Stars in the night Sky - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the nadir, direct ...
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the nadir, direct ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... above the horizon at sunset so observe Saturn as soon as you can this month, in the south-west. Uranus is at opposition on the 15th and is visible throughout the night this month. At a magnitude of 5.70 it may well be seen with binoculars. A small telescope might show a blue hue, but since Uranus us ...
... above the horizon at sunset so observe Saturn as soon as you can this month, in the south-west. Uranus is at opposition on the 15th and is visible throughout the night this month. At a magnitude of 5.70 it may well be seen with binoculars. A small telescope might show a blue hue, but since Uranus us ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... another another possibility: spectral classes. Stars are classified according to their spectral class which consists of a letter and a number. This historical classification is based on the strength of different spectral lines found in the spectra of the stars. It turned out later that these spectra ...
... another another possibility: spectral classes. Stars are classified according to their spectral class which consists of a letter and a number. This historical classification is based on the strength of different spectral lines found in the spectra of the stars. It turned out later that these spectra ...
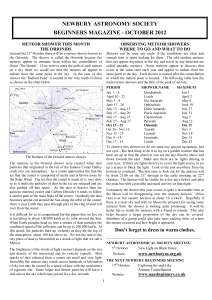
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... Very few constellations look like the characters after which they are named. Cygnus the Swan, Leo the Lion and Orion the Hunter are perhaps exceptions and do (with a little imagination) look remotely like those characters. The stars making up the constellations are not generally physically associate ...
... Very few constellations look like the characters after which they are named. Cygnus the Swan, Leo the Lion and Orion the Hunter are perhaps exceptions and do (with a little imagination) look remotely like those characters. The stars making up the constellations are not generally physically associate ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... location on the Earth and to see the celestial sphere move overhead. The Celestial Sphere Ancient astronomers believed that the Earth was at the center of an enormous Celestial Sphere, to which the stars, Sun, Moon and planets were fixed. For purposes of finding one's way around the sky, this simple ...
... location on the Earth and to see the celestial sphere move overhead. The Celestial Sphere Ancient astronomers believed that the Earth was at the center of an enormous Celestial Sphere, to which the stars, Sun, Moon and planets were fixed. For purposes of finding one's way around the sky, this simple ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... elements to burn at even higher temperatures, and causing sun-like stars to grow into red giants. Even though the cores of both hydrogen-burning and helium-burning stars have consistent, steady energy outputs, our sun's overall brightness varies by just ~0.1%, while red giants can have their brightn ...
... elements to burn at even higher temperatures, and causing sun-like stars to grow into red giants. Even though the cores of both hydrogen-burning and helium-burning stars have consistent, steady energy outputs, our sun's overall brightness varies by just ~0.1%, while red giants can have their brightn ...
Stars - WhatisOutThere
... brighter than the faint glow coming from the stars. If you were standing on the moon for example, you would be able to see the stars both day and night. This is because there is no atmosphere on the moon, meaning that it is always dark. Therefore you can see the stars. ...
... brighter than the faint glow coming from the stars. If you were standing on the moon for example, you would be able to see the stars both day and night. This is because there is no atmosphere on the moon, meaning that it is always dark. Therefore you can see the stars. ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... are more diverse and complicated than this diagram would lead you to believe. For instance, there are many more stellar classes than OBAFGKM; however for simplicity’s sake, only the classes that contain a large majority are shown. Absolute magnitude – the intrinsic brightness of stars – is similar ...
... are more diverse and complicated than this diagram would lead you to believe. For instance, there are many more stellar classes than OBAFGKM; however for simplicity’s sake, only the classes that contain a large majority are shown. Absolute magnitude – the intrinsic brightness of stars – is similar ...
Polaris
... about 2400 AU (360 billion kilometers, or 224 billion miles). Polaris B can be seen with even a modest telescope and was first noticed by William Herschel in 1780. In 1929, it was discovered by examining the spectrum of Polaris A that it had another very close dwarf companion (variously α UMi P, α U ...
... about 2400 AU (360 billion kilometers, or 224 billion miles). Polaris B can be seen with even a modest telescope and was first noticed by William Herschel in 1780. In 1929, it was discovered by examining the spectrum of Polaris A that it had another very close dwarf companion (variously α UMi P, α U ...
Lecture 3
... • The parallax effect is the apparent motion of a nearby object compared to distant background objects because of a change in viewing angle. • Put a finger in front of your nose and watch it move with respect to the back of the room as you look through one eye and then the other. ...
... • The parallax effect is the apparent motion of a nearby object compared to distant background objects because of a change in viewing angle. • Put a finger in front of your nose and watch it move with respect to the back of the room as you look through one eye and then the other. ...