Septic arthritis due to Salmonella Typhi in children—A case series
... look for involvement of Salmonella Typhi is strongly warranted. ...
... look for involvement of Salmonella Typhi is strongly warranted. ...
Digestive System Pathology
... • Diverticulitis – inflammation of a diverticulum (pouch or sac occurring in the lining or wall of the intestines) • Inflammatory Bowel Diseases – chronic disorders – Colitis is inflammation of the colon – Crohn’s disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes scarring and thickening, most commonly i ...
... • Diverticulitis – inflammation of a diverticulum (pouch or sac occurring in the lining or wall of the intestines) • Inflammatory Bowel Diseases – chronic disorders – Colitis is inflammation of the colon – Crohn’s disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes scarring and thickening, most commonly i ...
幻灯片 1 - 上海交通大学医学院精品课程
... Antibiotics should not be used unless in those young, infant patients which are suspected to complicate bacterial infections. ...
... Antibiotics should not be used unless in those young, infant patients which are suspected to complicate bacterial infections. ...
History of U.S. Military Contributions to the Study of Vaccines against
... Smallpox and the Inoculation of the Continental Army Smallpox, caused by the brick-shaped virus variola, was endemic in Europe and elsewhere during the early modern period (1400–1700), periodically erupting in epidemics that ravaged whole cities, killing nearly 30% of the victims and leaving the res ...
... Smallpox and the Inoculation of the Continental Army Smallpox, caused by the brick-shaped virus variola, was endemic in Europe and elsewhere during the early modern period (1400–1700), periodically erupting in epidemics that ravaged whole cities, killing nearly 30% of the victims and leaving the res ...
Approved
... It is necessary to protect people from expansion of plague diseases. This work is carried out by workers of sanitation center, ambulatory - polyclinic network and antiplague establishments. Plague is the quarantine diseases, so on it the international medicosanitary rules (WOPH, 1969) there are dist ...
... It is necessary to protect people from expansion of plague diseases. This work is carried out by workers of sanitation center, ambulatory - polyclinic network and antiplague establishments. Plague is the quarantine diseases, so on it the international medicosanitary rules (WOPH, 1969) there are dist ...
(Microsoft PowerPoint - 2014_15 Communicable diseases 2
... (laboratory investigation prooved )about the infectious agent playing role in the given case –by the laboratory (supplier) should be reported –with (Bacillus anthracis,Bordetella pertussis,Borrelia recurrentis,,Clostridium botulinum,Corynebacterium diphtheriae,Ebola-vírus,poxvírus,Humán –disease ...
... (laboratory investigation prooved )about the infectious agent playing role in the given case –by the laboratory (supplier) should be reported –with (Bacillus anthracis,Bordetella pertussis,Borrelia recurrentis,,Clostridium botulinum,Corynebacterium diphtheriae,Ebola-vírus,poxvírus,Humán –disease ...
Evaluation for the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System
... are available in Table III) and no case reported since 2003 (Yellow fever, Marburg fever, Ebola fever, Lassa fever, African Trypanosomiasis, Schistosomiasis, Yaws, Pinta, Smallpox, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Avian influenza infection in humans, Tularemia, and Newly everging infectious diseas ...
... are available in Table III) and no case reported since 2003 (Yellow fever, Marburg fever, Ebola fever, Lassa fever, African Trypanosomiasis, Schistosomiasis, Yaws, Pinta, Smallpox, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Avian influenza infection in humans, Tularemia, and Newly everging infectious diseas ...
Cotrimoxazole for childhood febrile illness in Malaria
... resources are few, and diagnosis must rely on clinical findings alone. Two of the commonest causes of childhood mortality in sub-Saharan Mrica are malaria and acute lower respiratory wct infection (ALRI), Because of limitations in diagnostic technology and personnel, disease-specific clinical case d ...
... resources are few, and diagnosis must rely on clinical findings alone. Two of the commonest causes of childhood mortality in sub-Saharan Mrica are malaria and acute lower respiratory wct infection (ALRI), Because of limitations in diagnostic technology and personnel, disease-specific clinical case d ...
