See Q. “Sampler” on packet, pages 12
... *Their strength and other properties may be different from one another and may affect further weathering, infiltration, water storage, etc. Two Sedimentary Rock Types: 1) Detrital (aka Clastic): with rock fragments/grains and cement 2) Chemical: with soluble materials - These may be precipitated by ...
... *Their strength and other properties may be different from one another and may affect further weathering, infiltration, water storage, etc. Two Sedimentary Rock Types: 1) Detrital (aka Clastic): with rock fragments/grains and cement 2) Chemical: with soluble materials - These may be precipitated by ...
ACROSS 3 ______ is the way a mineral reflects light off it`s surface 6
... 2 ______ rock forms from cooling magma below the surface or cooling lava on the surface 4 Igneous rocks found under the surface of the Earth are known as ______ rocks 5 When a mineral does not split apart evenly it is known as ______ 10 ______ and pressure can create metamorphic rock 12 ______ is wh ...
... 2 ______ rock forms from cooling magma below the surface or cooling lava on the surface 4 Igneous rocks found under the surface of the Earth are known as ______ rocks 5 When a mineral does not split apart evenly it is known as ______ 10 ______ and pressure can create metamorphic rock 12 ______ is wh ...
WEATHERING AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
... Conglomerate - Detrital rock made up of more or less rounded fragments, an appreciable percentage of which are pebble size or larger Sandstone - Consists primarily of grains in the sand size range. Dominant mineral in sandstones is always quartz. Further subdivide sandstones based on other minerals ...
... Conglomerate - Detrital rock made up of more or less rounded fragments, an appreciable percentage of which are pebble size or larger Sandstone - Consists primarily of grains in the sand size range. Dominant mineral in sandstones is always quartz. Further subdivide sandstones based on other minerals ...
Sedimentary Rock Notes
... section (under the slide). You will have to scroll in the notes section for most of the slides to get the answers/notes. ...
... section (under the slide). You will have to scroll in the notes section for most of the slides to get the answers/notes. ...
Rocks and Minerals
... As sediment is buried several kilometers beneath the surface, heated from below, pressure from overlying layers and chemically-active water converts the loose sediment into solid sedimentary rock ...
... As sediment is buried several kilometers beneath the surface, heated from below, pressure from overlying layers and chemically-active water converts the loose sediment into solid sedimentary rock ...
Study Guide for 3rd nine week assessment 2017
... Study Guide for 3rd nine week assessment 1. Slate is a metamorphic rock that is created from Shale during regional metamorphism 2. Igneous rocks can be created from any other rocks as long as it becomes magma or lava and then crystallize(become solid) 3. An independent variable is the only variable ...
... Study Guide for 3rd nine week assessment 1. Slate is a metamorphic rock that is created from Shale during regional metamorphism 2. Igneous rocks can be created from any other rocks as long as it becomes magma or lava and then crystallize(become solid) 3. An independent variable is the only variable ...
Science Chapter 4 Study Guide Vocabulary
... Vocabulary pollution—harmful materials in the air, water, or land and burning fossil fuels causes pollution nonrenewable resource—resources that can not be replace (example-fuel, coal, natural gas) ...
... Vocabulary pollution—harmful materials in the air, water, or land and burning fossil fuels causes pollution nonrenewable resource—resources that can not be replace (example-fuel, coal, natural gas) ...
Metamorphic Rock by Leila, John*S, and Samantha
... in the earth or on the earth. Metamorphic rock usually appear in big clusters of rock. They can also be different in size shape and color. ...
... in the earth or on the earth. Metamorphic rock usually appear in big clusters of rock. They can also be different in size shape and color. ...
3 Principal Types of Rocks
... 3 Principal Types of Rocks Igneous – Rocks formed from molten, liquid magma or lava. Sedimentary – Rocks formed after being deposited by running water. These sediments often occur in horizontal beds and are cemented together as other sediments pile on top. Metamorphic – Either Igneous or sediment ...
... 3 Principal Types of Rocks Igneous – Rocks formed from molten, liquid magma or lava. Sedimentary – Rocks formed after being deposited by running water. These sediments often occur in horizontal beds and are cemented together as other sediments pile on top. Metamorphic – Either Igneous or sediment ...
Bedrock in Ohio
... transport because of wind and water, sediments become rock when they get compacted. Common sedimentary rocks are: Limestone Sandstone Conglomerate ...
... transport because of wind and water, sediments become rock when they get compacted. Common sedimentary rocks are: Limestone Sandstone Conglomerate ...
