Friday, April 25 - Otterbein University
... • Appears as a milky band of light across the sky • A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) • Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes from a combination of observation and comparison to other ...
... • Appears as a milky band of light across the sky • A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) • Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes from a combination of observation and comparison to other ...
Recap: High Mass Stars
... – As nebula contracts, a small star is formed • Called a protostar – Eventually, the protostar will begin nuclear FUSION • Hydrogen protons attract to each other ...
... – As nebula contracts, a small star is formed • Called a protostar – Eventually, the protostar will begin nuclear FUSION • Hydrogen protons attract to each other ...
PH607lec12
... tidal forces from the central black-hole to prevent their formation. They are much too young to have migrated far, but it seems even more improbable that they formed in their current orbits where the tidal forces of the black hole act. This paradox of youth is even more remarkable for stars that are ...
... tidal forces from the central black-hole to prevent their formation. They are much too young to have migrated far, but it seems even more improbable that they formed in their current orbits where the tidal forces of the black hole act. This paradox of youth is even more remarkable for stars that are ...
Full 11x8.5" Calendar, High Resolution - Chandra X
... This deep image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory shows the Vela pulsar, a neutron star that was formed when a massive star collapsed. In the upper right is a fast moving jet of particles produced by the pulsar. The pulsar is about 1,000 light years from Earth, and makes over 11 complete rotatio ...
... This deep image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory shows the Vela pulsar, a neutron star that was formed when a massive star collapsed. In the upper right is a fast moving jet of particles produced by the pulsar. The pulsar is about 1,000 light years from Earth, and makes over 11 complete rotatio ...
Correct answers shown in boldface. Be sure to write your name and
... a. results in broadening the spectral lines from active nuclei in the cluster b. causes the cluster to glow all over as things fall into it c. makes the emission lines of the galaxies in the cluster shift wavelength significantly due to relativity d. is almost all concentrated in its giant central g ...
... a. results in broadening the spectral lines from active nuclei in the cluster b. causes the cluster to glow all over as things fall into it c. makes the emission lines of the galaxies in the cluster shift wavelength significantly due to relativity d. is almost all concentrated in its giant central g ...
Document
... object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to determine their distance from Earth ...
... object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to determine their distance from Earth ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
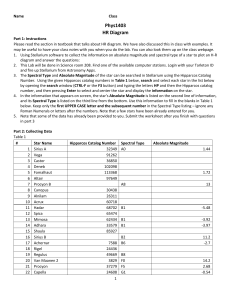
... 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on absolute magnitude and spectral type of a star to plot an H-R diagram and answer the questions: 2. This Lab will be done in Science room 208. Find one of the available computer stations. Login with your Tarleton ID and fire up Stellarium fro ...
... 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on absolute magnitude and spectral type of a star to plot an H-R diagram and answer the questions: 2. This Lab will be done in Science room 208. Find one of the available computer stations. Login with your Tarleton ID and fire up Stellarium fro ...
Wednesday, November 7, 2007
... proceeding more efficiently. Conversion of (stored) energy from mass into heat & light proceeds faster, so the star has a higher luminosity. We’re talking about the theory of the structure of a star here, because we are using physical laws to draw conclusions about ...
... proceeding more efficiently. Conversion of (stored) energy from mass into heat & light proceeds faster, so the star has a higher luminosity. We’re talking about the theory of the structure of a star here, because we are using physical laws to draw conclusions about ...
Mr. Scharff
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
Light as a Wave (1) Distances to Stars
... The flux received from the light is proportional to its intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): ...
... The flux received from the light is proportional to its intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): ...
Binary Star - Armagh Observatory
... diameter is about 100 times bigger than it was originally, and has become cooler (the surface temperature is under 6,500 K). They are frequently orange in colour. Betelgeuse is a red giant. It is about 20 times as massive as the Sun, but about 14,000 times brighter than the Sun, and about 600 light- ...
... diameter is about 100 times bigger than it was originally, and has become cooler (the surface temperature is under 6,500 K). They are frequently orange in colour. Betelgeuse is a red giant. It is about 20 times as massive as the Sun, but about 14,000 times brighter than the Sun, and about 600 light- ...
Slide 1 - Physics @ IUPUI
... • RR Lyrae – lower mass stars after they undergo their Helium flash (the sun will do this someday). • RR Lyrae are Horizontal Branch stars. • Metal rich and Metal poor Cepheid variables (Type I and II). • These are the higher mass stars which pass back and forth through the instability strip. ...
... • RR Lyrae – lower mass stars after they undergo their Helium flash (the sun will do this someday). • RR Lyrae are Horizontal Branch stars. • Metal rich and Metal poor Cepheid variables (Type I and II). • These are the higher mass stars which pass back and forth through the instability strip. ...
Stellar Evolution
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
The Milky Way: Home to Star Clusters
... was the original extent of the galaxy, and that this was created first, from the primordial gas that eventually collapsed in on itself, also demonstrated by the old stars contained within the globular clusters. This matter condensed to create the central bulge, which ultimately began to rotate, crea ...
... was the original extent of the galaxy, and that this was created first, from the primordial gas that eventually collapsed in on itself, also demonstrated by the old stars contained within the globular clusters. This matter condensed to create the central bulge, which ultimately began to rotate, crea ...
Solutions
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
Document
... begins to clump together. The young star can react quite violently, and produce a very strong stellar wind. Some of the clumps are large and dense enough to avoid being blown away by this wind, they likely become planets. 6. A star spends most of its life burning hydrogen into helium in its core and ...
... begins to clump together. The young star can react quite violently, and produce a very strong stellar wind. Some of the clumps are large and dense enough to avoid being blown away by this wind, they likely become planets. 6. A star spends most of its life burning hydrogen into helium in its core and ...
Practice Questions for Final
... C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However, they will fade from view as the light they emit (or reflect) becomes more and more redshifted. ...
... C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However, they will fade from view as the light they emit (or reflect) becomes more and more redshifted. ...
- Amazing Space, STScI
... center of the star at 1.5 million miles per hour. At the bottom-left corner of the image is an irregularly shaped object called a dark globule. These are dark clouds of dust and gas that resist erosion by the stellar winds. New stars may be forming in their depths. Moving along the lower-left quadra ...
... center of the star at 1.5 million miles per hour. At the bottom-left corner of the image is an irregularly shaped object called a dark globule. These are dark clouds of dust and gas that resist erosion by the stellar winds. New stars may be forming in their depths. Moving along the lower-left quadra ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
Superwind - The University of Sydney
... The team includes scientists from the Universities of Manchester, Sydney, ParisDiderot, Oxford and Macquarie University, New South Wales. They used the Very Large Telescope in Chile, operated by the European Southern Observatory. At the resolution used by the scientists, one could, from the UK, dist ...
... The team includes scientists from the Universities of Manchester, Sydney, ParisDiderot, Oxford and Macquarie University, New South Wales. They used the Very Large Telescope in Chile, operated by the European Southern Observatory. At the resolution used by the scientists, one could, from the UK, dist ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.