Nebulae
... Trigger of Star Birth: Shock Waves from O and B Stars • The most massive protostars to form out of a dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II ...
... Trigger of Star Birth: Shock Waves from O and B Stars • The most massive protostars to form out of a dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
Implications of the Search and Discovery
... Where to look in galaxy? • Disk region of galaxy – Population I stars that have access to heavy elements during formation • Star like our Sun worked at least once ...
... Where to look in galaxy? • Disk region of galaxy – Population I stars that have access to heavy elements during formation • Star like our Sun worked at least once ...
Stars - Science
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... A white dwarf is what stars like the Sun become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel. Near the end of its nuclear burning stage, this type of star expels most of its outer material. Only the hot core of the star remains. This core becomes a very hot white dwarf, with a temperature exceeding ...
... A white dwarf is what stars like the Sun become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel. Near the end of its nuclear burning stage, this type of star expels most of its outer material. Only the hot core of the star remains. This core becomes a very hot white dwarf, with a temperature exceeding ...
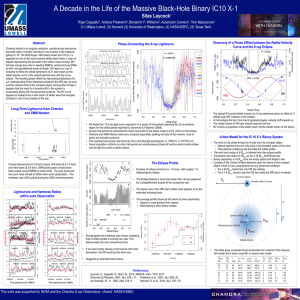
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... A white dwarf is what stars like the Sun become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel. Near the end of its nuclear burning stage, this type of star expels most of its outer material. Only the hot core of the star remains. This core becomes a very hot white dwarf, with a temperature exceeding ...
... A white dwarf is what stars like the Sun become after they have exhausted their nuclear fuel. Near the end of its nuclear burning stage, this type of star expels most of its outer material. Only the hot core of the star remains. This core becomes a very hot white dwarf, with a temperature exceeding ...
Lecture 10 - Concord University
... Mass Transfer in Binaries The scenario that leads to nova explosions can produce an even wilder phenomenon. In the early 1900s `novae’ were sometimes observed in other galaxies and were used to help set the distances to galaxies. But, when it became clear that even the nearest galaxies were much ...
... Mass Transfer in Binaries The scenario that leads to nova explosions can produce an even wilder phenomenon. In the early 1900s `novae’ were sometimes observed in other galaxies and were used to help set the distances to galaxies. But, when it became clear that even the nearest galaxies were much ...
Stars Study Guide KEY
... Gravity pulls the gas and dust in a nebula together. A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts 2. How is the mass of a star related to how long the star will live? How long the star lasts depends upon how massive it is. The more mass a star has, the fa ...
... Gravity pulls the gas and dust in a nebula together. A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts 2. How is the mass of a star related to how long the star will live? How long the star lasts depends upon how massive it is. The more mass a star has, the fa ...
Eclipsing Binaries
... In the 1900s, scientists didn’t know why stars had different line strengths. Not knowing the physical reason, they just classified them from A to O. A-stars had the strongest hydrogen lines. O-stars the weakest. Later they found many classifications were actually the same ...
... In the 1900s, scientists didn’t know why stars had different line strengths. Not knowing the physical reason, they just classified them from A to O. A-stars had the strongest hydrogen lines. O-stars the weakest. Later they found many classifications were actually the same ...
spectral-type
... In the 1900s, scientists didn’t know why stars had different line strengths. Not knowing the physical reason, they just classified them from A to O. A-stars had the strongest hydrogen lines. O-stars the weakest. Later they found many classifications were actually the same ...
... In the 1900s, scientists didn’t know why stars had different line strengths. Not knowing the physical reason, they just classified them from A to O. A-stars had the strongest hydrogen lines. O-stars the weakest. Later they found many classifications were actually the same ...
Final review - Physics and Astronomy
... R* =The rate of formation of stars suitable for the development of intelligent life. fp = The fraction of those stars with planetary systems. ne = The number of planets, per solar system, with an environment suitable for life. fl = The fraction of suitable planets on which life actually appears. fi ...
... R* =The rate of formation of stars suitable for the development of intelligent life. fp = The fraction of those stars with planetary systems. ne = The number of planets, per solar system, with an environment suitable for life. fl = The fraction of suitable planets on which life actually appears. fi ...
Black Holes, Part 9, Star Eaters
... the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
... the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
Chapter 15 part 1
... To compare intrinsic, or absolute, properties of stars, however, astronomers imagine looking at all stars from a standard distance of 10 pc (arbitrary choice). Because the distance is fixed in this definition, absolute magnitude is a measure of a star’s absolute brightness, or luminosity. ...
... To compare intrinsic, or absolute, properties of stars, however, astronomers imagine looking at all stars from a standard distance of 10 pc (arbitrary choice). Because the distance is fixed in this definition, absolute magnitude is a measure of a star’s absolute brightness, or luminosity. ...
