Absolute Magnitude - School
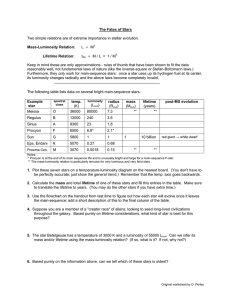
... this formula:M = m + 5 – 5 log d involving powers of 10 only (students are not required to calculate d using this equation, only M and m) ...
... this formula:M = m + 5 – 5 log d involving powers of 10 only (students are not required to calculate d using this equation, only M and m) ...
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
source
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
Galaxies - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... Galaxies contain millions or billions of stars held together by gravity Gravity holds galaxies together in clusters Clusters of galaxies can form even larger groups called superclusters How do we see galaxies? We can see our own Milky Way without the use of a telescope Spyglasses let us see further ...
... Galaxies contain millions or billions of stars held together by gravity Gravity holds galaxies together in clusters Clusters of galaxies can form even larger groups called superclusters How do we see galaxies? We can see our own Milky Way without the use of a telescope Spyglasses let us see further ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... Unlike the gradual disappearance of a planet (small disc) a star vanishes instantly demonstrating that it is a point source of light as viewed from the Earth. For all occultation events start observing 10 to 15 minutes before the predicted time to identify the required star and to allow for slightly ...
... Unlike the gradual disappearance of a planet (small disc) a star vanishes instantly demonstrating that it is a point source of light as viewed from the Earth. For all occultation events start observing 10 to 15 minutes before the predicted time to identify the required star and to allow for slightly ...
properties of stars 2012
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
Stars - Images
... Gravity squeezes the clumps of gas and dust together with so much friction/pressure that it caused them to begin to glow and get hot. Sizes can vary ...
... Gravity squeezes the clumps of gas and dust together with so much friction/pressure that it caused them to begin to glow and get hot. Sizes can vary ...
here - Boise State University
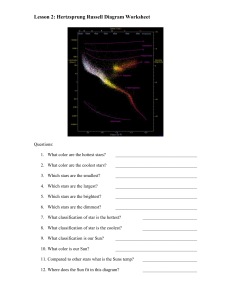
... 9. Explain the relationship between star color and temperature: What color stars are the hottest in space? What color stars are the coolest? 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which size stars are the brightest???? Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List ...
... 9. Explain the relationship between star color and temperature: What color stars are the hottest in space? What color stars are the coolest? 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which size stars are the brightest???? Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List ...
Astronomy – Studying the Stars & Space
... • an object so massive • massive blue stars and dense that even use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may in ...
... • an object so massive • massive blue stars and dense that even use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may in ...
Lifecycle of Stars - Mrs. Plante Science
... contraction results in high pressure and temperature, and a protostar is formed. ...
... contraction results in high pressure and temperature, and a protostar is formed. ...
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
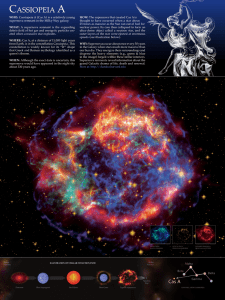
... WHO: Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a relatively young supernova remnant in the Milky Way galaxy. WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constell ...
... WHO: Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a relatively young supernova remnant in the Milky Way galaxy. WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constell ...
Astron 104 Laboratory #11 The Scale of the Milky Way
... 2. The table below lists five bright stars in the night sky. Write the letter of the dot (A through E) on the picture above that best represents the location of each star. You can use letters more than once. Star Distance Letter from the Sun (lt-yr) Sirius ...
... 2. The table below lists five bright stars in the night sky. Write the letter of the dot (A through E) on the picture above that best represents the location of each star. You can use letters more than once. Star Distance Letter from the Sun (lt-yr) Sirius ...
Binary Star Systems Discussion Points 1. What characteristic of a
... 13. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most different from one another? 14. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most similar to one another? 15. Label the primary and secondary minimums on the V809 Cygnii curve. 16. For the V809 Cygnii light curve, ...
... 13. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most different from one another? 14. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most similar to one another? 15. Label the primary and secondary minimums on the V809 Cygnii curve. 16. For the V809 Cygnii light curve, ...
Chapter 24 Vocabulary
... mythological character, or other object and is thus named for it 2. magnitude- in earthquake studies, a measure of the energy released by an earthquake; the Richter scale is used to describe earthquake magnitude 3. parallax- the apparent shift in position of an object when viewed from two different ...
... mythological character, or other object and is thus named for it 2. magnitude- in earthquake studies, a measure of the energy released by an earthquake; the Richter scale is used to describe earthquake magnitude 3. parallax- the apparent shift in position of an object when viewed from two different ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... 2. the total amount of energy a star gives off each second 3. the graph that illustrates the pattern revealed when the surface temperatures of stars are plotted against their luminosity 4. The temperature of a star’s surface is plotted on the horizontal axis; the luminosity is plotted on the vertica ...
... 2. the total amount of energy a star gives off each second 3. the graph that illustrates the pattern revealed when the surface temperatures of stars are plotted against their luminosity 4. The temperature of a star’s surface is plotted on the horizontal axis; the luminosity is plotted on the vertica ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) The basics: GRAVITY vs. PRESSURE
... we’ll return to this). Make sure you understand the H-R diagrams in Figs. 19.1819.19. Can you explain what determines the lifetime of a star clusters? Why do open clusters survive (on average) for a much shorter time than globular clusters? (This is actually a fairly complicated question, but a good ...
... we’ll return to this). Make sure you understand the H-R diagrams in Figs. 19.1819.19. Can you explain what determines the lifetime of a star clusters? Why do open clusters survive (on average) for a much shorter time than globular clusters? (This is actually a fairly complicated question, but a good ...
Patterns in the Sky - Plano Independent School District
... There are many stars being formed in this cloud. ...
... There are many stars being formed in this cloud. ...
Chapter 15 Stars, Galaxies
... 2. binary stars 3. a, d 4. eclipsing binary 5. They observed the effects of the planet’s gravity on the star. 6. Any small planets would be hard to detect because their gravitational effect on their star would be quite small. 7. open cluster 8. globular cluster ...
... 2. binary stars 3. a, d 4. eclipsing binary 5. They observed the effects of the planet’s gravity on the star. 6. Any small planets would be hard to detect because their gravitational effect on their star would be quite small. 7. open cluster 8. globular cluster ...
Document
... The Horsehead Nebula is a dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
... The Horsehead Nebula is a dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... • Matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. • If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. • What is left be ...
... • Matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. • If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. • What is left be ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
... Types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, and irregular Spiral galaxy – look like pinwheels; they have bright, bulging middles and wispy arms that fan out from the center • ¾ of the galaxies discovered have been spiral galaxies • Milky Way Galaxy is considered a spiral galaxy – Diameter about 100,000 l ...
... Types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, and irregular Spiral galaxy – look like pinwheels; they have bright, bulging middles and wispy arms that fan out from the center • ¾ of the galaxies discovered have been spiral galaxies • Milky Way Galaxy is considered a spiral galaxy – Diameter about 100,000 l ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.