Fundamental properties of the Sun - University of Iowa Astronomy
... The Lesson for Other Stars • Do they also have sunspots, sunspot cycles, etc? • How does all this (magnetic fields, solar wind, rotation) relate to the age of a star? ...
... The Lesson for Other Stars • Do they also have sunspots, sunspot cycles, etc? • How does all this (magnetic fields, solar wind, rotation) relate to the age of a star? ...
chapterS1time - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... • How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods? – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) i ...
... • How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods? – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) i ...
Chapter S1 How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary
... •! Sidereal month: Moon orbits Earth in 27.3 days. •! Earth & Moon travel 30° around Sun during that time (30°/360° = 1/12) •! Synodic month: A cycle of lunar phases; therefore takes about 29.5 days, 1/12 longer than a sidereal month ...
... •! Sidereal month: Moon orbits Earth in 27.3 days. •! Earth & Moon travel 30° around Sun during that time (30°/360° = 1/12) •! Synodic month: A cycle of lunar phases; therefore takes about 29.5 days, 1/12 longer than a sidereal month ...
Section 26.1 - CPO Science
... While the Ptolemaic model could predict the positions of the planets, Nicholas Copernicus found that its predictions became less and less accurate over the centuries. In Copernicus’ model, the Sun was at the center of the solar system and the planets orbited in circles around the Sun. ...
... While the Ptolemaic model could predict the positions of the planets, Nicholas Copernicus found that its predictions became less and less accurate over the centuries. In Copernicus’ model, the Sun was at the center of the solar system and the planets orbited in circles around the Sun. ...
Day-11
... the idea of “uniform circular motion.” • Objects moved in perfect circles at uniform speeds. ...
... the idea of “uniform circular motion.” • Objects moved in perfect circles at uniform speeds. ...
S1_LectureOutlines
... because Earth moves about 1° in orbit each day 1/365.2422 of a day approximately 3 minutes 56 seconds ...
... because Earth moves about 1° in orbit each day 1/365.2422 of a day approximately 3 minutes 56 seconds ...
ppt - The Eclecticon of Dr French
... The Great Pyramid of Giza has many mysterious design features (specifically the angle of shafts connecting the Pharaoh burial chamber to the outside world). It is thought that the Egyptians believed the soul of the Pharaoh would be transported via these shafts to particular star constellations, whi ...
... The Great Pyramid of Giza has many mysterious design features (specifically the angle of shafts connecting the Pharaoh burial chamber to the outside world). It is thought that the Egyptians believed the soul of the Pharaoh would be transported via these shafts to particular star constellations, whi ...
Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015
... Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015 - 2016 Dr David Clements Course Aims: To become familiar with the structure and evolution of the Sun and other stars. To become familiar with the key physical principles that determine the current state of the planets in our own Solar System, and that allow us t ...
... Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015 - 2016 Dr David Clements Course Aims: To become familiar with the structure and evolution of the Sun and other stars. To become familiar with the key physical principles that determine the current state of the planets in our own Solar System, and that allow us t ...
Astronomical Ideas – Math Review practice problems 1. The radius
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
Astronomy Miscellaneous Items Test
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
lung volumes and capacities
... When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The path an object follows when it revolves around another object. ORBIT PHOTOVOLTAIC Solar cells ar ...
... When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The path an object follows when it revolves around another object. ORBIT PHOTOVOLTAIC Solar cells ar ...
Problems 4 File
... of its orbit around the sun? (b) In 1682 a bright comet appeared. Edmond Halley computed its orbit and found it very similar to those of comets seen in 1607 and 1531. He predicted the comet would return in 1758. By then Halley was dead, but Halley’s comet did return on Christmas night 1758. What is ...
... of its orbit around the sun? (b) In 1682 a bright comet appeared. Edmond Halley computed its orbit and found it very similar to those of comets seen in 1607 and 1531. He predicted the comet would return in 1758. By then Halley was dead, but Halley’s comet did return on Christmas night 1758. What is ...
Bumi, Bulan Dan Matahari Tip 1 The Solar System
... same time, both the Earth and the Moon move around the Sun. ...
... same time, both the Earth and the Moon move around the Sun. ...
Earth Science 2nd 9 wk review
... leucite (KAISi206) may be grouped together because they all contain silicon. ...
... leucite (KAISi206) may be grouped together because they all contain silicon. ...
