
File
... Gasses start to expand. The outer layers begin to cool, causing a red color. We call this a ‘red giant’. ...
... Gasses start to expand. The outer layers begin to cool, causing a red color. We call this a ‘red giant’. ...
BrainPOP - The Science Spot
... pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a ____________ begins to generate _________. 2. The heat and pressure builds until __________ __________ reactions begin to take place inside the core. Gravity pulls _____________ ...
... pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a ____________ begins to generate _________. 2. The heat and pressure builds until __________ __________ reactions begin to take place inside the core. Gravity pulls _____________ ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Only 6 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky are closer to us than 10pc 14 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky must have absolute magnitude of at least 1.5 (20 times brighter than the Sun) Out of the 6000 stars visible, only 50 are dimmer than the Sun in absolute magnitude. Question: Is the Sun be ...
... Only 6 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky are closer to us than 10pc 14 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky must have absolute magnitude of at least 1.5 (20 times brighter than the Sun) Out of the 6000 stars visible, only 50 are dimmer than the Sun in absolute magnitude. Question: Is the Sun be ...
Sample Exam 3
... A) the Sun was near the middle of a disk-like system of millions of stars. B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer edge of a giant spiral nebula. D) other stars orbit the Sun but look faint because they are in the outer part of the ...
... A) the Sun was near the middle of a disk-like system of millions of stars. B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer edge of a giant spiral nebula. D) other stars orbit the Sun but look faint because they are in the outer part of the ...
File - greenscapes4you
... luminosity, but still much brighter than main sequence stars of same spectral type. The hot, white, small radius stars near the lower left are called white dwarfs. Giants and Supergiants are stars nearing the ends of their lives because they have already exhausted their core hydrogen. Surprisingly, ...
... luminosity, but still much brighter than main sequence stars of same spectral type. The hot, white, small radius stars near the lower left are called white dwarfs. Giants and Supergiants are stars nearing the ends of their lives because they have already exhausted their core hydrogen. Surprisingly, ...
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1. Two stars
... The HR diagram is a clock for the age of star clusters. We can look at the HR diagram to see which are the bluest stars burning on the main sequence. The bluest stars correspond to the most massive stars that are still burning hydrogen on the main sequence. (More massive stars burn faster, hotter an ...
... The HR diagram is a clock for the age of star clusters. We can look at the HR diagram to see which are the bluest stars burning on the main sequence. The bluest stars correspond to the most massive stars that are still burning hydrogen on the main sequence. (More massive stars burn faster, hotter an ...
Document
... – Semimajor axis: “how far you are away from that something” – Mass: “how much gravity is pulling you around in orbit” ...
... – Semimajor axis: “how far you are away from that something” – Mass: “how much gravity is pulling you around in orbit” ...
here
... Distances measured in fractions of a parsec usually involve objects within a single star system. So, for example: ...
... Distances measured in fractions of a parsec usually involve objects within a single star system. So, for example: ...
Characteristics of Stars ppt.
... it’s not hot or cool it’s not large or small. We can compare stars by color, temperature, size, brightness and spectrum. ...
... it’s not hot or cool it’s not large or small. We can compare stars by color, temperature, size, brightness and spectrum. ...
Aug 2015 supplement - Hermanus Astronomy
... encircles young stars in a disk. Over time, dust particles stick together until they build up bigger clumps. Eventually, these have enough mass that gravity becomes significant, and over millions of years the clumps crash together to make planets and moons. In our own solar system, this process took ...
... encircles young stars in a disk. Over time, dust particles stick together until they build up bigger clumps. Eventually, these have enough mass that gravity becomes significant, and over millions of years the clumps crash together to make planets and moons. In our own solar system, this process took ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... Pulsars in globular clusters: fast pulsars should be young but are actually old. Paradox resolved: Accretion spin-up. Maximum mass for neutron stars is somewhere around 3 M : collapse to black hole. Compare with Chandrasekhar Mass and Type Ia SN. \The" Binary Pulsar PSR 1913+16: Hulse & Taylor 1974 ...
