Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phosphonium salts can be used interchangeably with the phosphines t ...
... We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phosphonium salts can be used interchangeably with the phosphines t ...
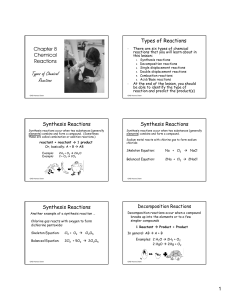
+ ∂ - CHEM171 – Lecture Series Seven : 2012/05
... Have a cation and an anion forming. If a carbon-carbon bond breaks in this fashion then we have a carbocation and a carbanion resulting CHEM171 – Lecture Series Seven : 2012/02 ...
... Have a cation and an anion forming. If a carbon-carbon bond breaks in this fashion then we have a carbocation and a carbanion resulting CHEM171 – Lecture Series Seven : 2012/02 ...
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... The reactions of Ni- and Pd-catalyzed diamination are believed to proceed as outlined in Fig. 2. Details on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involve ...
... The reactions of Ni- and Pd-catalyzed diamination are believed to proceed as outlined in Fig. 2. Details on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involve ...
esterification of palmitic acid with methanol in the
... The esterification of palmitic acid with methanol was carried out in a batch reactor system. The data were obtained to study the kinetics of the reaction and to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the esterification process. A pre-mixed method was opted in order to study the behavior of the heterogen ...
... The esterification of palmitic acid with methanol was carried out in a batch reactor system. The data were obtained to study the kinetics of the reaction and to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the esterification process. A pre-mixed method was opted in order to study the behavior of the heterogen ...
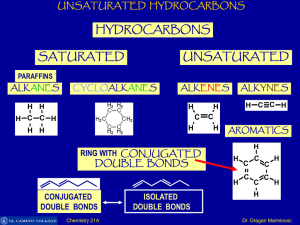
Cracking (chemistry)

In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products are strongly dependent on the temperature and presence of catalysts. Cracking is the breakdown of a large alkane into smaller, more useful alkanes and alkenes. Simply put, hydrocarbon cracking is the process of breaking a long-chain of hydrocarbons into short ones. More loosely, outside the field of petroleum chemistry, the term ""cracking"" is used to describe any type of splitting of molecules under the influence of heat, catalysts and solvents, such as in processes of destructive distillation or pyrolysis. Fluid catalytic cracking produces a high yield of petrol and LPG, while hydrocracking is a major source of jet fuel, Diesel fuel, naphtha, and again yields LPG.