Lesson Power Point
... the rest of the objects in the solar system put together. The next largest object is the planet Jupiter. ...
... the rest of the objects in the solar system put together. The next largest object is the planet Jupiter. ...
direct - grade 4High peaks elementary
... at its highest point in the sky at noon appears to be moving from east to west, however, Earth is moving, not the sun. planets and other bodies orbit around the sun Earth rotates on its axis as it revolves around the sun, this causes day and night. Earth’s axis is tilted which causes seasons. Gravit ...
... at its highest point in the sky at noon appears to be moving from east to west, however, Earth is moving, not the sun. planets and other bodies orbit around the sun Earth rotates on its axis as it revolves around the sun, this causes day and night. Earth’s axis is tilted which causes seasons. Gravit ...
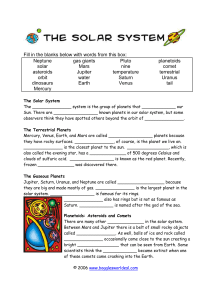
Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: Neptune solar
... they are big and made mostly of gas. _______________ is the largest planet in the solar system. _________________ is famous for its rings. _______________ also has rings but is not as famous as Saturn. _____________ is named after the god of the sea. Planetoids: Asteroids and Comets There are many o ...
... they are big and made mostly of gas. _______________ is the largest planet in the solar system. _________________ is famous for its rings. _______________ also has rings but is not as famous as Saturn. _____________ is named after the god of the sea. Planetoids: Asteroids and Comets There are many o ...
Chapter Notes - Alpcentauri.info
... The plane of the ecliptic (also known as the ecliptic plane) is the plane of the Earth’s orbit about the Sun. It is the primary reference plane when describing the position of bodies in the Solar System, with celestial latitude being measured relative to the ecliptic plane. In the course of a year, ...
... The plane of the ecliptic (also known as the ecliptic plane) is the plane of the Earth’s orbit about the Sun. It is the primary reference plane when describing the position of bodies in the Solar System, with celestial latitude being measured relative to the ecliptic plane. In the course of a year, ...
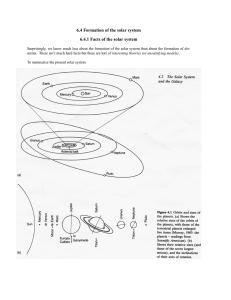
Formation of the solar system
... Assume gas cloud - contracts due to the gravitation; is opposed by the gas pressure. As the nebula (protostar) contracts energy is released, which causes the nebula to heat up. The spherical nebula is becoming a disck due to its rotation which combines with gravity to produce a force directed toward ...
... Assume gas cloud - contracts due to the gravitation; is opposed by the gas pressure. As the nebula (protostar) contracts energy is released, which causes the nebula to heat up. The spherical nebula is becoming a disck due to its rotation which combines with gravity to produce a force directed toward ...
Scale Model of the Solar System
... 1:1,000,000,000. This sounds difficult to do but actually it’s very easy because at this scale 1mm = 1,000 kilometres. Good approximations of the sizes of the planets are shown in the table below. Object Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Asteroid belt Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Proxima Centauri ...
... 1:1,000,000,000. This sounds difficult to do but actually it’s very easy because at this scale 1mm = 1,000 kilometres. Good approximations of the sizes of the planets are shown in the table below. Object Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Asteroid belt Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Proxima Centauri ...
2.13 Understanding our Universe
... centre of the Solar System • Because the Sun is so huge, its gravity holds the planets in their orbits around it ...
... centre of the Solar System • Because the Sun is so huge, its gravity holds the planets in their orbits around it ...
Chapter 2
... 4. Which of these diagrams below best illustrates the Earth's orbit around the Sun as viewed looking directly down on the orbit? ...
... 4. Which of these diagrams below best illustrates the Earth's orbit around the Sun as viewed looking directly down on the orbit? ...
The Sun, The Moon and The Earth
... • The sun appears to be yellow but it is actually white the earths atmosphere makes it look yellow ...
... • The sun appears to be yellow but it is actually white the earths atmosphere makes it look yellow ...
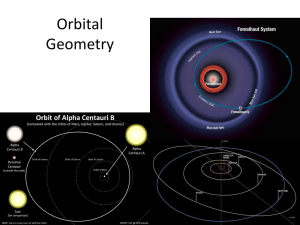
Orbital Geometry Notes
... • The center of an ellipse differs from a circle in that there are two fixed points (foci) rather than one. ...
... • The center of an ellipse differs from a circle in that there are two fixed points (foci) rather than one. ...
Solar System scale model
... The Solar System is often portrayed as a line of planets, closely packed to each other. But this picture is misleading! There is a lot of space in space! Astronomical distances are measured in km and in Astronomical Units (AU). 1 AU is 149,600,000km and is the same distance between the Sun and the E ...
... The Solar System is often portrayed as a line of planets, closely packed to each other. But this picture is misleading! There is a lot of space in space! Astronomical distances are measured in km and in Astronomical Units (AU). 1 AU is 149,600,000km and is the same distance between the Sun and the E ...
