Properties of Stars
... • Red Giants – a large, cool star of high luminosity • Supergiants – a very large, very bright red giant star • Cepheid Variables – A star whose brightness varies periodically because it expands and contracts, a type of pulsating star • Nova – A star that explosively increases its brightness ...
... • Red Giants – a large, cool star of high luminosity • Supergiants – a very large, very bright red giant star • Cepheid Variables – A star whose brightness varies periodically because it expands and contracts, a type of pulsating star • Nova – A star that explosively increases its brightness ...
SNC1PL The Life Cycle of Stars
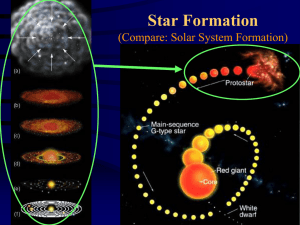
... The Solar system formed ~5 billion years ago from a massive cloud of dust and gas (nebula) that began to contract The contraction caused a protostar to ...
... The Solar system formed ~5 billion years ago from a massive cloud of dust and gas (nebula) that began to contract The contraction caused a protostar to ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... ____ 19. According to Figure 25-1, the sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 c. 5 b. 0 d. 5000 ____ 20. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ____. a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. nebula ____ 21. A star is said to be born when ____. a. a prot ...
... ____ 19. According to Figure 25-1, the sun has an absolute magnitude of ____. a. –5 c. 5 b. 0 d. 5000 ____ 20. Another name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star is ____. a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. nebula ____ 21. A star is said to be born when ____. a. a prot ...
Milky Way
... variable stars” in some of them. • Cepheids are evolved supergiant stars that brighten and fade periodically as their size oscillates. Remember, these are standard candles. • If Cepheids appear faint, then they must be way outside the Milky Way Galaxy. • From the distance and angular size of spiral ...
... variable stars” in some of them. • Cepheids are evolved supergiant stars that brighten and fade periodically as their size oscillates. Remember, these are standard candles. • If Cepheids appear faint, then they must be way outside the Milky Way Galaxy. • From the distance and angular size of spiral ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
Codes of Life
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Star Formation & Lifecycle • Contraction of a cold interstellar cloud ...
... Star Formation & Lifecycle • Contraction of a cold interstellar cloud ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... How Stars Begin… • Inside vast clouds of gas and dust floating in space, gravity causes the denser areas to pull together, or coalesce. • These clouds are ...
... How Stars Begin… • Inside vast clouds of gas and dust floating in space, gravity causes the denser areas to pull together, or coalesce. • These clouds are ...
Cetus and Lepus
... The most notable star in Cetus is Mira ("the Wonderful"), designated Omicron Ceti, the first variable star to be discovered and the prototype of its class. Over a period of 332 days it reaches a maximum apparent magnitude of 3 - visible to the naked eye - and dips to a minimum magnitude of 10, invis ...
... The most notable star in Cetus is Mira ("the Wonderful"), designated Omicron Ceti, the first variable star to be discovered and the prototype of its class. Over a period of 332 days it reaches a maximum apparent magnitude of 3 - visible to the naked eye - and dips to a minimum magnitude of 10, invis ...
Life Cycle of a Star worksheet
... Learning Goal: I can describe the life cycle of various types of stars. All stars start as a ______________. A ______________ is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The contracting cloud is then called a ___________. A protostar is the earli ...
... Learning Goal: I can describe the life cycle of various types of stars. All stars start as a ______________. A ______________ is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The contracting cloud is then called a ___________. A protostar is the earli ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... years away. Their orbital period is over 500 years. In 2009, a giant planet was found orbiting one of these stars. ...
... years away. Their orbital period is over 500 years. In 2009, a giant planet was found orbiting one of these stars. ...
Globular Cluster in Canes Venatici
... stars within each cubic light year) than in the Sun’s neighborhood. If the earth orbitted a star located in a globular cluster, the next nearest star would be light months away rather than light years. ...
... stars within each cubic light year) than in the Sun’s neighborhood. If the earth orbitted a star located in a globular cluster, the next nearest star would be light months away rather than light years. ...
How do stars form?
... Oldest Earth rock: 3.98 Ga Acasta Gneiss Oldest Earth minerals: 4.4 Ga Chemistry of the Sun and rate of fusion Age of oldest Moon Rocks: 3.3 - 4.2 Ga Age of Meteorites: 4.5 Ga ...
... Oldest Earth rock: 3.98 Ga Acasta Gneiss Oldest Earth minerals: 4.4 Ga Chemistry of the Sun and rate of fusion Age of oldest Moon Rocks: 3.3 - 4.2 Ga Age of Meteorites: 4.5 Ga ...
