Evidence of the Big Bang and Structure of the Universe
... Type of galaxy is based on shape: elliptical (football-shaped), irregular, and spiral The Milky Way galaxy is a spiral galaxy, which has over 200 billion stars ...
... Type of galaxy is based on shape: elliptical (football-shaped), irregular, and spiral The Milky Way galaxy is a spiral galaxy, which has over 200 billion stars ...
December 1, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... The vertical position represents the star's luminosity. This could be the luminosity in watts. More commonly it is in units of the Sun's luminosity. In either case, a ``ratio scale'' is used. Absolute magnitude is also commonly used. The horizontal position represent ...
... The vertical position represents the star's luminosity. This could be the luminosity in watts. More commonly it is in units of the Sun's luminosity. In either case, a ``ratio scale'' is used. Absolute magnitude is also commonly used. The horizontal position represent ...
Name ______KEY Date Core ______ Study Guide Galaxies and the
... happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than a second. 300,000 years later, the first elements formed, then stars, planets and galaxies the next ...
... happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than a second. 300,000 years later, the first elements formed, then stars, planets and galaxies the next ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
... but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
solution
... 18.15 What happens inside a protostar to slow and eventually halt its gravitational contraction? The gravitational energy causes Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction, which increases the pressure, density and temperature of the central region of a protostar. Once the temperature exceeds a few million K, H b ...
... 18.15 What happens inside a protostar to slow and eventually halt its gravitational contraction? The gravitational energy causes Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction, which increases the pressure, density and temperature of the central region of a protostar. Once the temperature exceeds a few million K, H b ...
Magnitude Scale
... • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
... • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
Scientists classify stars by
... If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightne ...
... If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightne ...
Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
... Stars do move in space, but because they are so distant, their motion is hard for us to measure Over thousands of years, their movement would be obvious ...
... Stars do move in space, but because they are so distant, their motion is hard for us to measure Over thousands of years, their movement would be obvious ...
Galaxy Classification - Starry Night Education
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
Where do you find yourself now??
... Our galaxy is just one of thousands that lie within 100 million light years. The above map shows how galaxies tend to cluster into groups, the largest nearby cluster is the Virgo cluster a concentration of several hundred galaxies which dominates the galaxy groups around it. Collectively, all of the ...
... Our galaxy is just one of thousands that lie within 100 million light years. The above map shows how galaxies tend to cluster into groups, the largest nearby cluster is the Virgo cluster a concentration of several hundred galaxies which dominates the galaxy groups around it. Collectively, all of the ...
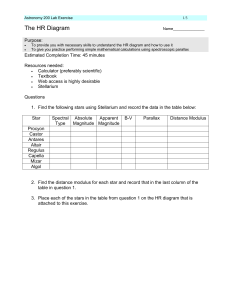
labex7
... Castor Antares Altair Regulus Capella Mizar Algol 5. Find the mass of each of the stars by using the Mass-Luminosity Relation (See online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the dista ...
... Castor Antares Altair Regulus Capella Mizar Algol 5. Find the mass of each of the stars by using the Mass-Luminosity Relation (See online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the dista ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Main Types of Galaxies
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Galaxy and Beyond
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
Report Sheet
... 35. Where will humanity have to live, if we are still around? __________________________________________ 36. What part of a star’s life cycle is the Eight Burst nebula? ____________________________ 37. Where did the carbon and oxygen in your body originally come from? _______________________________ ...
... 35. Where will humanity have to live, if we are still around? __________________________________________ 36. What part of a star’s life cycle is the Eight Burst nebula? ____________________________ 37. Where did the carbon and oxygen in your body originally come from? _______________________________ ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 12 - 9th Edition 1. Consider a star
... Answer: “Why” first. Nearly all stars in a cluster formed about the same time. High mass stars, in the upper part of the Main Sequence, have shorter lifetimes. Lifetime on the Main Sequence increases smoothly as mass decreases. So: the first stars to turn into Red Giants (and pass rapidly through ot ...
... Answer: “Why” first. Nearly all stars in a cluster formed about the same time. High mass stars, in the upper part of the Main Sequence, have shorter lifetimes. Lifetime on the Main Sequence increases smoothly as mass decreases. So: the first stars to turn into Red Giants (and pass rapidly through ot ...
Star Life Cycles
... something called a Supernova. A supernova occurs when a star with many times the mass of the Sun runs out of usable nuclear fuel. The Crab Nebula is an example of the remnants of supernova. ...
... something called a Supernova. A supernova occurs when a star with many times the mass of the Sun runs out of usable nuclear fuel. The Crab Nebula is an example of the remnants of supernova. ...
Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam
... a. Describe how shell fusion in a star causes the star to become giants. b. Identify the “ashes” of H-burning and He-burning 4. Mass loss and Death of Low-Mass Stars a. Match the stage of the Sun’s future evolution with the mechanism of energy production in that stage. b. Identify on an HR diagram t ...
... a. Describe how shell fusion in a star causes the star to become giants. b. Identify the “ashes” of H-burning and He-burning 4. Mass loss and Death of Low-Mass Stars a. Match the stage of the Sun’s future evolution with the mechanism of energy production in that stage. b. Identify on an HR diagram t ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.