Fourth Grade Science Vocabulary
... slowly=larger mineral grains-course texture Molten rock above ground=lava cools more quickly=small grains =fine texture or no grains = volcanic glass C10 Form from smaller bits of rock that become Some are made of substances that were once Sedimentary pressed or cemented together in layers. living; ...
... slowly=larger mineral grains-course texture Molten rock above ground=lava cools more quickly=small grains =fine texture or no grains = volcanic glass C10 Form from smaller bits of rock that become Some are made of substances that were once Sedimentary pressed or cemented together in layers. living; ...
Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Formation and Characteristics
... The _____________forces the sediment grains to get closer and closer together causing physical changes to ...
... The _____________forces the sediment grains to get closer and closer together causing physical changes to ...
Rock cycle, snap! - Teachit Geography
... the process of changing from a solid rock to a liquid rock ...
... the process of changing from a solid rock to a liquid rock ...
28 - KaterinaCLHSportfolio
... layer of igneous or metamorphic rock, i.e. granite or marble, the eroded surface is easier to identify. o Pg603: Radiometric dating is not useful for sedimentary rocks because the minerals in most sedimentary rocks were formed from pre-existing rocks. o Pg604: Tree Rings can show the past environmen ...
... layer of igneous or metamorphic rock, i.e. granite or marble, the eroded surface is easier to identify. o Pg603: Radiometric dating is not useful for sedimentary rocks because the minerals in most sedimentary rocks were formed from pre-existing rocks. o Pg604: Tree Rings can show the past environmen ...
Biochemical Sedimentary Rock
... To understand Earth history, a geologist seeks to interpret the “Environment of Deposition” of a sedimentary rock…this reveals something about changes occurring on Earth’s surface ...
... To understand Earth history, a geologist seeks to interpret the “Environment of Deposition” of a sedimentary rock…this reveals something about changes occurring on Earth’s surface ...
Sedimentary Rock
... Sedimentary rock contains sediment grains, cement holding them together, and empty space called “pores” ...
... Sedimentary rock contains sediment grains, cement holding them together, and empty space called “pores” ...
Science 8—Chapter 13 Vocab PP Less 2 Quiz
... • rock that forms when sediments become pressed or cemented together or when sediments fall out of solution ...
... • rock that forms when sediments become pressed or cemented together or when sediments fall out of solution ...
Examining Minerals and Rocks
... pre-existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat (greater than 150 degrees Celsius) and/or extreme pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change. The protolith may be sedimentary rock, igneous rock o ...
... pre-existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat (greater than 150 degrees Celsius) and/or extreme pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change. The protolith may be sedimentary rock, igneous rock o ...
pressure calcite fluorite geologists gypsum
... any of various minerals that contain silicon and can be separated easily into thin, often transparent, sheets ...
... any of various minerals that contain silicon and can be separated easily into thin, often transparent, sheets ...
types of rocks powerpoint
... Clastic – made of fragments of rock cemented together with calcite or quartz Breccia is a term most often used for clastic sedimentary rocks that are composed of large angular fragments (over two millimeters in diameter). ...
... Clastic – made of fragments of rock cemented together with calcite or quartz Breccia is a term most often used for clastic sedimentary rocks that are composed of large angular fragments (over two millimeters in diameter). ...
Geology 208 History of Earth System Midterm Topics 1 Topics
... Compostition of Earth: Four major cations and prominence of silicate minerals Mineralogy: Three ways to make minerals and corresponding rock types Polymorphs: diamond graphite, olivine to spinel in transition zone Diagnostic features from structure and composition Igneous Rocks questions can ...
... Compostition of Earth: Four major cations and prominence of silicate minerals Mineralogy: Three ways to make minerals and corresponding rock types Polymorphs: diamond graphite, olivine to spinel in transition zone Diagnostic features from structure and composition Igneous Rocks questions can ...
Unit 17 STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
... chemical means) are pressed and cemented together by dissolved minerals • may contain fossils • ex. – sandstone, limestone, shale, conglomerate, breccias ...
... chemical means) are pressed and cemented together by dissolved minerals • may contain fossils • ex. – sandstone, limestone, shale, conglomerate, breccias ...
