Measuring the Milky Way
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... • in spherical halo around centre of Galaxy Galactic (or open) clusters: • open, irregular, 102-103 stars; ...
... • in spherical halo around centre of Galaxy Galactic (or open) clusters: • open, irregular, 102-103 stars; ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the Main Sequence. ...
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the Main Sequence. ...
Measuring stars Part I
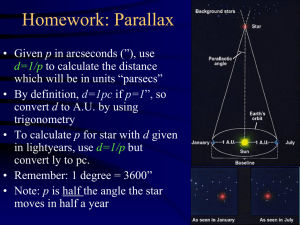
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
Wednesday, April 2 - Otterbein University
... The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
... The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
Chapter 9 / Adobe Acrobat Document
... 1. A spiral galaxy is roundish but flat with a bulge in the centre. It has major and minor spiral arms that come from the centre. An elliptical galaxy is oval or cigar shaped with no visible arm structure. An irregular galaxy does not have a regular shape. 2. Galaxies form when gravity causes a larg ...
... 1. A spiral galaxy is roundish but flat with a bulge in the centre. It has major and minor spiral arms that come from the centre. An elliptical galaxy is oval or cigar shaped with no visible arm structure. An irregular galaxy does not have a regular shape. 2. Galaxies form when gravity causes a larg ...
14 The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation
... Dust grains are known to be elongated, rather than spherical, because they polarize light passing through them. They also may be slightly conductive because they polarize and rotate radio waves. ...
... Dust grains are known to be elongated, rather than spherical, because they polarize light passing through them. They also may be slightly conductive because they polarize and rotate radio waves. ...
Ursa Major, the Great Bear
... “handle” of the dipper, it will lead to a bright orange star known as Arcturus in constellation Bootes. If we continue to extend this arc further south, we will reach Spica in Virgo and finally end up at constellation Corvus. This is known as “Follow the Arc”. Mizar (ζ) – the second star from the en ...
... “handle” of the dipper, it will lead to a bright orange star known as Arcturus in constellation Bootes. If we continue to extend this arc further south, we will reach Spica in Virgo and finally end up at constellation Corvus. This is known as “Follow the Arc”. Mizar (ζ) – the second star from the en ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... chases the bears around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
... chases the bears around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
Grand Tour Worksheet - School District of La Crosse
... 5. As of 1920’s the estimated size of the universe was: 6. How far is a light year? 7. What happened as early as the 1930’s? ...
... 5. As of 1920’s the estimated size of the universe was: 6. How far is a light year? 7. What happened as early as the 1930’s? ...
The Family of Stars
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
Earth`s Motion and Seasons
... Devices used to detect radio waves from objects in space. Most have curved, reflective surfaces that focus radio waves the way reflecting telescopes focus light. The larger the radio telescope the more radio waves it can collect. Other types of telescopes collect the shorter waves such as gamma rays ...
... Devices used to detect radio waves from objects in space. Most have curved, reflective surfaces that focus radio waves the way reflecting telescopes focus light. The larger the radio telescope the more radio waves it can collect. Other types of telescopes collect the shorter waves such as gamma rays ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... as far as we can see Cepheids – about 50 million ly • In 1920 Hubble used this technique to measure the distance to Andromeda (about 2 million ly) • Works best for periodic variables ...
... as far as we can see Cepheids – about 50 million ly • In 1920 Hubble used this technique to measure the distance to Andromeda (about 2 million ly) • Works best for periodic variables ...
Monday, April 15
... Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
... Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Identify the conditions necessary for fusion to occur inside a star. Describe the information that spectroscopy provides about stars. Relate the color of a star to its temperature. Explain the factors that determine the brightness of a star in the sky. Discuss the importance of the H-R diagram to as ...
... Identify the conditions necessary for fusion to occur inside a star. Describe the information that spectroscopy provides about stars. Relate the color of a star to its temperature. Explain the factors that determine the brightness of a star in the sky. Discuss the importance of the H-R diagram to as ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
Stellar Spire in the Eagle Nebula
... from a stellar nursery called the Eagle Nebula. The soaring tower is 9.5 light-years or about 57 trillion miles high, about twice the distance from our Sun to the next nearest star. Stars in the Eagle Nebula are born in clouds of cold hydrogen gas that reside in chaotic neighborhoods, where energy f ...
... from a stellar nursery called the Eagle Nebula. The soaring tower is 9.5 light-years or about 57 trillion miles high, about twice the distance from our Sun to the next nearest star. Stars in the Eagle Nebula are born in clouds of cold hydrogen gas that reside in chaotic neighborhoods, where energy f ...
Geller Slides on Contact with ET
... Where to look in galaxy? • Disk region of galaxy – Population I stars that have access to heavy elements during formation • Star like our Sun worked at least once ...
... Where to look in galaxy? • Disk region of galaxy – Population I stars that have access to heavy elements during formation • Star like our Sun worked at least once ...
File
... 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of these characteristics? Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then ...
... 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of these characteristics? Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Appears as a milky band of light across the sky • A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) • Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes from a combination of observation and comparison to other ...
... • Appears as a milky band of light across the sky • A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) • Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes from a combination of observation and comparison to other ...
Our Community`s Place Among the Stars
... through D to show the locations of stars that are: a. Hot and bright b. Hot and dim c. Cool and dim d. Cool and bright 2a. Plot the locations of the stars from Table 1. 3. Classify each of the stars. ...
... through D to show the locations of stars that are: a. Hot and bright b. Hot and dim c. Cool and dim d. Cool and bright 2a. Plot the locations of the stars from Table 1. 3. Classify each of the stars. ...
Russell Diagram
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
"Stars" Power Point notes
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three ...
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three ...
solutions
... pressure depends on the star’s surface gravity and therefore, roughly, on its size telling whether it is a giant, dwarf, or something in between. The size and surface brightness in turn yield the star’s luminosity (its total light output, or absolute magnitude) and often its evolutionary status (you ...
... pressure depends on the star’s surface gravity and therefore, roughly, on its size telling whether it is a giant, dwarf, or something in between. The size and surface brightness in turn yield the star’s luminosity (its total light output, or absolute magnitude) and often its evolutionary status (you ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.