Nebula – • The most abundant element in the universe is hydrogen
... A star is a sphere of super-hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium that is held together by its own gravity. No two stars contain exactly the same elements in the same proportions. Stars are born by contraction of gasses inside a nebula. ...
... A star is a sphere of super-hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium that is held together by its own gravity. No two stars contain exactly the same elements in the same proportions. Stars are born by contraction of gasses inside a nebula. ...
Unit 1
... As starlight passes through a dust cloud, the dust particles scatter blue photons, allowing red photons to pass through easily The star appears red (reddening) – it looks older and dimmer (extinction) than it really is. ...
... As starlight passes through a dust cloud, the dust particles scatter blue photons, allowing red photons to pass through easily The star appears red (reddening) – it looks older and dimmer (extinction) than it really is. ...
Life and Death Of A Star - EarthSpaceScience
... • Leaving a halo of gas and dust – planetary nebula (where new stars form) • And a dense hot core – white dwarf ...
... • Leaving a halo of gas and dust – planetary nebula (where new stars form) • And a dense hot core – white dwarf ...
Starry Starry Night Vocabulary
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
Lecture 16 - Yet More Evolution of Stars
... • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off ...
... • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
Star Life Cycle Worksheet Directions: Write in the correct stages of a
... core. The outer layer of this red star expands as the core contracts. 3. Nebula can form either an _______ star that is about the size of our Sun or a _________ star which can be over three times as big as our Sun! These stars stay in this period for most of their lives and they convert hydrogen to ...
... core. The outer layer of this red star expands as the core contracts. 3. Nebula can form either an _______ star that is about the size of our Sun or a _________ star which can be over three times as big as our Sun! These stars stay in this period for most of their lives and they convert hydrogen to ...
Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System
... Total time is 5 hours. Total distance is 380 miles. If you were observed traveling at 60 mph and had covered 380 miles, the assumption would be made that you had traveled for 6 hours and 20 minutes (380miles/60mph) rather than 5 hours. ...
... Total time is 5 hours. Total distance is 380 miles. If you were observed traveling at 60 mph and had covered 380 miles, the assumption would be made that you had traveled for 6 hours and 20 minutes (380miles/60mph) rather than 5 hours. ...
The Sun and Beyond - Valhalla High School
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
ppp
... • Java3D is a viable tool for creating scientific simulations and visualizations • Performance losses from using Java3D are relatively big compared with pure OpenGL • Development time is significantly less, due to higher level abstraction of Java3D’s API ...
... • Java3D is a viable tool for creating scientific simulations and visualizations • Performance losses from using Java3D are relatively big compared with pure OpenGL • Development time is significantly less, due to higher level abstraction of Java3D’s API ...
Unit Two Worksheet – Astronomy
... It is thought that before the Big Bang, all the matter and energy in the universe was in the form of one ___. (A) extremely small volume (C) solar system (B) expanding cloud (D) galaxy ...
... It is thought that before the Big Bang, all the matter and energy in the universe was in the form of one ___. (A) extremely small volume (C) solar system (B) expanding cloud (D) galaxy ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical Societies, this is IT
... years away, on the other side of the galaxy, while our sun is a mere 8.3 light minutes from Earth. The bright star is detectable only with instruments that measure infrared light, which has longer wavelengths that can better penetrate the dust. One big problem with gauging the brightness of stars at ...
... years away, on the other side of the galaxy, while our sun is a mere 8.3 light minutes from Earth. The bright star is detectable only with instruments that measure infrared light, which has longer wavelengths that can better penetrate the dust. One big problem with gauging the brightness of stars at ...
Chapter 25 - OG
... of light start gives OFF. Apparent Magnitude: measure of the amount of light RECEIVED on Earth. A dim star can appear bright if closer to Earth. ...
... of light start gives OFF. Apparent Magnitude: measure of the amount of light RECEIVED on Earth. A dim star can appear bright if closer to Earth. ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 7 Due: 30 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... we derived earlier.] This mass is much larger than determined from the luminous matter, so there should be a lot of invisible “dark” mass in the NGC 4378. ...
... we derived earlier.] This mass is much larger than determined from the luminous matter, so there should be a lot of invisible “dark” mass in the NGC 4378. ...
ASTR101 Unit 14 Assessment Answer Key 1. It is believed that the
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... _______ 32. A star moving away from Earth has a spectrum that is a. losing its color. b. shifted toward blue. c. shifted toward red. d. unchanged. _______ 33. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? a. elliptical b. irregular c. spherical d. spiral _______ 34. Why are scientists able to use spectra to ...
... _______ 32. A star moving away from Earth has a spectrum that is a. losing its color. b. shifted toward blue. c. shifted toward red. d. unchanged. _______ 33. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? a. elliptical b. irregular c. spherical d. spiral _______ 34. Why are scientists able to use spectra to ...
Where is the Solar System in the Universe?
... • Pretend you have an alien friend coming to visit you from another galaxy. You need to give your friend directions, so what information would you need to give the alien to help ...
... • Pretend you have an alien friend coming to visit you from another galaxy. You need to give your friend directions, so what information would you need to give the alien to help ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Herschel didn’t know about different kinds of stars, he thought they were all the same (like the sun) and therefore all the same luminosity. Using this assumption, he could just simply compute the distance from the brightness. Brightness = Luminosity/(distance)2 This was before we knew how to measur ...
... Herschel didn’t know about different kinds of stars, he thought they were all the same (like the sun) and therefore all the same luminosity. Using this assumption, he could just simply compute the distance from the brightness. Brightness = Luminosity/(distance)2 This was before we knew how to measur ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 6. What two star characteristics does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram compare? 7. What is a star’s spectrum? ...
... 6. What two star characteristics does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram compare? 7. What is a star’s spectrum? ...
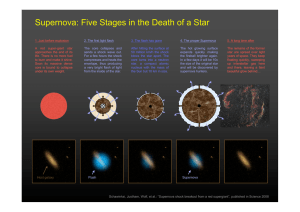
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
... After hitting the surface at 50 million km/h the shock blows the star apart. The core turns into a neutron star, a compact atomic nucleus with the mass of the Sun but 10 km in size. ...
... After hitting the surface at 50 million km/h the shock blows the star apart. The core turns into a neutron star, a compact atomic nucleus with the mass of the Sun but 10 km in size. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
The Milky Way
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.