Numbers to Keep in Mind
... the light-travel time from an astronomical object may vary by up to ± 8.3 min. This is the heliocentric time correction (sometimes called the Rømer delay). (Note: there is also a heliocentric velocity correction, due to the Earth’s motion about the Sun.) Time is often quoted using HJD, i.e., Helioce ...
... the light-travel time from an astronomical object may vary by up to ± 8.3 min. This is the heliocentric time correction (sometimes called the Rømer delay). (Note: there is also a heliocentric velocity correction, due to the Earth’s motion about the Sun.) Time is often quoted using HJD, i.e., Helioce ...
El sistema solar en una cancha de futbol
... • The universe and its dimensions. To sum up, Sergio will show us the distance between the planets in our Solar System and we will therefore understand that we need a very wide area of the city in order to make all the planets fit in. With a 1-meter diameter sun, our dear planet Earth will be reduce ...
... • The universe and its dimensions. To sum up, Sergio will show us the distance between the planets in our Solar System and we will therefore understand that we need a very wide area of the city in order to make all the planets fit in. With a 1-meter diameter sun, our dear planet Earth will be reduce ...
Early history of astronomy
... • Declination – the angular distance north or south of the celestial equator • Right Ascension – the angular distance measured eastward along the celestial equator from the position of the vernal equinox ...
... • Declination – the angular distance north or south of the celestial equator • Right Ascension – the angular distance measured eastward along the celestial equator from the position of the vernal equinox ...
Understand Planetary Motion
... Possibly the best observational astronomer… ever Measured stellar and planetary positions with outstanding precision! ...
... Possibly the best observational astronomer… ever Measured stellar and planetary positions with outstanding precision! ...
15 September: Basic properties of the Sun
... increases rapidly from very low values in interplanetary space to very high values, and it becomes opaque within an interval of altitude of about 200 kilometers (out of 696,000) ...
... increases rapidly from very low values in interplanetary space to very high values, and it becomes opaque within an interval of altitude of about 200 kilometers (out of 696,000) ...
Time
... • What Time Is It? Before 1884, almost every town in the world kept its own local time. There were no national or international conventions which set how time should be measured, or when the day would begin and end, or what length an hour might be. However, with the vast expansion of the railway and ...
... • What Time Is It? Before 1884, almost every town in the world kept its own local time. There were no national or international conventions which set how time should be measured, or when the day would begin and end, or what length an hour might be. However, with the vast expansion of the railway and ...
Spring
... neither points toward nor away from the Sun. (However, the tilt of Earth relative to its plane of orbit, called the ecliptic plane, is always about 23.5 degrees.) Vernal Equinox Questions and Answers Question: Why doesn’t the vernal equinox (equal night) on March 20 have the same number of hours for ...
... neither points toward nor away from the Sun. (However, the tilt of Earth relative to its plane of orbit, called the ecliptic plane, is always about 23.5 degrees.) Vernal Equinox Questions and Answers Question: Why doesn’t the vernal equinox (equal night) on March 20 have the same number of hours for ...
Homework Assignment 1 — Solutions
... (a). The first day of summer is the summer solstice, when the Sun is at a declination +23◦ 300 above the celestial equator (see Fig. 1.12). For an observer at 42◦ N latitude, the Sun will appear 42◦ − 23◦ 300 = 18◦ 300 from the zenith, corresponding to an altitude of 71◦ 300 above the horizon. (b). ...
... (a). The first day of summer is the summer solstice, when the Sun is at a declination +23◦ 300 above the celestial equator (see Fig. 1.12). For an observer at 42◦ N latitude, the Sun will appear 42◦ − 23◦ 300 = 18◦ 300 from the zenith, corresponding to an altitude of 71◦ 300 above the horizon. (b). ...
Saint Mary`s College ASTRONOMY EXAM -
... 27. List the solar system's members according to their distance from the sun? Keywords: Segregation & Chemical Differentiation. 28. Arrange the members of the solar system according to their mass? 29. Which planets have the greatest and least mean density, size , mass, and distance from the Sun, res ...
... 27. List the solar system's members according to their distance from the sun? Keywords: Segregation & Chemical Differentiation. 28. Arrange the members of the solar system according to their mass? 29. Which planets have the greatest and least mean density, size , mass, and distance from the Sun, res ...
Charting The Universe - University of Windsor
... • Our calendars are based on Tropical years. • If it were on the Sidereal year, then summer would be in February 13,000 years from now! • Therefore, we keep summer fixed…and let the constellations move! In 13,000 years Orion will be a summer constellation. • Gregorian Calendar (1582AD) maintains se ...
... • Our calendars are based on Tropical years. • If it were on the Sidereal year, then summer would be in February 13,000 years from now! • Therefore, we keep summer fixed…and let the constellations move! In 13,000 years Orion will be a summer constellation. • Gregorian Calendar (1582AD) maintains se ...
February 6
... • Right ascension – east-west position (hours, minutes, seconds) • Declination – north-south position (degrees) ...
... • Right ascension – east-west position (hours, minutes, seconds) • Declination – north-south position (degrees) ...