B. Agglutination reaction
... A.Water is safe to be consumed B.Water is of doubtful quality C.Water is of highly doubtful quality D.Water is contaminated E.Water is highly conaminated 11. A patient had been provisionally diagnosed with syphilis. A laboratory assistant took the blood serum for an immunologic test based on the det ...
... A.Water is safe to be consumed B.Water is of doubtful quality C.Water is of highly doubtful quality D.Water is contaminated E.Water is highly conaminated 11. A patient had been provisionally diagnosed with syphilis. A laboratory assistant took the blood serum for an immunologic test based on the det ...
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers
... dengue virus infection can lead to serious haemorrhagic disease, known as dengue haemorrhagic fever (DHF). • The VHFs are caused by distinct RNA viruses that are members of four viral families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, and Flaviviridae. • Arenaviruses: six viruses are currently known ...
... dengue virus infection can lead to serious haemorrhagic disease, known as dengue haemorrhagic fever (DHF). • The VHFs are caused by distinct RNA viruses that are members of four viral families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, and Flaviviridae. • Arenaviruses: six viruses are currently known ...
Hepatitis A - Ministry of Health
... immunoglobulin if appropriate) may be indicated for all previously unimmunised staff and children at the service and unimmunised new staff and children for up to 6 weeks after the last case has been identified, including cases in the household of attendees. The number of infected cases should determ ...
... immunoglobulin if appropriate) may be indicated for all previously unimmunised staff and children at the service and unimmunised new staff and children for up to 6 weeks after the last case has been identified, including cases in the household of attendees. The number of infected cases should determ ...
Medical arthropod
... a poison into the body of humans and animals. e.g. Biting from toxic spiders. ...
... a poison into the body of humans and animals. e.g. Biting from toxic spiders. ...
Document
... and the reported instances in children continued to decrease. The second dose is given to ensure that infants and children who have a primary vaccine failure or a limited initial immune response have more complete and persisting protection. The efficacy of the VZV is 97% after the initial vaccinatio ...
... and the reported instances in children continued to decrease. The second dose is given to ensure that infants and children who have a primary vaccine failure or a limited initial immune response have more complete and persisting protection. The efficacy of the VZV is 97% after the initial vaccinatio ...
HSE - Tdap and MenC booster vaccines
... who should not get MenC vaccine? There are very few children who should not get MenC vaccine. Your child should not get the vaccine if they had a very severe reaction (anaphylaxis) to a previous MenC vaccine. You should delay getting the MenC vaccine if your child is ill with a high fever. ...
... who should not get MenC vaccine? There are very few children who should not get MenC vaccine. Your child should not get the vaccine if they had a very severe reaction (anaphylaxis) to a previous MenC vaccine. You should delay getting the MenC vaccine if your child is ill with a high fever. ...
Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters
... Unknown for Ebola and Marburg infections. In Africa, human index cases have been linked to exposure to monkeys, chimpanzees, gorillas, duikers, and porcupines and other animals found dead or killed in the rain forests.1 For dengue fever, in tropical urban centres, a cycle between humans and aedes ae ...
... Unknown for Ebola and Marburg infections. In Africa, human index cases have been linked to exposure to monkeys, chimpanzees, gorillas, duikers, and porcupines and other animals found dead or killed in the rain forests.1 For dengue fever, in tropical urban centres, a cycle between humans and aedes ae ...
immunology and medical microbiology
... hemorrhage, delusions and confusion are also ssen. Diagnosis Diagnosis is made by blood, bone marrow or stool cultures and with the Widal test (demonstration of salmonella antibodies against antigens O-somatic and H – flagellar). In epidemics, and in under developed countries, after excluding malari ...
... hemorrhage, delusions and confusion are also ssen. Diagnosis Diagnosis is made by blood, bone marrow or stool cultures and with the Widal test (demonstration of salmonella antibodies against antigens O-somatic and H – flagellar). In epidemics, and in under developed countries, after excluding malari ...
