Learning material
... inside of an atom. Recall that even up to the beginning of the 20th century atoms were regarded as indivisible. Thompson was led to a different conclusion by his discovery of the electron as a constituent of atoms. Thomson’s model distributed the positive and negative charge uniformly through the at ...
... inside of an atom. Recall that even up to the beginning of the 20th century atoms were regarded as indivisible. Thompson was led to a different conclusion by his discovery of the electron as a constituent of atoms. Thomson’s model distributed the positive and negative charge uniformly through the at ...
Physics 2 Homework 23_2013 We started discussing
... Physics 2 Homework 23_2013 We started discussing the structure of atoms. As we already know, atom consists of nucleus which includes positively charged protons and neutral particles – neutrons. The nucleus is surrounded by electron “clouds”. I deliberately not use the picture describing the electron ...
... Physics 2 Homework 23_2013 We started discussing the structure of atoms. As we already know, atom consists of nucleus which includes positively charged protons and neutral particles – neutrons. The nucleus is surrounded by electron “clouds”. I deliberately not use the picture describing the electron ...
Atoms, X-rays and Synchrotron Radiation
... the others because extremely energetic electrons emitting X-rays radiate away their energy more quickly than the lower-energy electrons emitting optical and infrared light. The Crab Nebula is one of the most studied objects in the sky, truly making it a cosmic icon. ...
... the others because extremely energetic electrons emitting X-rays radiate away their energy more quickly than the lower-energy electrons emitting optical and infrared light. The Crab Nebula is one of the most studied objects in the sky, truly making it a cosmic icon. ...
Unit 2 Atomic structure
... weak force eventually causes it to break up into a proton and an electron. • The force of gravity inside the atom is much weaker even than the weak force. Every process we know in the universe can be explained in terms of these fundamental forces. ...
... weak force eventually causes it to break up into a proton and an electron. • The force of gravity inside the atom is much weaker even than the weak force. Every process we know in the universe can be explained in terms of these fundamental forces. ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 3
... The compound that gives vinegar its sour taste is acetic acid, which contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. When 5.00g of acetic acid is analyzed it is found to contain 2.00g of carbon, 0.336g of hydrogen, and 2.66g of oxygen. What is the empirical formula of acetic acid? ...
... The compound that gives vinegar its sour taste is acetic acid, which contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. When 5.00g of acetic acid is analyzed it is found to contain 2.00g of carbon, 0.336g of hydrogen, and 2.66g of oxygen. What is the empirical formula of acetic acid? ...
lecture1
... IR absorption due to II and III of CO2 occur at “fundamental frequencies”. These are frequencies at which intense absorption bands occur for complex molecules (ν1, ν2 etc). Less intense bands called “overtones” may occur at multiples of the fundamental frequencies, e.g. (2ν1, 2ν2 etc). There could a ...
... IR absorption due to II and III of CO2 occur at “fundamental frequencies”. These are frequencies at which intense absorption bands occur for complex molecules (ν1, ν2 etc). Less intense bands called “overtones” may occur at multiples of the fundamental frequencies, e.g. (2ν1, 2ν2 etc). There could a ...
The Mystery of Matter: The Course
... as observed by a stationary observer. A moving length is shortened in the direction of flight, as seen by a stationary observer. The mass of a body or particle at rest contains energy E = mc2 This “rest mass” increases with v as the particle speeds up to the speed of light. ...
... as observed by a stationary observer. A moving length is shortened in the direction of flight, as seen by a stationary observer. The mass of a body or particle at rest contains energy E = mc2 This “rest mass” increases with v as the particle speeds up to the speed of light. ...
Bohr Model of the Atom
... surrounded by electrons that orbit some distance away. The electrons must be moving, otherwise they would fall into the nucleus due to Coulomb interaction Measured closest distance between alpha particle and nucleus from its KE which is converted to electric PE q1q2 ...
... surrounded by electrons that orbit some distance away. The electrons must be moving, otherwise they would fall into the nucleus due to Coulomb interaction Measured closest distance between alpha particle and nucleus from its KE which is converted to electric PE q1q2 ...
Structure of atoms and solids
... Spin quantum number m s = 1/2 Each electron in an atom has a unique set of these four quantum numbers (Pauli Exclusion Principle). Electrons in an atom have their total energy (kinetic + potential) quantized. For a given atom, there is a set of discrete energy values that the electrons bound to th ...
... Spin quantum number m s = 1/2 Each electron in an atom has a unique set of these four quantum numbers (Pauli Exclusion Principle). Electrons in an atom have their total energy (kinetic + potential) quantized. For a given atom, there is a set of discrete energy values that the electrons bound to th ...