Unit E - Topic 1.0 Notes
... astronomers to make accurate charts of star positions • Cross-staff: invented by Levi ben Gurson to measure the angle between the Moon and any given star • Early Telescope (late 16th century): invented in the late 16th century and it allowed astronomers such as Galileo to discover details about Eart ...
... astronomers to make accurate charts of star positions • Cross-staff: invented by Levi ben Gurson to measure the angle between the Moon and any given star • Early Telescope (late 16th century): invented in the late 16th century and it allowed astronomers such as Galileo to discover details about Eart ...
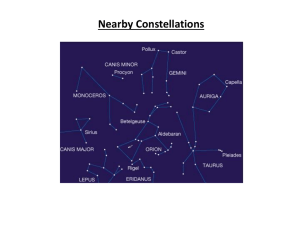
Nearby Constellations
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
Charting The Universe - University of Windsor
... • Our calendars are based on Tropical years. • If it were on the Sidereal year, then summer would be in February 13,000 years from now! • Therefore, we keep summer fixed…and let the constellations move! In 13,000 years Orion will be a summer constellation. • Gregorian Calendar (1582AD) maintains se ...
... • Our calendars are based on Tropical years. • If it were on the Sidereal year, then summer would be in February 13,000 years from now! • Therefore, we keep summer fixed…and let the constellations move! In 13,000 years Orion will be a summer constellation. • Gregorian Calendar (1582AD) maintains se ...
OH Science Standards for STARS
... o The sun appears to be the largest star in the sky because it is the closest star to Earth. Some stars are larger than the sun and some stars are smaller than the sun. Most of the cycles and patterns of motion between the Earth and sun are predictable. o Earth’s revolution around the sun takes ap ...
... o The sun appears to be the largest star in the sky because it is the closest star to Earth. Some stars are larger than the sun and some stars are smaller than the sun. Most of the cycles and patterns of motion between the Earth and sun are predictable. o Earth’s revolution around the sun takes ap ...
The Sun
... distance of the Earth's orbit (150,000,000 km), the rate at which solar energy is received, by a surface oriented perpendicular to the Sun's direction, is called the solar constant. The solar constant is measured to be 1370 W m-2. [The most accurate measurements are made by satellites circling the E ...
... distance of the Earth's orbit (150,000,000 km), the rate at which solar energy is received, by a surface oriented perpendicular to the Sun's direction, is called the solar constant. The solar constant is measured to be 1370 W m-2. [The most accurate measurements are made by satellites circling the E ...
Seasonal and Daily Temperatures and the Earth’s General
... • When the Sun reaches its farthest north or south point and begins to move back the other way, it can be thought that the earth “stands still” as far as the north or south axial movement is concerned – Latin: sol = sun; stice = standing ...
... • When the Sun reaches its farthest north or south point and begins to move back the other way, it can be thought that the earth “stands still” as far as the north or south axial movement is concerned – Latin: sol = sun; stice = standing ...
ASTR 100: Homework 1 Solutions McGaugh, Fall 2008
... most pennants? Which has won the most world series? These are all questions that can be answered clearly and quantitatively. The trick is agreeing which statistic qualifies a team as the ‘best of all time.’ It often happens that even when we agree on the facts, we may not agree on what they mean. Do ...
... most pennants? Which has won the most world series? These are all questions that can be answered clearly and quantitatively. The trick is agreeing which statistic qualifies a team as the ‘best of all time.’ It often happens that even when we agree on the facts, we may not agree on what they mean. Do ...
Sun: The Nearest Star
... Corona is the region that prominences appears. Prominences are immense clouds of glowing gas that erupt from the upper chromosphere. The Sun will be for 4.6 billion years and has enough fuel to go on for another five billion years or so. At the end of its life, the Sun will start to fuse helium into ...
... Corona is the region that prominences appears. Prominences are immense clouds of glowing gas that erupt from the upper chromosphere. The Sun will be for 4.6 billion years and has enough fuel to go on for another five billion years or so. At the end of its life, the Sun will start to fuse helium into ...
1 DS 3.10 Grade 9 Review
... space risks of space travel benefits of space travel technology in space types of galaxies neutron star big bang theory galaxy ...
... space risks of space travel benefits of space travel technology in space types of galaxies neutron star big bang theory galaxy ...
a planet rotates on its own axis and revolves around
... the force of gravity depends on the product of the masses of the objects divided by the square of the distance between them. Gravity is always working in the universe and it depends on the objects size, mass and location ...
... the force of gravity depends on the product of the masses of the objects divided by the square of the distance between them. Gravity is always working in the universe and it depends on the objects size, mass and location ...
Planetary Motions - LathamWHS13-14
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007299181x/student_view0/chapter2/sea sons_interactive.html How long does one rotation take? How would we measure this……..? ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007299181x/student_view0/chapter2/sea sons_interactive.html How long does one rotation take? How would we measure this……..? ...
Seasons On Earth Notes
... • The ecliptic is tilted at about 23.5 degrees. This tilt varies by 1 degree every 50,000 years. • The change in the angle at which solar rays reach the Earth at any time gives us the ...
... • The ecliptic is tilted at about 23.5 degrees. This tilt varies by 1 degree every 50,000 years. • The change in the angle at which solar rays reach the Earth at any time gives us the ...