamus and other parts • Amygdala – aggression and fear responses • Hippocampus – converts short-term memory to longterm memory • Olfactory bulb ...
Chapter 1
... increased confusion and restlessness in patients Behavioral problems begin to occur in the evening or while the sun is setting. more frequent during the middle stages of Alzheimer's disease and mixed dementia. subsides with the progression of dementia. 20–45% of Alzheimer's patients will experience ...
... increased confusion and restlessness in patients Behavioral problems begin to occur in the evening or while the sun is setting. more frequent during the middle stages of Alzheimer's disease and mixed dementia. subsides with the progression of dementia. 20–45% of Alzheimer's patients will experience ...
Glutamate
... such as feeding, sex, drinking, aggression and play and so has been thought of as the rest and relaxation NHT. This is not wholly accurate as stimulation of ...
... such as feeding, sex, drinking, aggression and play and so has been thought of as the rest and relaxation NHT. This is not wholly accurate as stimulation of ...
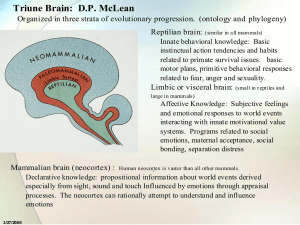
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.