Facts about Tularemia
... tularemia bacteria. These symptoms can include ulcers on the skin or mouth, swollen and painful lymph glands, swollen and painful eyes, and a sore throat. Symptoms usually appear 3 to 5 days after exposure to the bacteria, but can take as long as 14 days. Transmission Tularemia is not known to be sp ...
... tularemia bacteria. These symptoms can include ulcers on the skin or mouth, swollen and painful lymph glands, swollen and painful eyes, and a sore throat. Symptoms usually appear 3 to 5 days after exposure to the bacteria, but can take as long as 14 days. Transmission Tularemia is not known to be sp ...
Large Simple Trials of Vaccine Safety
... Effect of manufacturing change Effect of formulation change Effect of dose/schedule change (Effect of other vaccines given concomitantly) Validity of assumption that observed effect can be generalized to other populations ...
... Effect of manufacturing change Effect of formulation change Effect of dose/schedule change (Effect of other vaccines given concomitantly) Validity of assumption that observed effect can be generalized to other populations ...
11/2017 - NSW Health
... soil, dust and animal faeces. Disease occurs when the organism enters the body through a break in the skin (such as a puncture wound). When the bacterium grows it produces a neurotoxin which causes involuntary muscle contraction; the disease can be life threatening. Tetanus is not transmitted betwee ...
... soil, dust and animal faeces. Disease occurs when the organism enters the body through a break in the skin (such as a puncture wound). When the bacterium grows it produces a neurotoxin which causes involuntary muscle contraction; the disease can be life threatening. Tetanus is not transmitted betwee ...
Gastroenteritis – “stomach flu” but is not related to influenza at all
... Incubation 1-7 days; if bacterial toxins – hrs Fever common if cause inflammatory diarrhea (Salmonella, Shingella) Frequent bloody diarrhea Vomiting not common unless preformed toxins (S. aureus and bacillus cereus) Dx: leukocytes, blood/stool cultures to identify pathogens Tx: supportiv ...
... Incubation 1-7 days; if bacterial toxins – hrs Fever common if cause inflammatory diarrhea (Salmonella, Shingella) Frequent bloody diarrhea Vomiting not common unless preformed toxins (S. aureus and bacillus cereus) Dx: leukocytes, blood/stool cultures to identify pathogens Tx: supportiv ...
Communicable Diseases and Immunisation Guidelines
... students not wishing to be vaccinated for personal or other reasons must sign a Declaration of Understanding, stating that they understand why vaccination is being offered, and the potential health effects of being exposed to body fluids/tissues or infectious organisms. Personnel who do not have app ...
... students not wishing to be vaccinated for personal or other reasons must sign a Declaration of Understanding, stating that they understand why vaccination is being offered, and the potential health effects of being exposed to body fluids/tissues or infectious organisms. Personnel who do not have app ...
Chapter 22, GI Tract Diseases
... 1. Gram neg rod, H2S producer, noncoliform. Identified by biochemical characteristics plus serotyping. (Now there is also a special surveillance system, coordinated by CDC for keeping track of strains causing outbreaks.) 2. Cause gastroenteritis - often called “food poisoning” but is actually an inf ...
... 1. Gram neg rod, H2S producer, noncoliform. Identified by biochemical characteristics plus serotyping. (Now there is also a special surveillance system, coordinated by CDC for keeping track of strains causing outbreaks.) 2. Cause gastroenteritis - often called “food poisoning” but is actually an inf ...
Theileria parva infections
... controlled by the infection and treatment method of immunization using local isolates. Buffalo-derived T. parva is more difficult to control using conventional oxytetracycline dosing during immunization and higher reactor rates tend to occur. Buparvaquone controls the post-immunization reactions bet ...
... controlled by the infection and treatment method of immunization using local isolates. Buffalo-derived T. parva is more difficult to control using conventional oxytetracycline dosing during immunization and higher reactor rates tend to occur. Buparvaquone controls the post-immunization reactions bet ...
