stars - allenscience
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Chara and Cor Caroli represent the "southern dog," the "northern dog" is represented by a small group of stars to the Northeast of Cor Caroli. Chara was originally the name for the southern dog itself, with the northern called "Asterion". But with the brighter of the stars that make the southern dog ...
... Chara and Cor Caroli represent the "southern dog," the "northern dog" is represented by a small group of stars to the Northeast of Cor Caroli. Chara was originally the name for the southern dog itself, with the northern called "Asterion". But with the brighter of the stars that make the southern dog ...
The Life of a Star
... after the main-sequence stage. • This is a star that expands and cools because it has used up all of its hydrogen. • The center of the star shrinks, but the atmosphere gets very large. • The star may become a supergiant (100 times bigger than the sun). ...
... after the main-sequence stage. • This is a star that expands and cools because it has used up all of its hydrogen. • The center of the star shrinks, but the atmosphere gets very large. • The star may become a supergiant (100 times bigger than the sun). ...
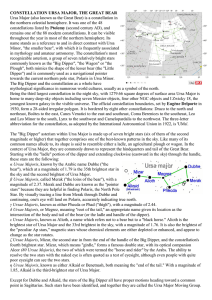
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation boundaries, set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, form a 28-sided irregular polygon. It is bordered by eight other constellations: Draco to the north and northeast, Boötes to the east, Canes Venatici to the east and southeast, Coma ...
... youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation boundaries, set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, form a 28-sided irregular polygon. It is bordered by eight other constellations: Draco to the north and northeast, Boötes to the east, Canes Venatici to the east and southeast, Coma ...
Astronomy practice questions for 3-6 test
... 4. Is the Andromeda galaxy red or blue shifted? __________________________________________________________ 5. According to Hubble’s law, which galaxy or planet is moving fastest away from the nearby star? __________________________________________________________ 6. Which galaxy or planet is moving ...
... 4. Is the Andromeda galaxy red or blue shifted? __________________________________________________________ 5. According to Hubble’s law, which galaxy or planet is moving fastest away from the nearby star? __________________________________________________________ 6. Which galaxy or planet is moving ...
White Dwarfs - Astronomy - The University of Texas at Austin
... White dwarfs are the most common stellar “corpse.” Come from low mass stars → plentiful. Examples of planetary nebulae surrounding new-born white dwarfs ...
... White dwarfs are the most common stellar “corpse.” Come from low mass stars → plentiful. Examples of planetary nebulae surrounding new-born white dwarfs ...
Big bang and Stars
... Stars start from clouds Clouds provide the gas and dust from which stars form. But not this kind of dust Rather: Irregular Grains Of Carbon or Silicon ...
... Stars start from clouds Clouds provide the gas and dust from which stars form. But not this kind of dust Rather: Irregular Grains Of Carbon or Silicon ...
answers - Salem State University
... 13. A white dwarf will not have exhausted its potential carbon fuel, but there is not sufficient gravity to compress its carbon nuclei and electrons further. So there will be emission but not sufficient to be a very luminous star given its size (slight bigger than our Sun). 14. A nova is fusion on t ...
... 13. A white dwarf will not have exhausted its potential carbon fuel, but there is not sufficient gravity to compress its carbon nuclei and electrons further. So there will be emission but not sufficient to be a very luminous star given its size (slight bigger than our Sun). 14. A nova is fusion on t ...
1.1 Stars in the Broader Context of Modern Astro
... The study of stars continues to be at the very core of modern astrophysics more than 5000 years since its inception. Astronomy may well be the oldest science, and when early bronze age man looked up at the night sky he or she saw mostly stars. The signs of the zodiac—the first attempt at classifying ...
... The study of stars continues to be at the very core of modern astrophysics more than 5000 years since its inception. Astronomy may well be the oldest science, and when early bronze age man looked up at the night sky he or she saw mostly stars. The signs of the zodiac—the first attempt at classifying ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Galaxies and Stars
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
What have we learned?
... • How were neutron stars discovered? – Beams of radiation from a rotating neutron star sweep through space like lighthouse beams, making them appear to pulse. – Observations of these pulses were the first evidence for neutron stars. ...
... • How were neutron stars discovered? – Beams of radiation from a rotating neutron star sweep through space like lighthouse beams, making them appear to pulse. – Observations of these pulses were the first evidence for neutron stars. ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... star formation history and hence the effect of the spread in the lower panel of this figure can be used to improve the mass estimate. Importantly, such a technique for determine accurate stellar masses can then be applied to all galaxies, regular or peculiar, irrespective of their dynamical state an ...
... star formation history and hence the effect of the spread in the lower panel of this figure can be used to improve the mass estimate. Importantly, such a technique for determine accurate stellar masses can then be applied to all galaxies, regular or peculiar, irrespective of their dynamical state an ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
Stars and the Sun
... dwarf) • Eventually fuses up to carbon, ends as small cold ball of carbon (black dwarf) ...
... dwarf) • Eventually fuses up to carbon, ends as small cold ball of carbon (black dwarf) ...
The Milky Way as a Spiral galaxy
... comparing star counts in the region on the right to the region on the left. ...
... comparing star counts in the region on the right to the region on the left. ...
Earth Science 11 Chapter 28 Answers: 28.1 1. All are forms of
... blasts the layers into space in a brilliant burst of light called a supernova. Left behind is a black hole (if the original star was at least 15 times more massive than the sun), or a neutron star. 4. It is unlikely that a star with 10 times the sun’s mass will live long enough to allow organisms on ...
... blasts the layers into space in a brilliant burst of light called a supernova. Left behind is a black hole (if the original star was at least 15 times more massive than the sun), or a neutron star. 4. It is unlikely that a star with 10 times the sun’s mass will live long enough to allow organisms on ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
deep space - altaastronomy
... • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained within its Schwa ...
... • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained within its Schwa ...
Slide 1
... • Consists of over 200 billion stars • 16,000 light years thick (central bulge) • 100,000 light years across (long end to end) • The arm that our solar system is in (Orion Arm) is about 30,000 light years long ...
... • Consists of over 200 billion stars • 16,000 light years thick (central bulge) • 100,000 light years across (long end to end) • The arm that our solar system is in (Orion Arm) is about 30,000 light years long ...
the size and structure of the universe
... much mass concentrated in it that there is no way for a nearby object to escape its gravitational pull. Black holes are the evolutionary endpoints of stars at least 10 to 15 times as massive as the Sun. ...
... much mass concentrated in it that there is no way for a nearby object to escape its gravitational pull. Black holes are the evolutionary endpoints of stars at least 10 to 15 times as massive as the Sun. ...
The Brightness of Stars
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye – This fact obscures a ...
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye – This fact obscures a ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 31. Create a flow-map that properly sequences the formation of the solar system? solar nebula forms, nuclear fusion begins in the sun, planetesimals form, planets form 32. A group of stars that form patterns in the sky is called constellation. 33. To express the distance between the Milky Way galaxy ...
... 31. Create a flow-map that properly sequences the formation of the solar system? solar nebula forms, nuclear fusion begins in the sun, planetesimals form, planets form 32. A group of stars that form patterns in the sky is called constellation. 33. To express the distance between the Milky Way galaxy ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... 12. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from the Earth, which one is brighter in the sky? The blue star produces more energy per unit surface area than the red star based on Stephan’s Law. If the two stars have the same radius, they have the same su ...
... 12. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from the Earth, which one is brighter in the sky? The blue star produces more energy per unit surface area than the red star based on Stephan’s Law. If the two stars have the same radius, they have the same su ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.