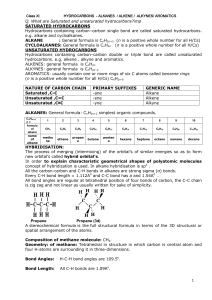
CHEMISTRY 263
... 1. Stereochemistry – Walden Inversion (inversion of configuration) 2. Substitution of primary and secondary alkyl halides D. SN1 Reactions 1. Stereochemical Aspects (loss of stereochemistry via carbocations) 2. Substitution of tertiary alkyl halides and other tertiary carbons 3. Synthesis of alcohol ...
... 1. Stereochemistry – Walden Inversion (inversion of configuration) 2. Substitution of primary and secondary alkyl halides D. SN1 Reactions 1. Stereochemical Aspects (loss of stereochemistry via carbocations) 2. Substitution of tertiary alkyl halides and other tertiary carbons 3. Synthesis of alcohol ...
Organic Chemistry Naming Branched Hydrocarbons
... Organic Chemistry Naming Branched Hydrocarbons 2nd Add the ending –yl to every group branching off the longest chain (if more than one of the same group add the prefixes) (di=2, tri=3, tetra=4) alphabetically according to –yl group CH3CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH-CH2 –CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 Alkyl groups: 3 met ...
... Organic Chemistry Naming Branched Hydrocarbons 2nd Add the ending –yl to every group branching off the longest chain (if more than one of the same group add the prefixes) (di=2, tri=3, tetra=4) alphabetically according to –yl group CH3CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH-CH2 –CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 Alkyl groups: 3 met ...
Synthesis of Four Diastereomeric 3,5-Dialkoxy-2,4
... to 9 and 11, derived from the epoxy alcohols having the opposite stereochemistry about the epoxide (5 and 6), did not react under these conditions, giving back mostly starting materials. However, treatment of the mesylate alcohol 13 (prepared from 5 in four steps and 61% overall yield) with TESCl fo ...
... to 9 and 11, derived from the epoxy alcohols having the opposite stereochemistry about the epoxide (5 and 6), did not react under these conditions, giving back mostly starting materials. However, treatment of the mesylate alcohol 13 (prepared from 5 in four steps and 61% overall yield) with TESCl fo ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 1. Determine the longest continuous chain of carbon. (Parent chain) 2. Number carbons in parent chain. Do this by starting at the end that gives the attached groups the smallest number. 3. Add numbers to the names of the attached groups to identify their position. Numbers become prefixes to the name ...
... 1. Determine the longest continuous chain of carbon. (Parent chain) 2. Number carbons in parent chain. Do this by starting at the end that gives the attached groups the smallest number. 3. Add numbers to the names of the attached groups to identify their position. Numbers become prefixes to the name ...
ALKANE ALKYL HALIDE Halogenation of Alkanes
... reagents: 1) CH2N2 (diazomethane), heat carbene mechanism (write on back of card) 2) CH2I2, Zn/Hg (Simmons-Smith reaction) gives fewer side products 3) CHCl3, (CH3)3COK carbene mechanism (write on back of card) two of the halogens remain attached not subject to rearrangements ...
... reagents: 1) CH2N2 (diazomethane), heat carbene mechanism (write on back of card) 2) CH2I2, Zn/Hg (Simmons-Smith reaction) gives fewer side products 3) CHCl3, (CH3)3COK carbene mechanism (write on back of card) two of the halogens remain attached not subject to rearrangements ...
Future perspectives in catalysis - NRSC
... A good catalyst is stable enough to survive many process cycles. That is why noble metals – that are intrinsically very stable – are so popular in catalyst design. However, the materials required are often costly. Platinum costs €40,000 per kilogram, and the price is increasing. Cheaper metals also ...
... A good catalyst is stable enough to survive many process cycles. That is why noble metals – that are intrinsically very stable – are so popular in catalyst design. However, the materials required are often costly. Platinum costs €40,000 per kilogram, and the price is increasing. Cheaper metals also ...
친환경 촉매 Iron (III) phosphate: 실온/무용매 반응조건에서 알코올과
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
Cracking (chemistry)

In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products are strongly dependent on the temperature and presence of catalysts. Cracking is the breakdown of a large alkane into smaller, more useful alkanes and alkenes. Simply put, hydrocarbon cracking is the process of breaking a long-chain of hydrocarbons into short ones. More loosely, outside the field of petroleum chemistry, the term ""cracking"" is used to describe any type of splitting of molecules under the influence of heat, catalysts and solvents, such as in processes of destructive distillation or pyrolysis. Fluid catalytic cracking produces a high yield of petrol and LPG, while hydrocracking is a major source of jet fuel, Diesel fuel, naphtha, and again yields LPG.