Epsilon Aurigae Mystery and Opportunity
... The secondary orbits at the distance of Uranus from the Sun. Both components are 14-15 solar masses. ...
... The secondary orbits at the distance of Uranus from the Sun. Both components are 14-15 solar masses. ...
AST 207 Homework 7 Due 4 November 2011
... single star, Pickering’s spectrum showed it to be a binary star. You will need to refer to the spectrum shown in class on Oct. 28th. The speed of light is 3105 km/s. a. (3 pts.) What are the big ideas needed to answer this question? b. (2 pts.) Look at the drawing of the orbit of the binary star. B ...
... single star, Pickering’s spectrum showed it to be a binary star. You will need to refer to the spectrum shown in class on Oct. 28th. The speed of light is 3105 km/s. a. (3 pts.) What are the big ideas needed to answer this question? b. (2 pts.) Look at the drawing of the orbit of the binary star. B ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... Do you understand? Reading HertzsprungRussell Diagram Main sequence is a mass sequence Lifetime of stars Do you understand? HR Diagram of star cluster ...
... Do you understand? Reading HertzsprungRussell Diagram Main sequence is a mass sequence Lifetime of stars Do you understand? HR Diagram of star cluster ...
HR Diagram of One Solar Mass Evolution
... • All Type Ia supernovae have the same intrinsic brightness • Same absolute magnitude ...
... • All Type Ia supernovae have the same intrinsic brightness • Same absolute magnitude ...
HR Diagram of a Star Cluster
... (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from us. Then we can use their apparent magnitude (V) in place of the (preferred) absolute ...
... (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from us. Then we can use their apparent magnitude (V) in place of the (preferred) absolute ...
Slide 1
... In larger mass stars, alpha particles are added one by one, creating elements with an even atomic number. Sometimes this is called the triple alpha process as well, even though more than three alpha particles are involved. ...
... In larger mass stars, alpha particles are added one by one, creating elements with an even atomic number. Sometimes this is called the triple alpha process as well, even though more than three alpha particles are involved. ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and the inverse square law, the star’s luminosity and ...
... above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and the inverse square law, the star’s luminosity and ...
H-R Diagram Student
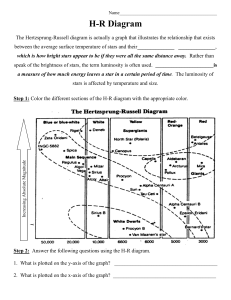
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
Life Cycle of a Star - Intervention Worksheet
... Black hole Supernova White dwarf Planetary nebula Main Sequence Black dwarf ...
... Black hole Supernova White dwarf Planetary nebula Main Sequence Black dwarf ...
Lives of Stars - Madison County Schools
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
... between brightness and temp. Hotter things are brighter Hotter temp = more energy is radiated. Bigger stars are brighter. Bigger surface area = more energy radiated. ...
Stars - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... • The Brightness of a star depends on three things: – Size – Temperature – Distance from us • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star is when viewed from Earth. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. (how bright we see it) ...
... • The Brightness of a star depends on three things: – Size – Temperature – Distance from us • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star is when viewed from Earth. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. (how bright we see it) ...
Stars
... • The Brightness of a star depends on three things: – Size – Temperature – Distance from us • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star is when viewed from Earth. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. (how bright we see it) ...
... • The Brightness of a star depends on three things: – Size – Temperature – Distance from us • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star is when viewed from Earth. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. (how bright we see it) ...
A Star is Born worksheet and key
... 10. How is a planetary nebula formed? When the outer layers of the red giant drift into space. 11. For how long do white dwarfs radiate their leftover heat? Billions of years. 12. How long is the life phase of a red supergiant? Millions of years. 13. What’s two differences between red giants and red ...
... 10. How is a planetary nebula formed? When the outer layers of the red giant drift into space. 11. For how long do white dwarfs radiate their leftover heat? Billions of years. 12. How long is the life phase of a red supergiant? Millions of years. 13. What’s two differences between red giants and red ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... What is the size of stars? Vary from the size of Earth to 2,000 times the size of the ...
... What is the size of stars? Vary from the size of Earth to 2,000 times the size of the ...
Introduction to the Earth
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
Ch.1, Sec.3 - Mapping the Stars
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
Stars - Montville.net
... A neutron star is about 20 km in diameter and has the mass of about 1.4 times that of our Sun. This means that a neutron star is so dense that on Earth, one teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! ...
... A neutron star is about 20 km in diameter and has the mass of about 1.4 times that of our Sun. This means that a neutron star is so dense that on Earth, one teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.