1133693644_460433
... • Conjunctivitis (young children and adults) • Coinfection with chlamydia is common • Treatment: ceftriaxone, cefixime, azithromycin ...
... • Conjunctivitis (young children and adults) • Coinfection with chlamydia is common • Treatment: ceftriaxone, cefixime, azithromycin ...
noninfectious vaccines - Extension Veterinary Medicine
... establishes a desired infection in the vaccinated animal. Immunity prevents the desired infection of a modified live vaccine from being established; therefore an infectious vaccine generally is not effective when administered after a noninfectious vaccine. The infectious vaccine may give properly va ...
... establishes a desired infection in the vaccinated animal. Immunity prevents the desired infection of a modified live vaccine from being established; therefore an infectious vaccine generally is not effective when administered after a noninfectious vaccine. The infectious vaccine may give properly va ...
Infectious Bronchitis
... • Many serotypes and strains with great antigenic variation have been identified. • Mass 41 & Conn 46 are used as vaccine and protect against closely related serotypes. • Different strains affect different organ systems: respiratory, renal, reproductive. • Some important field strains are JMK, Ark. ...
... • Many serotypes and strains with great antigenic variation have been identified. • Mass 41 & Conn 46 are used as vaccine and protect against closely related serotypes. • Different strains affect different organ systems: respiratory, renal, reproductive. • Some important field strains are JMK, Ark. ...
Intern Case Report - Emergency Medicine
... There is a metallic fixation rod in the midportion of the right scapula. Cardiomediastinal contours are normal. Lungs and pleural ...
... There is a metallic fixation rod in the midportion of the right scapula. Cardiomediastinal contours are normal. Lungs and pleural ...
Antibiotics for Pediatric Diseases
... radiologic studies • Treat with antibiotics as per acute otitis media recommendations • BUT. . . . ...
... radiologic studies • Treat with antibiotics as per acute otitis media recommendations • BUT. . . . ...
Workshop Instructions
... Pre and post workshop surveys have indicated the workshop is considered useful. We believe the format of this workshop is easy to reproduce and can serve as a foundation for a curriculum in emerging infections and communicable disease management, and can easily be applied to other educational topi ...
... Pre and post workshop surveys have indicated the workshop is considered useful. We believe the format of this workshop is easy to reproduce and can serve as a foundation for a curriculum in emerging infections and communicable disease management, and can easily be applied to other educational topi ...
Fact Sheet for Menjugate (Meningococcal-C Vaccine)
... The bacteria that cause IMD can live in the body, in particular at the back of the nose and throat, without causing symptoms. Up to 10 per cent of the population carry the bacteria at any time, however, most people never develop active disease (IMD). The bacteria are spread through droplets in the a ...
... The bacteria that cause IMD can live in the body, in particular at the back of the nose and throat, without causing symptoms. Up to 10 per cent of the population carry the bacteria at any time, however, most people never develop active disease (IMD). The bacteria are spread through droplets in the a ...
Diphtheria, Tetanus and Acellular Pertussis
... Treatment for diphtheria includes an antitoxin, followed by antibiotics. However, it is becoming more difficult to treat the diphtheria bacteria due to antibiotic resistance. Diphtheria kills 1 out of every 10 people who get the disease. What is tetanus? Tetanus or lockjaw is a serious disease that ...
... Treatment for diphtheria includes an antitoxin, followed by antibiotics. However, it is becoming more difficult to treat the diphtheria bacteria due to antibiotic resistance. Diphtheria kills 1 out of every 10 people who get the disease. What is tetanus? Tetanus or lockjaw is a serious disease that ...
The Bubonic Plague - SFA ScholarWorks
... delays immune response. If the bacterium is not treated by an antibiotic, it will advance and become more and more deadly. The plague is fatal unless necessary actions are made. The bubonic plague has the ability to surpass the first stages of immune response, making the disease deadly because it is ...
... delays immune response. If the bacterium is not treated by an antibiotic, it will advance and become more and more deadly. The plague is fatal unless necessary actions are made. The bubonic plague has the ability to surpass the first stages of immune response, making the disease deadly because it is ...