The galaxies that host powerful radio sources
... • Optically faint (R>25). • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
... • Optically faint (R>25). • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
About SDSS - Astro Projects
... If you look up at the night sky from a dark location you will see a few thousand stars, probably a planet or two, possibly the Moon, and occasionally a comet or shooting star (meteorite). With a pair of binoculars the number of stars you can see rises to about 10,000, and with a 15 cm telescope more ...
... If you look up at the night sky from a dark location you will see a few thousand stars, probably a planet or two, possibly the Moon, and occasionally a comet or shooting star (meteorite). With a pair of binoculars the number of stars you can see rises to about 10,000, and with a 15 cm telescope more ...
SGL 9 NGC Galaxy magnitude 9/10 observing challenge Up for
... Once you have seen a few spirals face on you will find you can identify them even before you have looked them up on google! Object 3 – Leo triplet (Taki page 50) No not the famous one. Look half way between delta and theta Leo and then a fraction left. This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are ...
... Once you have seen a few spirals face on you will find you can identify them even before you have looked them up on google! Object 3 – Leo triplet (Taki page 50) No not the famous one. Look half way between delta and theta Leo and then a fraction left. This group NGC3605 / NGC 3607 and NGC 3608 are ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... – These objects are similar to novae, but have two or more slightly smaller-amplitude outbursts during their recorded history. ...
... – These objects are similar to novae, but have two or more slightly smaller-amplitude outbursts during their recorded history. ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 45. Large stars evolve much more slowly than do small stars. 46. Only the most massive stars evolve to become black holes. 47. Hot stars evolve much more rapidly than do cool stars. 48. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushed in, towards the cente ...
... 45. Large stars evolve much more slowly than do small stars. 46. Only the most massive stars evolve to become black holes. 47. Hot stars evolve much more rapidly than do cool stars. 48. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushed in, towards the cente ...
Images from the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope
... The name ‘Cancer’ means ‘the crab’ in Latin. It is the faintest of the 12 zodiac constellations and contains some famous DSOs: the open cluster Praesepe, aka the Beehive Cluster (M44), and the open cluster M67. Cancer does not have any stars brighter than 4th mag. Stars α, δ, and γ Cancri lie close ...
... The name ‘Cancer’ means ‘the crab’ in Latin. It is the faintest of the 12 zodiac constellations and contains some famous DSOs: the open cluster Praesepe, aka the Beehive Cluster (M44), and the open cluster M67. Cancer does not have any stars brighter than 4th mag. Stars α, δ, and γ Cancri lie close ...
Photometric Surveys and Variable stars
... Gamma Doradus stars • sp. type mid-late F, lum. class V, Pop I • P: 8h - 3d (close to P(rot)!) • sometimes multiperiodic • g-mode pulsators (n < 0) The gamma Doradus class is a new designation (early 1990’s). Before they were discovered, they were sometimes unknowingly used as comp stars! ...
... Gamma Doradus stars • sp. type mid-late F, lum. class V, Pop I • P: 8h - 3d (close to P(rot)!) • sometimes multiperiodic • g-mode pulsators (n < 0) The gamma Doradus class is a new designation (early 1990’s). Before they were discovered, they were sometimes unknowingly used as comp stars! ...
AGN-Hubble
... You must use nearby galaxies to calibrate distance indicators that can be seen across the Universe. ...
... You must use nearby galaxies to calibrate distance indicators that can be seen across the Universe. ...
TAURUS ZODIAC CONSTELLATION In Greek mythology, Taurus
... local spiral arm to which the Sun belongs. The belt contains bright stars in many constellations including (in order going more or less eastward) Cepheus, Lacerta, Perseus, Orion, Canis Major, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux, Centaurus, Lupus, and Scorpius The Milky Way also passes through most of these ...
... local spiral arm to which the Sun belongs. The belt contains bright stars in many constellations including (in order going more or less eastward) Cepheus, Lacerta, Perseus, Orion, Canis Major, Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux, Centaurus, Lupus, and Scorpius The Milky Way also passes through most of these ...
Homework #2
... Consider a typical (Type II) supernova with Lpeak = 109 solar luminosities. (This kind comes from the death of a massive star and is more common than the brighter Type Ia supernovae discussed so far in class). At what distance, in parsecs, would that supernova have a brightness equal to that of the ...
... Consider a typical (Type II) supernova with Lpeak = 109 solar luminosities. (This kind comes from the death of a massive star and is more common than the brighter Type Ia supernovae discussed so far in class). At what distance, in parsecs, would that supernova have a brightness equal to that of the ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.