Assignment 8 - utoledo.edu
... a. friction, as the atoms of the expelled shell rub against each other b. the explosion of the dying star c. ultraviolet radiation from the hot star at the center d. the fusion of hydrogen into helium in the shell e. the change of electrons and protons into neutrons ____ 22. After the core of a mass ...
... a. friction, as the atoms of the expelled shell rub against each other b. the explosion of the dying star c. ultraviolet radiation from the hot star at the center d. the fusion of hydrogen into helium in the shell e. the change of electrons and protons into neutrons ____ 22. After the core of a mass ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... prominent and brilliant star, Regulus, lying within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitud ...
... prominent and brilliant star, Regulus, lying within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitud ...
Shocking Truth about Massive Stars Lidia Oskinova Chandra’s First Decade of Discovery
... Our analysis indicates that star may be a FAST ROTATOR V rot sin i =4000 km/s. Current mass ~10 M ...
... Our analysis indicates that star may be a FAST ROTATOR V rot sin i =4000 km/s. Current mass ~10 M ...
17 The Deaths of Stars
... leaving stars of reduced mass called white dwarfs and remnants of expanding gases called planetary nebulae. High-mass stars die explosively as type II supernovae leaving cores of reduced mass, neutron stars or stellar black holes, and remnants of expanding gas and dust called a supernova remnants. ...
... leaving stars of reduced mass called white dwarfs and remnants of expanding gases called planetary nebulae. High-mass stars die explosively as type II supernovae leaving cores of reduced mass, neutron stars or stellar black holes, and remnants of expanding gas and dust called a supernova remnants. ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
Ch 19 Directed Reading
... 13. top of modern H-R diagram 14. bottom of modern H-R diagram 15. right side of modern H-R diagram 16. left side of modern H-R diagram ...
... 13. top of modern H-R diagram 14. bottom of modern H-R diagram 15. right side of modern H-R diagram 16. left side of modern H-R diagram ...
answers2006_07_BC
... H to He in core. This stage lasts for ~90% of star’s life, which ex-6. When core He runs out, star starts fusing He plains why most stars are on MS 2. When core H exhausted, starin shell around core, becoming a giant again shrinks under gravity, heating up until H outside core starts to fuse. ...
... H to He in core. This stage lasts for ~90% of star’s life, which ex-6. When core He runs out, star starts fusing He plains why most stars are on MS 2. When core H exhausted, starin shell around core, becoming a giant again shrinks under gravity, heating up until H outside core starts to fuse. ...
Lecture 17, PPT version
... All of these are stable (neither expanding nor contracting), so long as they are “left alone”. Pressure in white dwarf and neutron star is somewhat exotic (not normal gas pressure or radiation pressure) due to their highly-compressed states. ...
... All of these are stable (neither expanding nor contracting), so long as they are “left alone”. Pressure in white dwarf and neutron star is somewhat exotic (not normal gas pressure or radiation pressure) due to their highly-compressed states. ...
Be Stars
... Be stars have strong emission lines of Hydrogen in their spectrum. A characteristic of a Be star is that it has optical linear polarization and often their infra-red radiation is much greater than other B-type stars. This infra-red radiation is called infrared excess. Be stars show emission lines wh ...
... Be stars have strong emission lines of Hydrogen in their spectrum. A characteristic of a Be star is that it has optical linear polarization and often their infra-red radiation is much greater than other B-type stars. This infra-red radiation is called infrared excess. Be stars show emission lines wh ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Energy radiated per cm2 of area on surface every second T 4 (T = temperature at surface) And: Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperatur ...
... Energy radiated per cm2 of area on surface every second T 4 (T = temperature at surface) And: Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperatur ...
Stars - Mrs. Tosh`s class
... The entire sky is lit up for weeks. The temperature can be more than 100 billion degrees. The iron atoms fuse into uranium. ...
... The entire sky is lit up for weeks. The temperature can be more than 100 billion degrees. The iron atoms fuse into uranium. ...
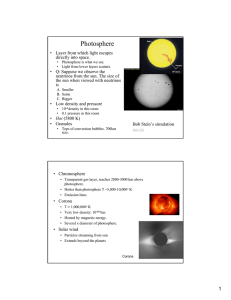
Photosphere
... Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. Luminosity (Lsun) Î ...
... Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. Luminosity (Lsun) Î ...
Brock physics - Brock University
... 10. The protostar phase of a star’s life is (a) * shorter for higher mass stars. (b) longer for higher mass stars. (c) [It depends on the size of the molecules comprising the star.] (d) [It depends on the whims of the head office of ProtoStar Inc.] 11. A brown dwarf is (a) a character in the Disney ...
... 10. The protostar phase of a star’s life is (a) * shorter for higher mass stars. (b) longer for higher mass stars. (c) [It depends on the size of the molecules comprising the star.] (d) [It depends on the whims of the head office of ProtoStar Inc.] 11. A brown dwarf is (a) a character in the Disney ...






![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)