Pre-lithification tectonic foliation development in a clastic
... The current orthodoxy regarding the development of regionally developed penetrative tectonic cleavage fabrics in sedimentary rocks is that it postdates lithification of those rocks. It is well established that fabric development under these circumstances is achieved by a combination of grain rigid b ...
... The current orthodoxy regarding the development of regionally developed penetrative tectonic cleavage fabrics in sedimentary rocks is that it postdates lithification of those rocks. It is well established that fabric development under these circumstances is achieved by a combination of grain rigid b ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 1. What is a vent? 2. What happens to magma after it forms in the earth’s mantle? 3. What is a hot spot? Give an example. 4. What type of lava is rich in silica? 5. What type of volcano is formed from alternating layers of lava flow & ash? 6. How does a caldera form? 7. What happens to temperature a ...
... 1. What is a vent? 2. What happens to magma after it forms in the earth’s mantle? 3. What is a hot spot? Give an example. 4. What type of lava is rich in silica? 5. What type of volcano is formed from alternating layers of lava flow & ash? 6. How does a caldera form? 7. What happens to temperature a ...
UNIT TITLE: Readers Theater
... of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of mountain ranges. 9. The continents formed one large supercontinent called Pangaea that ...
... of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of mountain ranges. 9. The continents formed one large supercontinent called Pangaea that ...
Teacher Pre-assessment
... d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which of these is most easily oxidized when exposed to air? a. quartz b. iron c. nitrogen d. carbon 26. Which of t ...
... d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which of these is most easily oxidized when exposed to air? a. quartz b. iron c. nitrogen d. carbon 26. Which of t ...
103-04-RocksIntrod-2006(Lesson08)
... – Abundant on the seafloor (veneer the basalt layer of crust below) – Mostly loose grains (eroded from previously existing rocks) – May be skeletal debris (shells, etc.), plant materials (coal) – May be chemical precipitates from seawater (salts) ...
... – Abundant on the seafloor (veneer the basalt layer of crust below) – Mostly loose grains (eroded from previously existing rocks) – May be skeletal debris (shells, etc.), plant materials (coal) – May be chemical precipitates from seawater (salts) ...
Bedrock geology map of North Clare
... The geological map shows the distribution of these three rock types. ...
... The geological map shows the distribution of these three rock types. ...
Igneous Rocks
... Sedimentary Rocks • Sedimentary rocks are rocks formed by the deposition, compaction and cementing of small particles (such as silt, sand and pebbles). These particles are deposited in layers or strata. • The compaction of these sediments is caused by the weight of more sediments laid down on top o ...
... Sedimentary Rocks • Sedimentary rocks are rocks formed by the deposition, compaction and cementing of small particles (such as silt, sand and pebbles). These particles are deposited in layers or strata. • The compaction of these sediments is caused by the weight of more sediments laid down on top o ...
Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi
... past each other or towards each other. ...
... past each other or towards each other. ...
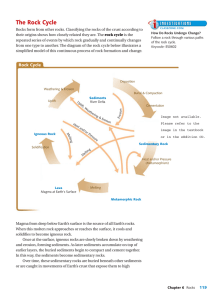
Rock Cycle - Prairie Spirit Blogs
... Sediments: loose materials such as rock fragments and mineral grains that have been transported by wind, water, or glacier Weathering: the breaking of rocks into smaller pieces, either mechanically or chemically Erosion: the process that moves weathered rocks from one location to another Deposition: ...
... Sediments: loose materials such as rock fragments and mineral grains that have been transported by wind, water, or glacier Weathering: the breaking of rocks into smaller pieces, either mechanically or chemically Erosion: the process that moves weathered rocks from one location to another Deposition: ...
Molten rock that comes to the surface of the earth is called:
... d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which of these is most easily oxidized when exposed to air? a. quartz b. iron c. nitrogen d. carbon 26. Which of t ...
... d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which of these is most easily oxidized when exposed to air? a. quartz b. iron c. nitrogen d. carbon 26. Which of t ...
SES4U ~5. Sedimentary Rocks_2010
... the extraction of building stone or slate from an open surface quarry.Quarrying plays a very important role in the use of dimension stone. Dimension stone is stored in a ‘quarry’ until it is needed by it’s manufacturer. Dimension stone may be used for many purposes. It can be, and often times is use ...
... the extraction of building stone or slate from an open surface quarry.Quarrying plays a very important role in the use of dimension stone. Dimension stone is stored in a ‘quarry’ until it is needed by it’s manufacturer. Dimension stone may be used for many purposes. It can be, and often times is use ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.