1 Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
Astronomy 1001
... • Tropical Year – 20 minutes shorter than sidereal year – Thus, your year would be off by a day every 72 years ...
... • Tropical Year – 20 minutes shorter than sidereal year – Thus, your year would be off by a day every 72 years ...
2.1d-f-g Planets in the zodiac, inclined to the ecliptic
... The period which brings the Earth back to the same angular position with respect to the Sun is called the tropical year and is 365.242 mean solar days. Formally this period is defined as the interval of time from one SPRING/VERNAL EQUINOX to the next. The sidereal period (the period with respect to ...
... The period which brings the Earth back to the same angular position with respect to the Sun is called the tropical year and is 365.242 mean solar days. Formally this period is defined as the interval of time from one SPRING/VERNAL EQUINOX to the next. The sidereal period (the period with respect to ...
SOLAR SYSTEM DEFINITIONS
... REVOLUTION: the path the Earth takes around the sun. The earth revolves around the sun once every 365 days; this combined with the earth’s tilt causes seasons! ORBIT: the path the Earth takes around the sun. The earth orbits the sun once every 365 days in an elliptical shape! ELLIPTICAL: the shape o ...
... REVOLUTION: the path the Earth takes around the sun. The earth revolves around the sun once every 365 days; this combined with the earth’s tilt causes seasons! ORBIT: the path the Earth takes around the sun. The earth orbits the sun once every 365 days in an elliptical shape! ELLIPTICAL: the shape o ...
How do the planets stay in orbit around the sun?
... The solar system was formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust which spun around a newly forming star, our sun, at its center. The planets all formed from this spinning diskshaped cloud, and continued this rotating course around the sun after they were formed. The gravity of the sun keeps the pla ...
... The solar system was formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust which spun around a newly forming star, our sun, at its center. The planets all formed from this spinning diskshaped cloud, and continued this rotating course around the sun after they were formed. The gravity of the sun keeps the pla ...
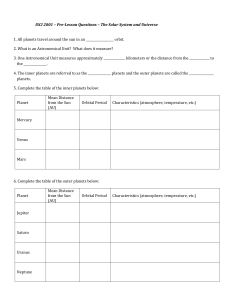
The Solar System and the Universe
... ISCI 2001 – Pre-Lesson Questions – The Solar System and Universe 1. All planets travel around the sun in an __________________ orbit. 2. What is an Astronomical Unit? What does it measure? 3. One Astronomical Unit measures approximately ______________ kilometers or the distance from the ____________ ...
... ISCI 2001 – Pre-Lesson Questions – The Solar System and Universe 1. All planets travel around the sun in an __________________ orbit. 2. What is an Astronomical Unit? What does it measure? 3. One Astronomical Unit measures approximately ______________ kilometers or the distance from the ____________ ...
16-6 How do astronomers measure distance?
... ____________________ 1. A light-year is equal to the distance that light travels in one day. ____________________ 2. One light-year is equal to a distance of about 10 trillion kilometers. ____________________ 3. An astronomical unit is equal to the distance between Earth and the Moon. ______________ ...
... ____________________ 1. A light-year is equal to the distance that light travels in one day. ____________________ 2. One light-year is equal to a distance of about 10 trillion kilometers. ____________________ 3. An astronomical unit is equal to the distance between Earth and the Moon. ______________ ...
Seasons powerpoint File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... Point 2 shows the revolution of the Earth around the sun. It takes 365 days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the sun. As a result it brings seasons to us. Point 3 shows the rotation of the earth on its axis. It take 24 hours for the Earth to complete one revolution and as a result it ...
... Point 2 shows the revolution of the Earth around the sun. It takes 365 days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the sun. As a result it brings seasons to us. Point 3 shows the rotation of the earth on its axis. It take 24 hours for the Earth to complete one revolution and as a result it ...
proposed another geocentric _ _ _ _ _.
... WORDBANK: rotated, Second, axis, mountains, astronomers, heliocentric, orbited, greater, theory, Sun, centre, orbit, position, motion, distant, planets, elliptical, speed , lunar, longer Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ ...
... WORDBANK: rotated, Second, axis, mountains, astronomers, heliocentric, orbited, greater, theory, Sun, centre, orbit, position, motion, distant, planets, elliptical, speed , lunar, longer Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ ...






![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-300x300.png)