December 2008 - NWMOinfo.org
... linked are the issues of vaccine safety and the strict maintenance of sterilization standards. Even as these have improved greatly over time, the fact that vaccines are biological agents often makes them much more difficult than drugs to produce. Jenner and his peers faced this problem, and history ...
... linked are the issues of vaccine safety and the strict maintenance of sterilization standards. Even as these have improved greatly over time, the fact that vaccines are biological agents often makes them much more difficult than drugs to produce. Jenner and his peers faced this problem, and history ...
Fever and Rash - people.vcu.edu
... between acute and convalescent IFA Ehrlichia titers. Alert the lab to look for cytoplasmic inclusions (morulae), which are diagnostic of ehrlichiosis. Morulae occur more frequently in HGE than HME. A complete blood count (CBC) should be obtained for possible neutropenia, lymphocytopenia, or thromboc ...
... between acute and convalescent IFA Ehrlichia titers. Alert the lab to look for cytoplasmic inclusions (morulae), which are diagnostic of ehrlichiosis. Morulae occur more frequently in HGE than HME. A complete blood count (CBC) should be obtained for possible neutropenia, lymphocytopenia, or thromboc ...
Pediatric Visual Diagnosis
... runny nose & cough • Koplik spots -white spot on buccal mucosa - 24-48 hours before rash - pathognomonic -difficult to see Rash: ◦ begins on face & behind ears ◦ usually with onset high fever ◦ spreads to body ◦ Usually spares palms/soles ...
... runny nose & cough • Koplik spots -white spot on buccal mucosa - 24-48 hours before rash - pathognomonic -difficult to see Rash: ◦ begins on face & behind ears ◦ usually with onset high fever ◦ spreads to body ◦ Usually spares palms/soles ...
Roseola
... from the nose or mouth travelling through the air or by direct contact. The tiny droplets of fluid are expelled when an infected person talks, coughs, sneezes or laughs. If people touch these droplets and then touch their own noses or mouths they can become infected. The incubation period (time from ...
... from the nose or mouth travelling through the air or by direct contact. The tiny droplets of fluid are expelled when an infected person talks, coughs, sneezes or laughs. If people touch these droplets and then touch their own noses or mouths they can become infected. The incubation period (time from ...
Document
... c. Used as an index for fecal pollution in food or water, done by coliform counts that tell if there is gut contamination but cannot tell if human or not or if it is pathogenic d. Lactose positive whereas Shigella and Salmonella are not, done on MacConkey agar plate, a positive test turns pink-the o ...
... c. Used as an index for fecal pollution in food or water, done by coliform counts that tell if there is gut contamination but cannot tell if human or not or if it is pathogenic d. Lactose positive whereas Shigella and Salmonella are not, done on MacConkey agar plate, a positive test turns pink-the o ...
Fatal case of diphtheria in an unvaccinated infant
... swab from an 11 year old boy from a religious community in Salford, north west England (1). The child had developed a sore throat on 5 January, six days after returning from a one week holiday with four members of his family in Jerusalem, Israel. The throat swab was taken on 7 January. A seven day c ...
... swab from an 11 year old boy from a religious community in Salford, north west England (1). The child had developed a sore throat on 5 January, six days after returning from a one week holiday with four members of his family in Jerusalem, Israel. The throat swab was taken on 7 January. A seven day c ...
Dengue Fever - johnbirchall
... Marked damage to blood and lymph vessels Bleeding from the nose, gums, or under the skin, causing purplish bruises ...
... Marked damage to blood and lymph vessels Bleeding from the nose, gums, or under the skin, causing purplish bruises ...
Handout-Bioterrorism
... Airborne spread, contact Secondary attack rate 50% (unvaccinated) Last death – 1978 UK. WHO 1980, eradicated. ...
... Airborne spread, contact Secondary attack rate 50% (unvaccinated) Last death – 1978 UK. WHO 1980, eradicated. ...