Ch.10 Stellar old age
... Core of helium is supported by electron degeneracy pressure When He ‘ignites’, whole core is ready to fuse He into C ...
... Core of helium is supported by electron degeneracy pressure When He ‘ignites’, whole core is ready to fuse He into C ...
characteristics of stars
... Our galaxy is called the Milky Way because when we view it, it looks like __________ __________. There are at least _____ billion stars in our galaxy. The Milky Way is _________ - shaped. The sun is located near the ______ of the disk. In the central bulge, the stars are so numerous that they appear ...
... Our galaxy is called the Milky Way because when we view it, it looks like __________ __________. There are at least _____ billion stars in our galaxy. The Milky Way is _________ - shaped. The sun is located near the ______ of the disk. In the central bulge, the stars are so numerous that they appear ...
Stars_and_Galaxies
... Brightness , continued • Two types of brightness: absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude • Apparent magnitude is the brightness we see here on Earth • Absolute magnitude is the actual light the star gives off. The more negative the number, the brighter the star is! • To figure out how far it is ...
... Brightness , continued • Two types of brightness: absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude • Apparent magnitude is the brightness we see here on Earth • Absolute magnitude is the actual light the star gives off. The more negative the number, the brighter the star is! • To figure out how far it is ...
Almach or Alberio
... daytime star. The dimmer blue star (known as Almach B,C, and D) is also actually a triple system of three white dwarf stars . The white dwarf stars together orbit the gold primary star at a distance of about 600 AU (600 times the Sun-Earth distance). Although the golden primary is 9.6 arc seconds on ...
... daytime star. The dimmer blue star (known as Almach B,C, and D) is also actually a triple system of three white dwarf stars . The white dwarf stars together orbit the gold primary star at a distance of about 600 AU (600 times the Sun-Earth distance). Although the golden primary is 9.6 arc seconds on ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting yellow and blue pair. 35 Com ds. (5.1,7,2) separation 1.2”. Yellow and purple (deep blue). Coma is a fine hunting ground for galaxies plus a very fine globular cluster. Sta ...
... 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting yellow and blue pair. 35 Com ds. (5.1,7,2) separation 1.2”. Yellow and purple (deep blue). Coma is a fine hunting ground for galaxies plus a very fine globular cluster. Sta ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
Classification and structure of galaxies
... How do we know what our Galaxy looks like? We can see: • Stars and star clusters – microwaves generated by water from H II regions (called the MASER technique) traces the Milky Way’s spiral arms • Nebulae – infrared light (detected by the Spitzer Space Telescope) shows the outline of the heat genera ...
... How do we know what our Galaxy looks like? We can see: • Stars and star clusters – microwaves generated by water from H II regions (called the MASER technique) traces the Milky Way’s spiral arms • Nebulae – infrared light (detected by the Spitzer Space Telescope) shows the outline of the heat genera ...
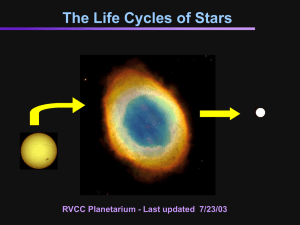
The Life of a Star
... reactions; the carbon in your DNA and the iron in your blood were all created in a star that is now dead. The outer layers will expand into thin shells of gas which move away form the sun out into interstellar space. The sun will now have become a planetary nebula. ...
... reactions; the carbon in your DNA and the iron in your blood were all created in a star that is now dead. The outer layers will expand into thin shells of gas which move away form the sun out into interstellar space. The sun will now have become a planetary nebula. ...
FRAC TRIVIA I QUIZ - Flint River Astronomy Club
... 14. ( 1 pt.) True or False: If you were standing on the floor at the center of the lunar crater Clavius, you could not see its 16,100-ft. walls in any direction. 15. (1 pt.) What is the largest of the 20 brightest stars in actual size? 16. (1 pt.) Which constellation contains the most naked-eye star ...
... 14. ( 1 pt.) True or False: If you were standing on the floor at the center of the lunar crater Clavius, you could not see its 16,100-ft. walls in any direction. 15. (1 pt.) What is the largest of the 20 brightest stars in actual size? 16. (1 pt.) Which constellation contains the most naked-eye star ...
Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... Capella is 42 ly away and is 130 times brighter than our sun. • Just beneath Capella is Epsilon Aurigau. It is one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,000 ly away. • Epsilon Aurigau has a companion star, which eclipses it every 27 years, making ...
... Capella is 42 ly away and is 130 times brighter than our sun. • Just beneath Capella is Epsilon Aurigau. It is one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,000 ly away. • Epsilon Aurigau has a companion star, which eclipses it every 27 years, making ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.