Space Jeopardy 2
... The Outer Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are also known by this name ...
... The Outer Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are also known by this name ...
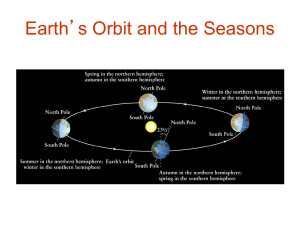
Reasons for the Seasons
... 1. A. The Earth’s orbit is close to circular, so our distance to the Sun does not vary much and does not affect our seasons. (We are actually closest in the beginning of Jan. and farthest the beginning of July) 2. C. is correct, because it most accurately represents the great distance between the Ea ...
... 1. A. The Earth’s orbit is close to circular, so our distance to the Sun does not vary much and does not affect our seasons. (We are actually closest in the beginning of Jan. and farthest the beginning of July) 2. C. is correct, because it most accurately represents the great distance between the Ea ...
Chapter 15 Notes - Valdosta State University
... day is the time required for the Earth to rotate through exactly 360˚. It is about 4 minutes shorter than the mean solar day due to the Earth’s movement in its orbit. ...
... day is the time required for the Earth to rotate through exactly 360˚. It is about 4 minutes shorter than the mean solar day due to the Earth’s movement in its orbit. ...
Export To Word
... This video segment produced for Teachers' Domain features a time-lapse video of clouds forming, changing, and moving across the sky from day to night. ...
... This video segment produced for Teachers' Domain features a time-lapse video of clouds forming, changing, and moving across the sky from day to night. ...
The Sun - Moodle
... The sun spins on its axis but different ___________ spin at different ___________ The Sun has Storms: Sunspot Cycles Scientists have observed for hundreds of years That is how they know different ______________ rotate at different rates the numbers and position of sunspots vary in a cycle that la ...
... The sun spins on its axis but different ___________ spin at different ___________ The Sun has Storms: Sunspot Cycles Scientists have observed for hundreds of years That is how they know different ______________ rotate at different rates the numbers and position of sunspots vary in a cycle that la ...
Gravity
... 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the Sun? 3. What did Galileo see in his telescope that confirmed that planets orbit the Sun? 4. How did Tycho Brahe attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? 5. What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Su ...
... 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the Sun? 3. What did Galileo see in his telescope that confirmed that planets orbit the Sun? 4. How did Tycho Brahe attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? 5. What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Su ...
Constellations and Planets in the Night Sky
... a. Stars are too far away to see their movement from Earth. b. Planets orbit around the sun. c. The motion of stars occurs over a long period of time such as 100 years. d. All of the above. ...
... a. Stars are too far away to see their movement from Earth. b. Planets orbit around the sun. c. The motion of stars occurs over a long period of time such as 100 years. d. All of the above. ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the end of a large star’s life. By this stage, the star has used up all of its fuel needed to continue nuclear fusion. 25. A __________ ________ is a small, very dens ...
... 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the end of a large star’s life. By this stage, the star has used up all of its fuel needed to continue nuclear fusion. 25. A __________ ________ is a small, very dens ...
Brobo_solarsystem_faceoff
... 58. What types of climate patterns are found on Mercury because of it’s thin atmosphere? 59. What is the most abundant element in the gas giants? 60. The Great Dark Spot belongs to what planet? 61-64. Name the four dwarf planets 65*. What is the difference between a dwarf planet and a plutoid? 66. C ...
... 58. What types of climate patterns are found on Mercury because of it’s thin atmosphere? 59. What is the most abundant element in the gas giants? 60. The Great Dark Spot belongs to what planet? 61-64. Name the four dwarf planets 65*. What is the difference between a dwarf planet and a plutoid? 66. C ...
Motions of the Earth and Sky. Seasons, Eclipses
... Is the Earth Flat? • Might seem so, but the ancient Greeks figured out it was a sphere. How? By watching eclipses of the moon and noting they always happened 180 degrees away from the sun. • They even measured how big it was, correctly! Way back in ~600BC Erotosthenes did this ...
... Is the Earth Flat? • Might seem so, but the ancient Greeks figured out it was a sphere. How? By watching eclipses of the moon and noting they always happened 180 degrees away from the sun. • They even measured how big it was, correctly! Way back in ~600BC Erotosthenes did this ...
Space is Big…
... You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that’s just peanuts to space.” ...
... You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that’s just peanuts to space.” ...
File
... Part I: Define the following terms 1. solstices - the longest and shortest days of the year 2. equinoxes - times of the year when the sun is located directly above the equator so that day and night are of equal length around the world (March 21 and September 22 – 23) 3. Apollo 11 - the 1st manned la ...
... Part I: Define the following terms 1. solstices - the longest and shortest days of the year 2. equinoxes - times of the year when the sun is located directly above the equator so that day and night are of equal length around the world (March 21 and September 22 – 23) 3. Apollo 11 - the 1st manned la ...
7.1 Space Flight to the Stars
... A light year is a unit of distance, not time! There is a reason why it is called a light-year: it is equal to the distance that a beam of light can travel through space in 1 year. It is equivalent to: -63 000 AU -9000 billion kilometres ...