Chapter 7
... • The Amplitude is the vertical height (of depth of a trough) AND determines its intensity or brightness of the light • The wavelength is the distance between crests. It is measured in units of distance (meters) – we use nanometers (nm) – 10-9 meters AND determines the color of the light ...
... • The Amplitude is the vertical height (of depth of a trough) AND determines its intensity or brightness of the light • The wavelength is the distance between crests. It is measured in units of distance (meters) – we use nanometers (nm) – 10-9 meters AND determines the color of the light ...
Course summary for Unit 4 "Interactions of Light and
... Maxwell had said that an electromagnetic wave which was carrying energy, E, also had momentum, p = E/c where c was the speed of light. So, substituting E = hf, the momentum of a photon is given by p = hf/c = h/. The De Broglie Wavelength De Broglie suggested that the relationship between wavelength ...
... Maxwell had said that an electromagnetic wave which was carrying energy, E, also had momentum, p = E/c where c was the speed of light. So, substituting E = hf, the momentum of a photon is given by p = hf/c = h/. The De Broglie Wavelength De Broglie suggested that the relationship between wavelength ...
Radioactivity Mid-Unit Review Questions
... 9. An element undergoes an alpha decay and then the daughter products go through a series of 2 beta decays. What happens to its atomic number? Mass number? Atomic Number goes down by 2 and mass number goes down by 4 for alpha decay (2p+ & 2n0 ), then a neutron changes into a proton during each of th ...
... 9. An element undergoes an alpha decay and then the daughter products go through a series of 2 beta decays. What happens to its atomic number? Mass number? Atomic Number goes down by 2 and mass number goes down by 4 for alpha decay (2p+ & 2n0 ), then a neutron changes into a proton during each of th ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
Modern physics
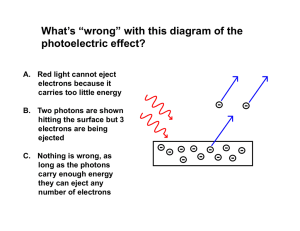
... quanta as particles, then special relativity implies that they are massless, always moving with the speed of light The quantum nature of light has been tested in the photoelectric effect. The quantum hypothesis suggests that the kinetic energy of photoelectrons is proportional to the frequency of th ...
... quanta as particles, then special relativity implies that they are massless, always moving with the speed of light The quantum nature of light has been tested in the photoelectric effect. The quantum hypothesis suggests that the kinetic energy of photoelectrons is proportional to the frequency of th ...
1 - Livonia Public Schools
... –0.1361 × 10–18 J n=3 –0.2420 × 10–18 J n=2 –0.5445 × 10–18 J n=1 –2.178 × 10–18 J ...
... –0.1361 × 10–18 J n=3 –0.2420 × 10–18 J n=2 –0.5445 × 10–18 J n=1 –2.178 × 10–18 J ...
Cherenkov Radiation From Faster-Than
... In this paper, the author evaluates the cosmic background radiation due to the Cherenkov effect from FTL virtual photons created in a ZPF background. The calculated result shows that the spectrum and the mass density of energy due to the Cherenkov radiation almost coincides the cosmic background rad ...
... In this paper, the author evaluates the cosmic background radiation due to the Cherenkov effect from FTL virtual photons created in a ZPF background. The calculated result shows that the spectrum and the mass density of energy due to the Cherenkov radiation almost coincides the cosmic background rad ...
4.4 The Bohr Atom
... *http://www.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/Bohr_to_Waves/Bohr_to_Waves.html ...
... *http://www.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/Bohr_to_Waves/Bohr_to_Waves.html ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 Test Multiple Choice (1.5% each) Identify the
... c. Quantum Mechanical Model b. Atomic Orbital 12. Calcium chloride is a pure substance used on roads to control dust and to melt ice and snow. Its formula unit shows that it contains one calcium ion for every two chloride ions. What type of matter is calcium chloride? a. molecular compound c. ionic ...
... c. Quantum Mechanical Model b. Atomic Orbital 12. Calcium chloride is a pure substance used on roads to control dust and to melt ice and snow. Its formula unit shows that it contains one calcium ion for every two chloride ions. What type of matter is calcium chloride? a. molecular compound c. ionic ...
sofia3_mac - University of Glasgow
... During a flare, stored magnetic energy is distributed through corona and efficiently converted to KE of fast particles. Flare ‘standard model’ does a pretty good job at providing a framework for the whole flare phenomenon. However, theory of energy transport by electron beams runs into some trouble ...
... During a flare, stored magnetic energy is distributed through corona and efficiently converted to KE of fast particles. Flare ‘standard model’ does a pretty good job at providing a framework for the whole flare phenomenon. However, theory of energy transport by electron beams runs into some trouble ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.