Preventive Pediatrics
... immunization hx: he had received 1 dose of BCG, 3 doses of DPT, TOPV & Hepatitis B. If you are the attending physician, how are you going to manage the patient? ...
... immunization hx: he had received 1 dose of BCG, 3 doses of DPT, TOPV & Hepatitis B. If you are the attending physician, how are you going to manage the patient? ...
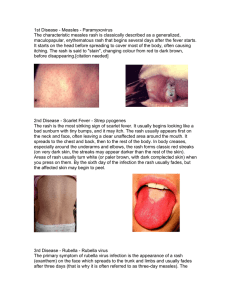
1st Disease - Measles
... with the upper arms and legs being the most common locations. The rash typically lasts a couple of days and may itch; some cases have been known to last for several weeks. Patients are usually no longer infectious once the rash has appeared. ...
... with the upper arms and legs being the most common locations. The rash typically lasts a couple of days and may itch; some cases have been known to last for several weeks. Patients are usually no longer infectious once the rash has appeared. ...
Campylobacter, Yersinia enterocolitica
... mild disease with watery or bloody diarrhea, they are more common in developed countries of temperate climate • S. flexneri is the main cause of endemic shigellosis in developing countries • S. dysenteriae typ 1 (Sd1, Shiga bacillus) is causing the most serious disease, it is causing epidemies in de ...
... mild disease with watery or bloody diarrhea, they are more common in developed countries of temperate climate • S. flexneri is the main cause of endemic shigellosis in developing countries • S. dysenteriae typ 1 (Sd1, Shiga bacillus) is causing the most serious disease, it is causing epidemies in de ...
Linköping University Post Print Serologic Analysis of Returned Travelers with Fever, Sweden
... was high compared with that of other studies, even after results of the additional serologic analysis (1–8,11). This large proportion of fever with unknown etiology may be explained by the unselected study population in a hospital setting and by a high patient turnover; febrile travelers with a nega ...
... was high compared with that of other studies, even after results of the additional serologic analysis (1–8,11). This large proportion of fever with unknown etiology may be explained by the unselected study population in a hospital setting and by a high patient turnover; febrile travelers with a nega ...
Update on Infectious Enterocolitides
... Aeromonas species • Aeromonas is now an accepted cause of infectious enterocolitis in humans • Cultures are key to diagnosis – Some recommend culturing all new onset IBD patients, especially kids – Molecular testing also available ...
... Aeromonas species • Aeromonas is now an accepted cause of infectious enterocolitis in humans • Cultures are key to diagnosis – Some recommend culturing all new onset IBD patients, especially kids – Molecular testing also available ...
Children - Simcoe Muskoka District Health Unit
... Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by influenza A and B viruses. In Canada influenza infection generally occurs in the late fall and winter months. Influenza is easily spread by direct contact or droplets expelled during breathing, talking, sneezing or coughing. Symptoms include sudden onse ...
... Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by influenza A and B viruses. In Canada influenza infection generally occurs in the late fall and winter months. Influenza is easily spread by direct contact or droplets expelled during breathing, talking, sneezing or coughing. Symptoms include sudden onse ...
Vaccines - Quest Garden
... to insure their continued effectiveness. In addition, neither killed nor acellular vaccines can cause disease and are therefore considered to be safe for use in immunocompromised patients. A third way of making a vaccine is to "attenuate" or weaken a live microorganism by aging it or altering its gr ...
... to insure their continued effectiveness. In addition, neither killed nor acellular vaccines can cause disease and are therefore considered to be safe for use in immunocompromised patients. A third way of making a vaccine is to "attenuate" or weaken a live microorganism by aging it or altering its gr ...
Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases
... Progression rates have changed dramatically in industrialized countries, where the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy in 1995 has contributed to decreases of up to 70% in the number of reported AIDS cases and AIDS-related deaths. 2.3. Diarrheal Diseases ...
... Progression rates have changed dramatically in industrialized countries, where the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy in 1995 has contributed to decreases of up to 70% in the number of reported AIDS cases and AIDS-related deaths. 2.3. Diarrheal Diseases ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.