Updated immunisation 20th september
... infected infants may become chronic carriers • Between 2-20% of infected adults become chronic carriers • Carriers may develop chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma ...
... infected infants may become chronic carriers • Between 2-20% of infected adults become chronic carriers • Carriers may develop chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma ...
Infectious Diseases
... Index – the first case identified Primary – the case that brings the infection into a population Secondary – infected by a primary case Tertiary – infected by a secondary case ...
... Index – the first case identified Primary – the case that brings the infection into a population Secondary – infected by a primary case Tertiary – infected by a secondary case ...
Medicine 8.0 Мікробіологія 1. Quite often the cause of secondary
... 1. Quite often the cause of secondary immunodeficiency is an infection involvement, when the causative agents propagate directly in the cells of immune system and destroy it. The following diseases are characterized by: A. Infectious mononucleosis, AIDS B. Tuberculosis, mycobacteriosis C. Poliomyeli ...
... 1. Quite often the cause of secondary immunodeficiency is an infection involvement, when the causative agents propagate directly in the cells of immune system and destroy it. The following diseases are characterized by: A. Infectious mononucleosis, AIDS B. Tuberculosis, mycobacteriosis C. Poliomyeli ...
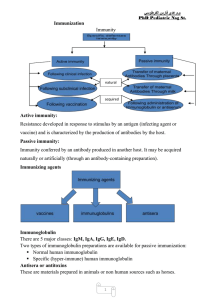
تحميل المحاضرة
... Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-containing preparation). Immunizing agents ...
... Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-containing preparation). Immunizing agents ...
Swedish Vaccination Programme
... is a highly contagious and often difficult viral disease with high fever, cough and rash. Measles can lead to complications such as meningitis, ear infections or bronchitis. There is no treatment for the illness and deaths occur among unvaccinated children. ...
... is a highly contagious and often difficult viral disease with high fever, cough and rash. Measles can lead to complications such as meningitis, ear infections or bronchitis. There is no treatment for the illness and deaths occur among unvaccinated children. ...
Revised: April 2012 AN: 01030/2011 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT
... No information is available on the safety and efficacy from the concurrent use of this vaccine with any other. It is therefore recommended that no other vaccines should be administered within 14 days before of after vaccination with the product. ...
... No information is available on the safety and efficacy from the concurrent use of this vaccine with any other. It is therefore recommended that no other vaccines should be administered within 14 days before of after vaccination with the product. ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... The activities of mecillinam and Ampicillin alone and in combination were evaluated in mice infected with the LT 2 strain of salmonella typhymurium. Ampicillin in doses of >=0.03 mg and mecillinam in doses of >= 0.5 mg reduced mortality rates from 77% in saline treated controls to a range of 0-47% ( ...
... The activities of mecillinam and Ampicillin alone and in combination were evaluated in mice infected with the LT 2 strain of salmonella typhymurium. Ampicillin in doses of >=0.03 mg and mecillinam in doses of >= 0.5 mg reduced mortality rates from 77% in saline treated controls to a range of 0-47% ( ...
General information
... Rabies is a viral infection which is usually transmitted following contact with the saliva of an infected animal most often via a bite, scratch or lick to an open wound or mucous membrane (such as on the eye, nose or mouth). Although many different animals can transmit the virus, most cases follow a ...
... Rabies is a viral infection which is usually transmitted following contact with the saliva of an infected animal most often via a bite, scratch or lick to an open wound or mucous membrane (such as on the eye, nose or mouth). Although many different animals can transmit the virus, most cases follow a ...
Revised: May 2012 AN: 00012/2012 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT
... Special precautions for the disposal of unused veterinary medicinal product or waste materials derived from the use of such products Dispose of waste material by boiling, incineration or immersion in an appropriate disinfectant approved for use by the competent authorities. ...
... Special precautions for the disposal of unused veterinary medicinal product or waste materials derived from the use of such products Dispose of waste material by boiling, incineration or immersion in an appropriate disinfectant approved for use by the competent authorities. ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.