KEY How Earth`s Rocks Were Formed Three Families of Rocks A
... Types of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks ...
... Types of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks ...
Name: Date: Class: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date
... 1. Metamorphic rocks are different from igneous and sedimentary rocks in that metamorphic rocks form ...
... 1. Metamorphic rocks are different from igneous and sedimentary rocks in that metamorphic rocks form ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... • Earth movements can push all types of rock deeper into the Earth. • These rocks are then subjected to massive temperatures and pressures, causing the crystalline structure and texture to change. • They do not become liquid, but become ...
... • Earth movements can push all types of rock deeper into the Earth. • These rocks are then subjected to massive temperatures and pressures, causing the crystalline structure and texture to change. • They do not become liquid, but become ...
Rocks Notes
... -Parent Rock – original rock before metamorphism -Types of Metamorphism 1) Regional metamorphism – when high temperature and pressure affect large regions of Earth’s crust. 2) Contact metamorphism – when molten rocks come into contact with a solid rock 3) Hydrothermal metamorphism – when very hot wa ...
... -Parent Rock – original rock before metamorphism -Types of Metamorphism 1) Regional metamorphism – when high temperature and pressure affect large regions of Earth’s crust. 2) Contact metamorphism – when molten rocks come into contact with a solid rock 3) Hydrothermal metamorphism – when very hot wa ...
8H - UCC Revision
... forced closer together (compacted) and the water is squeezed out from between the grains. Minerals from water that flows through the sediment ‘glue’ the grains of rock together (cementation). Eventually, sedimentary rock is formed. The composition and texture of sedimentary rocks vary and depend on ...
... forced closer together (compacted) and the water is squeezed out from between the grains. Minerals from water that flows through the sediment ‘glue’ the grains of rock together (cementation). Eventually, sedimentary rock is formed. The composition and texture of sedimentary rocks vary and depend on ...
Chapter 2 - Minerals and Rocks Extra Credit
... 13. A mixture containing a solvent and at least one solute that has the same properties throughout a mixture in which one substance is dissolved in another. 15. The chemical and physical processes that break down rock and other substances. 17. Small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or ...
... 13. A mixture containing a solvent and at least one solute that has the same properties throughout a mixture in which one substance is dissolved in another. 15. The chemical and physical processes that break down rock and other substances. 17. Small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or ...
Notes: Rocks
... forms on the earths surface (lava). It usually has small crystals - cools quickly creating a finegrained texture ex. basalt ...
... forms on the earths surface (lava). It usually has small crystals - cools quickly creating a finegrained texture ex. basalt ...
GEOL 333 - Lab 8 (Clastic Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and
... Introduction Sedimentary rock, which forms by the accumulation and lithification of sediment (loose grains), is by far the most abundant rock type at Earth's surface and it is important as an economic resource and for geologic research. Sandstone and limestone are used as building stone, which is ro ...
... Introduction Sedimentary rock, which forms by the accumulation and lithification of sediment (loose grains), is by far the most abundant rock type at Earth's surface and it is important as an economic resource and for geologic research. Sandstone and limestone are used as building stone, which is ro ...
Earth Science: Unit 1
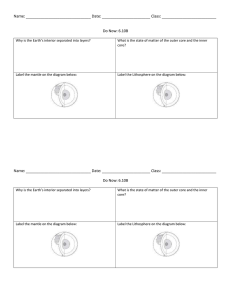
... The Earth’s Surface (C-38 to C-43) • Vocabulary: landforms, plateau, plains, volcano, lava, magma, crust, mantle, core, deposition, Pangea, tectonic plates, geologist • Highlight sheets: “Landforms”, “The Earth’s Interior” ...
... The Earth’s Surface (C-38 to C-43) • Vocabulary: landforms, plateau, plains, volcano, lava, magma, crust, mantle, core, deposition, Pangea, tectonic plates, geologist • Highlight sheets: “Landforms”, “The Earth’s Interior” ...
Vocabulary
... Rocks formed as sediments are pushed together or cemented by the weight of the water and layers of sediment above it. ...
... Rocks formed as sediments are pushed together or cemented by the weight of the water and layers of sediment above it. ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.