Diphtheria, Tetanus and Acellular Pertussis (Tdap) Vaccine
... Diphtheria is a serious disease of the nose, throat and skin. It is passed to others through coughing and sneezing. It causes sore throat, fever and chills. It can lead to breathing problems, heart failure and nerve damage. Treatment for diphtheria includes an antitoxin, followed by antibiotics. How ...
... Diphtheria is a serious disease of the nose, throat and skin. It is passed to others through coughing and sneezing. It causes sore throat, fever and chills. It can lead to breathing problems, heart failure and nerve damage. Treatment for diphtheria includes an antitoxin, followed by antibiotics. How ...
OVERVIEW OF COMMUNICABLE DISEASES SITUATION
... 2006 compared with 241 cases in 2005. However, there was a 28.4% increase in the number of Salmonellosis cases, from 296 in 2005 to 380 in 2006. Although most cases were sporadic in nature, strict measures were implemented to ensure that a high standard of food and environmental hygiene was maintain ...
... 2006 compared with 241 cases in 2005. However, there was a 28.4% increase in the number of Salmonellosis cases, from 296 in 2005 to 380 in 2006. Although most cases were sporadic in nature, strict measures were implemented to ensure that a high standard of food and environmental hygiene was maintain ...
STREP THROAT / SCARLET FEVER - Dickinson
... can occur at any age, but is most common in school age children. It can occur year round, but peaks in late winter and early spring. Scarlet Fever is also caused by streptococcal bacteria and is characterized by a skin rash. A fine red rash appears most often on the neck, chest, under arms, elbows, ...
... can occur at any age, but is most common in school age children. It can occur year round, but peaks in late winter and early spring. Scarlet Fever is also caused by streptococcal bacteria and is characterized by a skin rash. A fine red rash appears most often on the neck, chest, under arms, elbows, ...
Equine Science & Technology
... ability of the horse to resist and/or overcome disease through either (1) natural immunity or (2) acquired immunity. Natural Immunity First line of defense. However, it is nonspecific. The immune cells attack any bacteria they are not programmed for a specific organism. ...
... ability of the horse to resist and/or overcome disease through either (1) natural immunity or (2) acquired immunity. Natural Immunity First line of defense. However, it is nonspecific. The immune cells attack any bacteria they are not programmed for a specific organism. ...
Disease - Health Science
... Notifiable Diseases in the United States Notifiable diseases are those of considerable public health importance because of their seriousness Such diseases Cause serious morbidity or death Have the potential to spread Can be controlled with appropriate intervention ...
... Notifiable Diseases in the United States Notifiable diseases are those of considerable public health importance because of their seriousness Such diseases Cause serious morbidity or death Have the potential to spread Can be controlled with appropriate intervention ...
Slide 1
... Index – the first case identified Primary – the case that brings the infection into a population Secondary – infected by a primary case Tertiary – infected by a secondary case ...
... Index – the first case identified Primary – the case that brings the infection into a population Secondary – infected by a primary case Tertiary – infected by a secondary case ...
Lecture 15-CNS Infections
... Rapidly Fatal Bacterial Meningitis with Local Progressive mental deterioration and death ...
... Rapidly Fatal Bacterial Meningitis with Local Progressive mental deterioration and death ...
Vaccine discovery and translation of new vaccine technology
... and Delivery While we have seen phenomenal advances in the identification of potential immunogens, the way vaccines are formulated and delivered remains an area which will define future increases in efficacy. Indeed, the majority of killed vaccines are injectable products which are formulated with A ...
... and Delivery While we have seen phenomenal advances in the identification of potential immunogens, the way vaccines are formulated and delivered remains an area which will define future increases in efficacy. Indeed, the majority of killed vaccines are injectable products which are formulated with A ...
Fever of Unknown Origin in an 11-Year-Old Girl
... and rifampin may be effective.16 Several authors recommend that the best outcome is achieved with regimens that include rifampin.10,16 A randomized, placebocontrolled study of 5-day treatment with azithromycin in patients with adenitis demonstrated a more rapid decrease in node volume (as measured b ...
