KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
Life cycle of a star
... After a few billion years the center of a star runs out of hydrogen. It then begins to cool and contract. The outer layers of the star fall inwards and heat up the center. A shell surrounding the central core becomes hot enough to fuse protons so the star gains a new source of energy. Because it is ...
... After a few billion years the center of a star runs out of hydrogen. It then begins to cool and contract. The outer layers of the star fall inwards and heat up the center. A shell surrounding the central core becomes hot enough to fuse protons so the star gains a new source of energy. Because it is ...
Distance measurement in astronomy
... with time) called after delta Cephei, the first star of this type to be observed. The variation in brightness of this star was discovered by John Goodricke in 1784. Goodricke lived in York and was a promising young astronomer but tragically died at the age of twenty one. Since his discovery many oth ...
... with time) called after delta Cephei, the first star of this type to be observed. The variation in brightness of this star was discovered by John Goodricke in 1784. Goodricke lived in York and was a promising young astronomer but tragically died at the age of twenty one. Since his discovery many oth ...
Binary Star Systems
... “Half of all stars in the sky are members of binary systems.” Binary star systems consist of two stars that orbit around a point called the center of mass. ...
... “Half of all stars in the sky are members of binary systems.” Binary star systems consist of two stars that orbit around a point called the center of mass. ...
main sequence star
... • Small mass stars will collapse into white dwarfs after being red giants. • The outer gases are lost, which allows us to see the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainte ...
... • Small mass stars will collapse into white dwarfs after being red giants. • The outer gases are lost, which allows us to see the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainte ...
1 Astronomical Measurements and Quantities 2 Astronomical Objects
... Theorem to estimate Cluster Mass [K] and virialtheorem.pdf. Distance from Moving Cluster method. Hints about Secular and statistical parallaxes [BM]. Exercise. Milky Way: Structure of the Galaxy: stars, stellar clusters and interstellar medium. Dynamics: the Oort constants, the rotation velocity cur ...
... Theorem to estimate Cluster Mass [K] and virialtheorem.pdf. Distance from Moving Cluster method. Hints about Secular and statistical parallaxes [BM]. Exercise. Milky Way: Structure of the Galaxy: stars, stellar clusters and interstellar medium. Dynamics: the Oort constants, the rotation velocity cur ...
Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star
... needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
... needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
Sky Notes - February 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... objects. The first of these is VY Canis Majoris which is, in terms of radius, the largest star known. It’s brightness is somewhat variable, but with an average magnitude of +7.8, it is visible in binoculars and small telescopes. In addition, the constellation also contains the recently discovered Ca ...
... objects. The first of these is VY Canis Majoris which is, in terms of radius, the largest star known. It’s brightness is somewhat variable, but with an average magnitude of +7.8, it is visible in binoculars and small telescopes. In addition, the constellation also contains the recently discovered Ca ...
Astronomy
... heavens while the other constellations are allowed to dip below the horizon and bathe in the immortal waters every night. ...
... heavens while the other constellations are allowed to dip below the horizon and bathe in the immortal waters every night. ...
Due: January 15, 2014 Name
... a. the spherical cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion. b. the disk of material in which planets are forming around a star other than the Sun. c. a shell of ejected gases, glowing by fluorescence caused by ultraviolet light from a hot but dying central star. d. a gas cloud surrounding a ...
... a. the spherical cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion. b. the disk of material in which planets are forming around a star other than the Sun. c. a shell of ejected gases, glowing by fluorescence caused by ultraviolet light from a hot but dying central star. d. a gas cloud surrounding a ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... See if you can fill in the blank on these questions (our exam will still be multiple choice) The Milky Way is a _________ type galaxy. The Solar System is located in the ___________ spur. The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ ...
... See if you can fill in the blank on these questions (our exam will still be multiple choice) The Milky Way is a _________ type galaxy. The Solar System is located in the ___________ spur. The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ ...