... Pulsars in globular clusters: fast pulsars should be young but are actually old. Paradox resolved: Accretion spin-up. Maximum mass for neutron stars is somewhere around 3 M : collapse to black hole. Compare with Chandrasekhar Mass and Type Ia SN. \The" Binary Pulsar PSR 1913+16: Hulse & Taylor 1974 ...
Spectra of stars
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
OTA System Report For June 4, 2009 8:30 AM
... 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a single star (FGS 3 ...
... 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a single star (FGS 3 ...
Characterizing Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
The life of Stars
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
Navigation by the North Star - Science
... You can find the North Star by locating the two bowl stars of the Big Dipper. Follow those stars in a straight line to the first bright star you see. That is Polaris. ...
... You can find the North Star by locating the two bowl stars of the Big Dipper. Follow those stars in a straight line to the first bright star you see. That is Polaris. ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 24 Galaxies
... A rich cluster contains hundreds or even thousands of galaxies; a poor cluster, often called a group, may contain only a few dozen. A regular cluster has a nearly spherical shape with a central concentration of galaxies; in an irregular cluster, galaxies are distributed asymmetrically. ...
... A rich cluster contains hundreds or even thousands of galaxies; a poor cluster, often called a group, may contain only a few dozen. A regular cluster has a nearly spherical shape with a central concentration of galaxies; in an irregular cluster, galaxies are distributed asymmetrically. ...
Wadhurst Astronomical Society Newsletter May 2017
... degrees. This angle must be known to pico-metre accuracy. A human hair is about 10 pico-metres wide. Or to put another way it is the thickness of a pound coin when placed on the Moon and viewed from the Earth. It is expected to discover up to 8 extragalactic supernovae every day. GAIA will observe a ...
... degrees. This angle must be known to pico-metre accuracy. A human hair is about 10 pico-metres wide. Or to put another way it is the thickness of a pound coin when placed on the Moon and viewed from the Earth. It is expected to discover up to 8 extragalactic supernovae every day. GAIA will observe a ...
Small Wonders: Taurus
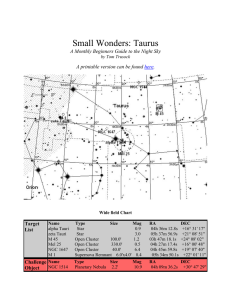
... been a little bull-headed when it comes to Taurus. It has the distinction of being one of the oldest recognized constellations in the night sky. According to some records, it's been in this form for 4000 years or longer. In ancient times, the appearance of the sun in the celestial bull - a plow anim ...
... been a little bull-headed when it comes to Taurus. It has the distinction of being one of the oldest recognized constellations in the night sky. According to some records, it's been in this form for 4000 years or longer. In ancient times, the appearance of the sun in the celestial bull - a plow anim ...
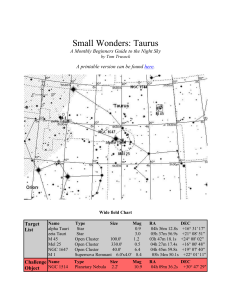
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... been a little bull-headed when it comes to Taurus. It has the distinction of being one of the oldest recognized constellations in the night sky. According to some records, it's been in this form for 4000 years or longer. In ancient times, the appearance of the sun in the celestial bull - a plow anim ...
... been a little bull-headed when it comes to Taurus. It has the distinction of being one of the oldest recognized constellations in the night sky. According to some records, it's been in this form for 4000 years or longer. In ancient times, the appearance of the sun in the celestial bull - a plow anim ...
Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date
... the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter primaries. Despite a large number of low mass stars present in our galaxy, masses and radii for these stars are st ...
... the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter primaries. Despite a large number of low mass stars present in our galaxy, masses and radii for these stars are st ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.





















![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)