Space
... What do we know about the Sun? • Is the Sun a planet? What is it? • Does the Sun move? • Is the Sun bigger than the Earth and Moon? The Sun is a star. The Sun does not move around the planets. The Sun stays in one place. The planets move around the Sun. The Sun is over 1,000,000 times larger than t ...
... What do we know about the Sun? • Is the Sun a planet? What is it? • Does the Sun move? • Is the Sun bigger than the Earth and Moon? The Sun is a star. The Sun does not move around the planets. The Sun stays in one place. The planets move around the Sun. The Sun is over 1,000,000 times larger than t ...
Solutions 1
... synodic months are there in a year? Explain the difference. The sidereal month is 27.3 days long; therefore, there are 13.4 sidereal months in a year. The synodic month is 29.53 days long; therefore, there are 12.4 synodic months in a year. Thus, there is roughly one more sidereal month in a year th ...
... synodic months are there in a year? Explain the difference. The sidereal month is 27.3 days long; therefore, there are 13.4 sidereal months in a year. The synodic month is 29.53 days long; therefore, there are 12.4 synodic months in a year. Thus, there is roughly one more sidereal month in a year th ...
Ay 101 - The Physics of Stars – fall 2015 -... Homework 3, due Friday Oct 23 at class (2 pm)
... Let us assume that the cross section for the absorption of light by nuetral hydrogen atoms is independent of frequency and is 100 times the area of the nucleus of a H atom. What is the absorption coefficient per gram of this gas ? If a tube 1 m long is filled with this H gas, maintaining the value o ...
... Let us assume that the cross section for the absorption of light by nuetral hydrogen atoms is independent of frequency and is 100 times the area of the nucleus of a H atom. What is the absorption coefficient per gram of this gas ? If a tube 1 m long is filled with this H gas, maintaining the value o ...
astronomy review - Earth Science R: 1(A,C)
... Celestial Sphere- an imaginary sphere on which objects of the night sky appear Motions of the Stars and Planets Stars appear to rise in the _____________ and set in the ___________ Circumpolar planets appear to revolve around Polaris __________________ The apparent motion of the stars is c ...
... Celestial Sphere- an imaginary sphere on which objects of the night sky appear Motions of the Stars and Planets Stars appear to rise in the _____________ and set in the ___________ Circumpolar planets appear to revolve around Polaris __________________ The apparent motion of the stars is c ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... Aquarius”? The Vernal Equinox moves through the constellations. Currently it is in the constellation Pisces and it is moving to the constellation Aquarius. ...
... Aquarius”? The Vernal Equinox moves through the constellations. Currently it is in the constellation Pisces and it is moving to the constellation Aquarius. ...
PHYS 1311: In Class Problems Chapter 5 Solutions Feb. 23, 2016
... estimate, the true center of mass of the Solar System is close to this result. What does this mean? The planets do NOT orbit about the center of the Sun. They orbit about the center of mass of the Solar System. Likewise, the Sun orbits about the Solar System center of mass, but with a period nearly ...
... estimate, the true center of mass of the Solar System is close to this result. What does this mean? The planets do NOT orbit about the center of the Sun. They orbit about the center of mass of the Solar System. Likewise, the Sun orbits about the Solar System center of mass, but with a period nearly ...
SunStructure17
... Our Sun Our sun is a medium sized, medium temperature (yellow) star in the middle of its life cycle. It only looks big because it’s so much closer to us than any other star ...
... Our Sun Our sun is a medium sized, medium temperature (yellow) star in the middle of its life cycle. It only looks big because it’s so much closer to us than any other star ...
Name Class Date Our Solar System The solar system consists of our
... Moons’ surface. The phases repeat in a cyclic pattern in about one month. The apparent motions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars across the sky can be explained by Earth’s rotation and revolution. Earth rotates on an axis that is tilted at 23.5 degrees. Earth’s rotation causes the length of one d ...
... Moons’ surface. The phases repeat in a cyclic pattern in about one month. The apparent motions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars across the sky can be explained by Earth’s rotation and revolution. Earth rotates on an axis that is tilted at 23.5 degrees. Earth’s rotation causes the length of one d ...
time astro 2014 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... night, the Earth points towards a different part of the universe, giving us a slightly different view of the stars. 1st night: you see a constellation at a specific coordinate at a specific time 2nd night: you see the constellation at the same coordinate, but in order to see this, you must view ...
... night, the Earth points towards a different part of the universe, giving us a slightly different view of the stars. 1st night: you see a constellation at a specific coordinate at a specific time 2nd night: you see the constellation at the same coordinate, but in order to see this, you must view ...
The Sun Worksheet
... 12. In which layer of the Sun do temperatures reach about 15 million degrees Celsius? ...
... 12. In which layer of the Sun do temperatures reach about 15 million degrees Celsius? ...
Observing the Sky - University of Northern Iowa
... The Sun orbits around the Earth during the course of the day. Seasons are caused by the Earth’s changing distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
... The Sun orbits around the Earth during the course of the day. Seasons are caused by the Earth’s changing distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
Measuring the Sun - Faculty Web Sites
... What did you or your group determine to be the diameter of the Sun? ACCEPTED VALUE 23,891,238 KM 100 EARTH RADII ...