14_creationism
... enough to burn Hydrogen into Helium. Our Sun will be on main sequence for 10 billion years. Red Giant: Outer part of star expands and cools. Core contracts and starts to burn He into Carbon and other heavier elements. Star dies: either as a planetary nebula (low mass star) or as a supernova (high ma ...
... enough to burn Hydrogen into Helium. Our Sun will be on main sequence for 10 billion years. Red Giant: Outer part of star expands and cools. Core contracts and starts to burn He into Carbon and other heavier elements. Star dies: either as a planetary nebula (low mass star) or as a supernova (high ma ...
Document
... 31. A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused by falling matter from the atmosphere of its binary companion, creates what kind of object? a) Nova., b) Type-I supernova., c) Type-II supernova., d) Contact binary. 32. An iron core cannot support a star because: a) Iron has poor nuclear binding ener ...
... 31. A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused by falling matter from the atmosphere of its binary companion, creates what kind of object? a) Nova., b) Type-I supernova., c) Type-II supernova., d) Contact binary. 32. An iron core cannot support a star because: a) Iron has poor nuclear binding ener ...
Tour of the Galaxy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... The Coma Cluster of Galaxies Almost every object in the above photograph is a galaxy. The Coma Cluster of Galaxies contains thousands of galaxies. Each of these galaxies houses billions of stars - just as our own Milky Way Galaxy does. Light from the Coma Cluster takes hundreds of millions of years ...
... The Coma Cluster of Galaxies Almost every object in the above photograph is a galaxy. The Coma Cluster of Galaxies contains thousands of galaxies. Each of these galaxies houses billions of stars - just as our own Milky Way Galaxy does. Light from the Coma Cluster takes hundreds of millions of years ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... frequently visible to the unaided eye. Situated 5,460 light years from the Sun, M11 is about 13’ in diameter. At low power, the cluster stars take on an apparent fan shape seemingly radiating from a warm yellow star. While this star seems to be a true member of the cluster, in fact it is not. Serpen ...
... frequently visible to the unaided eye. Situated 5,460 light years from the Sun, M11 is about 13’ in diameter. At low power, the cluster stars take on an apparent fan shape seemingly radiating from a warm yellow star. While this star seems to be a true member of the cluster, in fact it is not. Serpen ...
name - New York Science Teacher
... You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on the sheet of paper provided to ...
... You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on the sheet of paper provided to ...
Ch. 25 Properties of Stars
... Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
... Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
The Milky Way galaxy
... Your book gives estimates of the mass of the Galaxy from 1 to 4 X 1011 solar masses. A more recent determination of the mass of the Galaxy is even larger, 1.5-4.0 X 1012 solar masses. This is on the basis of stars of known absolute magnitude called horizontal branch stars. An analysis of 1000 of th ...
... Your book gives estimates of the mass of the Galaxy from 1 to 4 X 1011 solar masses. A more recent determination of the mass of the Galaxy is even larger, 1.5-4.0 X 1012 solar masses. This is on the basis of stars of known absolute magnitude called horizontal branch stars. An analysis of 1000 of th ...
I. Parallax
... has observed stars with magnitudes down to ____ at visible wavelengths and the Keck telescopes have located similarly faint stars in the infrared with _________________. F. There is a _________ difference in brightness for stars that differ by a _____________. For example, a star of magnitude 1 is 1 ...
... has observed stars with magnitudes down to ____ at visible wavelengths and the Keck telescopes have located similarly faint stars in the infrared with _________________. F. There is a _________ difference in brightness for stars that differ by a _____________. For example, a star of magnitude 1 is 1 ...
ppt
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
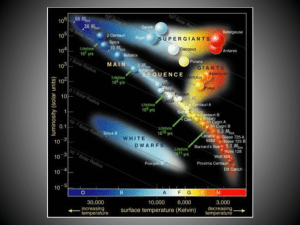
Stars - cmamath
... magnitude and temperature of stars. Can also show the relationship between temperature and luminosity As temperature increases, brightness increases and vice versa. ...
... magnitude and temperature of stars. Can also show the relationship between temperature and luminosity As temperature increases, brightness increases and vice versa. ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.