... A light year is a unit of distance, not time! There is a reason why it is called a light-year: it is equal to the distance that a beam of light can travel through space in 1 year. It is equivalent to: -63 000 AU -9000 billion kilometres ...
Astronomy_Main_Lesson_Book_Contents_2007
... a. Ancient Greeks – Eratosthenes - Sun-centered model, determining the size of the Earth b. Aristotle and Ptolemy – Earth-centered model c. Copernicus – Sun-centered model d. Galileo’s Discoveries: i. Phases of Venus ii. Craters on Moon iii. Sunspots iv. Moons of Jupiter v. Negative consequences for ...
... a. Ancient Greeks – Eratosthenes - Sun-centered model, determining the size of the Earth b. Aristotle and Ptolemy – Earth-centered model c. Copernicus – Sun-centered model d. Galileo’s Discoveries: i. Phases of Venus ii. Craters on Moon iii. Sunspots iv. Moons of Jupiter v. Negative consequences for ...
solar system - Teaching Children
... The sun is ______ Star of solar system. The Earth is the _______ of the universe. Mercury is _______ than Uranus. Jupiter is _______ than Venus. The Moon is ________ than mercury ...
... The sun is ______ Star of solar system. The Earth is the _______ of the universe. Mercury is _______ than Uranus. Jupiter is _______ than Venus. The Moon is ________ than mercury ...
Definitions
... • Polaris lies less than 1° from the north celestial pole • For observers in the Northern Hemisphere the stars are circumpolar • The viewer’s latitude will determine how much of the sky is circumpolar ...
... • Polaris lies less than 1° from the north celestial pole • For observers in the Northern Hemisphere the stars are circumpolar • The viewer’s latitude will determine how much of the sky is circumpolar ...
Earth`s Orbit and the Seasons
... Umbra – dark part of the shadow; Penumbra – lighter part of the shadow Earth’s maximum umbra at Moon’s distance is 9200 Kms; the penumbra is ...
... Umbra – dark part of the shadow; Penumbra – lighter part of the shadow Earth’s maximum umbra at Moon’s distance is 9200 Kms; the penumbra is ...
Astronomical co-ordinates
... 1B11 RA and Dec Right Ascension, RA or a, is measured in hours and a full circle (360O) = 24 hours. There are 60 minutes of time in one hour, and 60 seconds of time in one minute (h,m,s). Declination, Dec or d, is measured in degrees from –90O at the SCP to +90O at the NCP. There are 60 arcminutes ...
... 1B11 RA and Dec Right Ascension, RA or a, is measured in hours and a full circle (360O) = 24 hours. There are 60 minutes of time in one hour, and 60 seconds of time in one minute (h,m,s). Declination, Dec or d, is measured in degrees from –90O at the SCP to +90O at the NCP. There are 60 arcminutes ...
Time and Diurnal Motion
... • Eudoxus (360 BC) makes early map of constellations • Hipparchus (130 BC) made a star catalog of 850 stars with some sort of coordinates • Claudius Ptolemy (150 A.D.?): The first really accurate map, 48 constellations, 1025 stars with measured ecliptic longitude & latitude ...
... • Eudoxus (360 BC) makes early map of constellations • Hipparchus (130 BC) made a star catalog of 850 stars with some sort of coordinates • Claudius Ptolemy (150 A.D.?): The first really accurate map, 48 constellations, 1025 stars with measured ecliptic longitude & latitude ...
The Sun - bronzan.net
... moons orbit the Sun in nearly the same plane, the ecliptic plane. From the Earth, this means that each day they will all rise in nearly the same direction - and later set in the opposite direction. Ten years ago, a series of time exposures caught, left to right, the Sun, Venus, the Moon, and Jupiter ...
... moons orbit the Sun in nearly the same plane, the ecliptic plane. From the Earth, this means that each day they will all rise in nearly the same direction - and later set in the opposite direction. Ten years ago, a series of time exposures caught, left to right, the Sun, Venus, the Moon, and Jupiter ...
quiz 2
... 8. The wobble of the Earth’s axis is known as ________c_____ 9. It takes _______b________ years for one complete wobble as described above 10. Your “sun sign” is the constellation in _______d____ with the sun on the day you were born. 11. The sun signs were established in the year _____e_____ AD by ...
... 8. The wobble of the Earth’s axis is known as ________c_____ 9. It takes _______b________ years for one complete wobble as described above 10. Your “sun sign” is the constellation in _______d____ with the sun on the day you were born. 11. The sun signs were established in the year _____e_____ AD by ...
Astronomy Study Guide axis - A real or imaginary line through the
... axis - A real or imaginary line through the center of an object orbit - The curved path a planet, spacecraft, or heavenly body takes around another object in space rotate - To turn around an axis or a center NASA - An acronym for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration; an organization in ...
... axis - A real or imaginary line through the center of an object orbit - The curved path a planet, spacecraft, or heavenly body takes around another object in space rotate - To turn around an axis or a center NASA - An acronym for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration; an organization in ...