... and rifampin may be effective.16 Several authors recommend that the best outcome is achieved with regimens that include rifampin.10,16 A randomized, placebocontrolled study of 5-day treatment with azithromycin in patients with adenitis demonstrated a more rapid decrease in node volume (as measured b ...
outbreak - World Health Organization
... costly to contain, and more dangerous for the international community. The dangers of delayed detection and international spread – vividly illustrated by SARS – are magnified by the tendency of new diseases, especially zoonoses, to emerge under conditions of crowding and poor hygiene. Apart from pro ...
... costly to contain, and more dangerous for the international community. The dangers of delayed detection and international spread – vividly illustrated by SARS – are magnified by the tendency of new diseases, especially zoonoses, to emerge under conditions of crowding and poor hygiene. Apart from pro ...
Tdap for Healthcare Workers
... 43% decrease in ILI 44% decrease in mortality Potter J, et. Al. J Infectious Disease 1997 ...
... 43% decrease in ILI 44% decrease in mortality Potter J, et. Al. J Infectious Disease 1997 ...
YELLOW FEVER SURVEILLANCE KLIA EXPERIENCE
... However, 15% of patients enter a second, more toxic phase within 24 hours of the initial remission1,5,6. High fever returns and several body systems are affected. The patient rapidly develops jaundice and complains of abdominal pain with vomiting. Bleeding can occur from the mouth, nose, eyes or sto ...
... However, 15% of patients enter a second, more toxic phase within 24 hours of the initial remission1,5,6. High fever returns and several body systems are affected. The patient rapidly develops jaundice and complains of abdominal pain with vomiting. Bleeding can occur from the mouth, nose, eyes or sto ...
Winter Illnesses - Leamington School
... Meningitis and septicaemia (blood poisoning) are not always easy to recognise, and symptoms can appear in any order. Some may not appear at all. In the early stages, the signs and symptoms can be similar to many other more common illnesses, for example flu. Trust your instincts. If you suspect menin ...
... Meningitis and septicaemia (blood poisoning) are not always easy to recognise, and symptoms can appear in any order. Some may not appear at all. In the early stages, the signs and symptoms can be similar to many other more common illnesses, for example flu. Trust your instincts. If you suspect menin ...
Fever and Rash: Infectious Diseases of Leisure
... of typically on the sixth Late signs and day or later after onset symptoms of symptoms, and this •abdominal pain type of rash occurs in •arthragias only 35% to 60% of • diarrhea patients with Rocky •3-5% mortality due to Mountain spotted fever myocarditis Initial symptoms : •fever •nausea •vomiting ...
... of typically on the sixth Late signs and day or later after onset symptoms of symptoms, and this •abdominal pain type of rash occurs in •arthragias only 35% to 60% of • diarrhea patients with Rocky •3-5% mortality due to Mountain spotted fever myocarditis Initial symptoms : •fever •nausea •vomiting ...
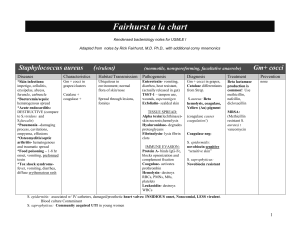
Rick Fairhurst Bacteria charts
... S.typhi –Typhoid fever, init by asymptomatic infection of gut phagocytes and dissemination to liver, Gall bladder (carrier state), Fever, RLQ abdominal pain, rose spots. Tx Cipro or ceftriaxone. S. cholerae-suis- Gm- sepsis. Esp patients with Sickle cell (risk for osteomyelitis b/c func. Asplenia) ...
... S.typhi –Typhoid fever, init by asymptomatic infection of gut phagocytes and dissemination to liver, Gall bladder (carrier state), Fever, RLQ abdominal pain, rose spots. Tx Cipro or ceftriaxone. S. cholerae-suis- Gm- sepsis. Esp patients with Sickle cell (risk for osteomyelitis b/c func. Asplenia) ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.