Star signs and horoscopes
... is the part of the sky in which the Sun appears to move across the heavens (of course it is actually the Earth that moves). The zodiac is divided into 12 equal parts, each of which has its own star sign. Then explain that long ago, people thought there was a special meaning behind the movements and ...
... is the part of the sky in which the Sun appears to move across the heavens (of course it is actually the Earth that moves). The zodiac is divided into 12 equal parts, each of which has its own star sign. Then explain that long ago, people thought there was a special meaning behind the movements and ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
Star Fromation and ISM
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age – those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the main sequence. ...
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age – those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the main sequence. ...
Practice Questions for Exam 3
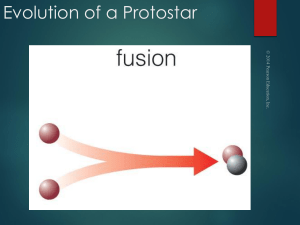
... C. The Sun initially began generating energy through nuclear fusion as it formed, but today it generates energy primarily through the sunspot cycle. D. As the Sun was forming, gravitational contraction increased the Sun's temperature until the core become hot enough for nuclear fusion, which ever si ...
... C. The Sun initially began generating energy through nuclear fusion as it formed, but today it generates energy primarily through the sunspot cycle. D. As the Sun was forming, gravitational contraction increased the Sun's temperature until the core become hot enough for nuclear fusion, which ever si ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... If a star is moving away from an observer, spectral lines are redshifted, or shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. An approaching star is blueshifted. ...
... If a star is moving away from an observer, spectral lines are redshifted, or shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. An approaching star is blueshifted. ...
Participant Handout - Math Machines Home
... a very large “red giant,” with a diameter about 600 times that of our Sun. (If our Sun were that large, it would engulf the Earth and extend well beyond the orbit of Mars.) The actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in ...
... a very large “red giant,” with a diameter about 600 times that of our Sun. (If our Sun were that large, it would engulf the Earth and extend well beyond the orbit of Mars.) The actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in ...
CASPEC Observations of the Most Metal-Deficient Main
... these stars may originate from lower initial masses. This raises the question: how small can the mass of a B[e] star in the MCs be? If future surveys confirm the presence of low mass B[e] stars in the MCs, this will have important implications for current models of massive star evolution in the Clou ...
... these stars may originate from lower initial masses. This raises the question: how small can the mass of a B[e] star in the MCs be? If future surveys confirm the presence of low mass B[e] stars in the MCs, this will have important implications for current models of massive star evolution in the Clou ...
Newfoundland Sky in Summer
... out in space. If we are viewing the stars on a moonlit night we may get the impression that the moon i s much larger than any of the stars. However, this is not so. The moon seems larger because it is much closer to us than even the nearest of the stars. ...
... out in space. If we are viewing the stars on a moonlit night we may get the impression that the moon i s much larger than any of the stars. However, this is not so. The moon seems larger because it is much closer to us than even the nearest of the stars. ...
The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... chemical testing of actual samples of stellar matter electromagnetic radiation spacecraft in orbit around distant stars both B and C above no data is used ...
... chemical testing of actual samples of stellar matter electromagnetic radiation spacecraft in orbit around distant stars both B and C above no data is used ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as a H II region. • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae fa ...
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as a H II region. • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae fa ...
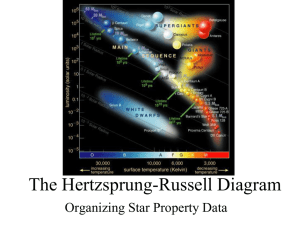
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... A: • Use the center of the vision to observe detail and color for bright object. • Use averted vision to detect/observe dim objects. More: • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and ...
... A: • Use the center of the vision to observe detail and color for bright object. • Use averted vision to detect/observe dim objects. More: • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and ...