C H A P T E R 2
... appears to us when viewing the star from here on Earth. Apparent visual magnitude does not take into account any corrections for the star's distance, size, temperature, or the amount of dust between us and the star. It is simply the brightness as it appears to us in the night sky. ...
... appears to us when viewing the star from here on Earth. Apparent visual magnitude does not take into account any corrections for the star's distance, size, temperature, or the amount of dust between us and the star. It is simply the brightness as it appears to us in the night sky. ...
DTU_9e_ch13
... A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star with a powerful magnetic field that makes it a source of periodic radio and other electromagnetic pulses. Energy pours out of the polar regions of the neutron star in intense beams that sweep across the sky. ...
... A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star with a powerful magnetic field that makes it a source of periodic radio and other electromagnetic pulses. Energy pours out of the polar regions of the neutron star in intense beams that sweep across the sky. ...
Comet Lulin - indstate.edu
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
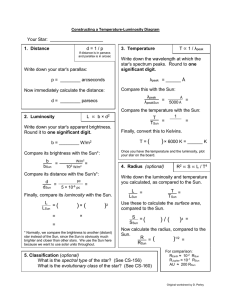
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... number of false positive transit detections (based on statistics to date, approximately 95% of the initial HATNet transit detections turn out to be false positives; see for example Latham et al. 2009). These false positives typically involve multiple star systems which produce light curves derived f ...
... number of false positive transit detections (based on statistics to date, approximately 95% of the initial HATNet transit detections turn out to be false positives; see for example Latham et al. 2009). These false positives typically involve multiple star systems which produce light curves derived f ...
A New Variable Star in Perseus
... robotic telescope operated without filters. A code of Schwarzenberg-Czerny (1989, 1996) was used in order to find the period of variable star. The period of variable star was determined as P=0d.55120.0005 using the first observational point as an initial epoch. Multi-colour observations of GSC 3692 ...
... robotic telescope operated without filters. A code of Schwarzenberg-Czerny (1989, 1996) was used in order to find the period of variable star. The period of variable star was determined as P=0d.55120.0005 using the first observational point as an initial epoch. Multi-colour observations of GSC 3692 ...
ppt
... • The V band gives magnitudes closely corresponding to those seen by the human eye • When an apparent magnitude is given without any further qualification, it is usually the V magnitude that is meant, more or less the same as visual magnitude. ...
... • The V band gives magnitudes closely corresponding to those seen by the human eye • When an apparent magnitude is given without any further qualification, it is usually the V magnitude that is meant, more or less the same as visual magnitude. ...
death_low_mass
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
Chapter 12 - Indiana State University
... understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Theref ...
... understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Theref ...
Solutions
... (c) No. Refer back to problem 1. Most of the stars in a globular cluster are low-mass main sequence stars who are burning their nuclear fuel slowly enough that they haven’t yet had time to leave the main sequence. In contrast, most of the light is coming from the most luminous stars (which in this ...
... (c) No. Refer back to problem 1. Most of the stars in a globular cluster are low-mass main sequence stars who are burning their nuclear fuel slowly enough that they haven’t yet had time to leave the main sequence. In contrast, most of the light is coming from the most luminous stars (which in this ...
ppt
... R: spectral resolving power S/N: signal to noise ratio Dl : wavelength coverage of spectrograph in Angstroms For R=110.000, S/N=150, Dl=2000 Å, s = 2 m/s ...
... R: spectral resolving power S/N: signal to noise ratio Dl : wavelength coverage of spectrograph in Angstroms For R=110.000, S/N=150, Dl=2000 Å, s = 2 m/s ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
FREE Sample Here
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
Letot STELLAR EVOLUTION By Kyle Letot Grade Level: 6
... Students will blow up their balloons a little larger to create a giant star. Here we will pause as I explain that as the star dies, it’ll continue to expand even larger. We will blow up our balloon more at this point. I’ll say that the Blue Supergiants burn helium giving their bluish tint and expand ...
... Students will blow up their balloons a little larger to create a giant star. Here we will pause as I explain that as the star dies, it’ll continue to expand even larger. We will blow up our balloon more at this point. I’ll say that the Blue Supergiants burn helium giving their bluish tint and expand ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
FREE Sample Here
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
... and planets and other celestial events control the events in our lives. These ideas have no scientific basis and have repeatedly been tested for accuracy and have repeatedly failed. Such methods or theories with no scientific basis are therefore classified under pseudoscience. 16. How Do We Know? – ...
Leaving the Main Sequence
... 5. Supernova explosion - Core of iron grows until it can not support itself under its own weight. So compressed that protons and electrons join to form neutrons. Core shrinks instantaneously. Rest of star falls in, then rebounds off of neutron star or black hole created in core collapse. Rebound is ...
... 5. Supernova explosion - Core of iron grows until it can not support itself under its own weight. So compressed that protons and electrons join to form neutrons. Core shrinks instantaneously. Rest of star falls in, then rebounds off of neutron star or black hole created in core collapse. Rebound is ...