... What did you or your group determine to be the diameter of the Sun? ACCEPTED VALUE 23,891,238 KM 100 EARTH RADII ...
Powerpoint Notes on Meteors, Asteroids and Comets
... Meteoroid – a chunk of rock or dust in space. (these come from comets or asteroids) Meteor – a chunk of rock or dust that enters our atomosphere and burns up, producing a streak of light time lapse photo of meteor shower Meteorite – a meteor so large it does not completely burn up and strikes the su ...
... Meteoroid – a chunk of rock or dust in space. (these come from comets or asteroids) Meteor – a chunk of rock or dust that enters our atomosphere and burns up, producing a streak of light time lapse photo of meteor shower Meteorite – a meteor so large it does not completely burn up and strikes the su ...
The Sun's Crowded Delivery Room
... show that Earth, Mars, and chondritic meteorites contain evidence for the presence of 60Fe (given by the 0.0 value of ε60Ni, the decay product of 60Fe) • In contrast, differentiated meteorites, which formed 1 My after initial solar system formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.haw ...
... show that Earth, Mars, and chondritic meteorites contain evidence for the presence of 60Fe (given by the 0.0 value of ε60Ni, the decay product of 60Fe) • In contrast, differentiated meteorites, which formed 1 My after initial solar system formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.haw ...
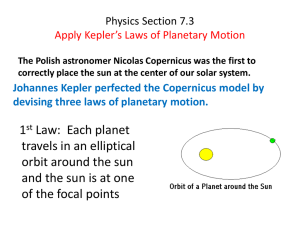
Physics Section 7.3 Apply Kepler*s Laws of Planetary
... The Polish astronomer Nicolas Copernicus was the first to correctly place the sun at the center of our solar system. ...
... The Polish astronomer Nicolas Copernicus was the first to correctly place the sun at the center of our solar system. ...
Introduction
... • "debate" between geocentric and heliocentric ideas • obviously favoured heliocentric ...
... • "debate" between geocentric and heliocentric ideas • obviously favoured heliocentric ...
Week 3
... Apparent diameter of the Sun is 0.5° At the equinox the centre of the Sun is above the horizon for 12 hours Sunrise is defined to be when the upper limb of the Sun crosses the horizon, so day is actually longer than night at the ...
... Apparent diameter of the Sun is 0.5° At the equinox the centre of the Sun is above the horizon for 12 hours Sunrise is defined to be when the upper limb of the Sun crosses the horizon, so day is actually longer than night at the ...
Solar System Notes
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
The Sun - University of Minnesota
... Sun’s Interior • Convection Zone – Energy travels up toward the surface via rising hot gas ...
... Sun’s Interior • Convection Zone – Energy travels up toward the surface via rising hot gas ...
Introduction to the EarthESci 100Dr. Albanese, Tuesdays and
... 4. The planets maintain circular orbits around the sun. 5. When the earth is the farthest from the sun it is said to be in the perihelion position. 6. The angular distance north and south of the celestial equator is called right ascension. 7. Patterns or configurations of stars named in honor of myt ...
... 4. The planets maintain circular orbits around the sun. 5. When the earth is the farthest from the sun it is said to be in the perihelion position. 6. The angular distance north and south of the celestial equator is called right ascension. 7. Patterns or configurations of stars named in honor of myt ...
Solar System Unit Review - Parma City School District
... About how long does it take for the earth to go from point A to point C in the picture? ...
... About how long does it take for the earth to go from point A to point C in the picture? ...
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Syllabus: Phys 200 (3 cr
... Geocentric model of the Universe. Heliocentric model of the Universe. The Kepler’s laws. Newton laws of motion. ...
... Geocentric model of the Universe. Heliocentric model of the Universe. The Kepler’s laws. Newton laws of motion. ...
Grade 9 Science – Unit 4
... SOLAR PROMINENCE – Large sheets of glowing gases bursting outward from the chromosphere. They can last for weeks and grow to be 400 000 kilometers high. SUNSPOTS – Dark, cooler regions of the photosphere that produce violent magnetic storms. These storms can disrupt radio communications on Earth ...
... SOLAR PROMINENCE – Large sheets of glowing gases bursting outward from the chromosphere. They can last for weeks and grow to be 400 000 kilometers high. SUNSPOTS – Dark, cooler regions of the photosphere that produce violent magnetic storms. These storms can disrupt radio communications on Earth ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... A star/ sun is a ball of burning gas in the middle of a solar system. A sun sends out light and heat. Planets orbit a sun. They don’t send out light, but the get light and heat from the sun. Moons orbit planets. It is possible that 1 or more moons orbit one planet. ...
... A star/ sun is a ball of burning gas in the middle of a solar system. A sun sends out light and heat. Planets orbit a sun. They don’t send out light, but the get light and heat from the sun. Moons orbit planets. It is possible that 1 or more moons orbit one planet. ...