Sky Science Review for Test Part A
... S.O. 4 – Understand that the Sun should never be viewed directly, nor by the use of simple telescopes or filters, and that safe viewing requires appropriate methods and safety precautions. Looking directly at the Sun causes damage to our eyes that cannot ...
... S.O. 4 – Understand that the Sun should never be viewed directly, nor by the use of simple telescopes or filters, and that safe viewing requires appropriate methods and safety precautions. Looking directly at the Sun causes damage to our eyes that cannot ...
slides
... The Julian calendar went into effect in 45 BCE. Julian calendar was very successful for many centuries, but later on a flaw began to appear. – the solar year is shorter than 365 ¼ days by 11 minutes 12 seconds which had been adding up (one day in 130 years). Over the span of a millennia it added up ...
... The Julian calendar went into effect in 45 BCE. Julian calendar was very successful for many centuries, but later on a flaw began to appear. – the solar year is shorter than 365 ¼ days by 11 minutes 12 seconds which had been adding up (one day in 130 years). Over the span of a millennia it added up ...
Stars, Sun, and Moon Test Study Guide
... 9. Circle the part of the sun that can only be seen during a solar eclipse, and draw a square around the part of the sun that we can normally see from Earth. Corona ...
... 9. Circle the part of the sun that can only be seen during a solar eclipse, and draw a square around the part of the sun that we can normally see from Earth. Corona ...
Natalie and Holly 7F
... Sunspots The surface of the Sun, which is known as the photosphere, is as hot as 5800 degrees celcius. Sunspots are only 3800 degrees celcius; some sunspots can be very large and they can reach to 50,000 km wide in diameter. Sun spots are caused by unknown interactions with the sun’s magnetic field ...
... Sunspots The surface of the Sun, which is known as the photosphere, is as hot as 5800 degrees celcius. Sunspots are only 3800 degrees celcius; some sunspots can be very large and they can reach to 50,000 km wide in diameter. Sun spots are caused by unknown interactions with the sun’s magnetic field ...
Solar System Study Guide 1
... energy in our solar system. Some of this energy reaches the Earth as light, and some reaches it as heat. The dark areas of the sun are called sunspots. They are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface and don’t give off as much light. The red streams and loops of gases that shoot out from the ...
... energy in our solar system. Some of this energy reaches the Earth as light, and some reaches it as heat. The dark areas of the sun are called sunspots. They are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface and don’t give off as much light. The red streams and loops of gases that shoot out from the ...
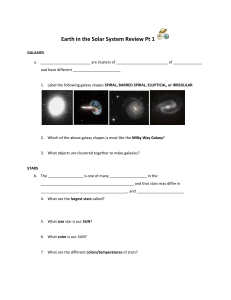
Earth in the Solar System - San Diego Unified School District
... between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from the Earth to the Asteroid Belt? 11. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from ...
... between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from the Earth to the Asteroid Belt? 11. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from ...
Earth and the sun The cycle of seasons is caused by the Earth`s tilt
... rotates around an (invisible) axis. At different times during the year, the northern or southern axis is closer to the sun. During these times, the hemisphere tipped toward the star experiences summer, while the hemisphere tilted away from the sun experiences winter. At other locations in Earth's an ...
... rotates around an (invisible) axis. At different times during the year, the northern or southern axis is closer to the sun. During these times, the hemisphere tipped toward the star experiences summer, while the hemisphere tilted away from the sun experiences winter. At other locations in Earth's an ...
HOMEWORK 5 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 9 4.A A red giant star will
... of the oldest stars in the Milky Way; they may have been the precursors to the Milky Way itself. 3.C The Sun is about 75 percent hydrogen and it formed about 5 billion years ago. Since that time, the makeup of the gas in the area around the Sun has changed. There is slightly less hydrogen than when ...
... of the oldest stars in the Milky Way; they may have been the precursors to the Milky Way itself. 3.C The Sun is about 75 percent hydrogen and it formed about 5 billion years ago. Since that time, the makeup of the gas in the area around the Sun has changed. There is slightly less hydrogen than when ...
Chapter 24.2 The Sun and the Seasons
... Marks the beginning or spring and autumn (halfway between the solstices) At an equinox neither hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, and the lengths of the days/nights are equal The vernal equinox which occurs about March 21st in the northern hemisphere marks the start of spring The autumnal e ...
... Marks the beginning or spring and autumn (halfway between the solstices) At an equinox neither hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, and the lengths of the days/nights are equal The vernal equinox which occurs about March 21st in the northern hemisphere marks the start of spring The autumnal e ...
Days and Nights
... During the night, we cannot see the Sun. But the Earth is still spinning on its axis. This means that the stars appear to move from east to west in the sky, just as the Sun does in the day. ...
... During the night, we cannot see the Sun. But the Earth is still spinning on its axis. This means that the stars appear to move from east to west in the sky, just as the Sun does in the day. ...