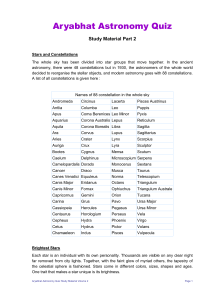
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars
... ! RA (right ascension) tells you when your object is up. • 12 hours is up highest Mar 21 • 0 hours is up highest Sept 21 ! DEC (declination) tells you how far away from the north pole. Polaris is at +90. Anything below 0 degrees is hard to observe from the northern hemisphere. ! Spectral types and ...
... ! RA (right ascension) tells you when your object is up. • 12 hours is up highest Mar 21 • 0 hours is up highest Sept 21 ! DEC (declination) tells you how far away from the north pole. Polaris is at +90. Anything below 0 degrees is hard to observe from the northern hemisphere. ! Spectral types and ...
H-RDiagramSE
... 5. Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer par ...
... 5. Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer par ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B PMS star
... massive nearby star-forming regions in the Galaxy (Hoffmeister et al. 2008; Broos et al. 2007; Povich et al. 2009). For the “normal” OB stars Hanson et al. (1997) found a good correspondence between the optical and K -band spectra, but the massive YSO optical spectra remained inconclusive. For four ...
... massive nearby star-forming regions in the Galaxy (Hoffmeister et al. 2008; Broos et al. 2007; Povich et al. 2009). For the “normal” OB stars Hanson et al. (1997) found a good correspondence between the optical and K -band spectra, but the massive YSO optical spectra remained inconclusive. For four ...
The Sun: Example of Radiation Laws
... in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernova was 180,000 lt.-yrs. from the Earth. Radiactive Ni, Co and Ti nuclei were also ...
... in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernova was 180,000 lt.-yrs. from the Earth. Radiactive Ni, Co and Ti nuclei were also ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... dead carbon core shrinks under its weight gravity pressure and heat heats helium shell surrounding core fusion of hydrogen surrounding helium shell star again puffs out to red giant Sun-like or smaller stars: terminal stage heavier stars: helium shell flashes pulsation (as in Cephied variable star ...
... dead carbon core shrinks under its weight gravity pressure and heat heats helium shell surrounding core fusion of hydrogen surrounding helium shell star again puffs out to red giant Sun-like or smaller stars: terminal stage heavier stars: helium shell flashes pulsation (as in Cephied variable star ...
THE PROPERTIES OF MAIN-SEQUENCE STARS - Cosmos
... in the Michigan catalogues and (ii) had spectroscopic parallaxes that placed them within 80 pc of the Sun. Of these, 3727 are well determined as luminosity class V and actually lie within 100 pc. From this subsample we can determine the distribution in MV of mainsequence stars of given spectral type ...
... in the Michigan catalogues and (ii) had spectroscopic parallaxes that placed them within 80 pc of the Sun. Of these, 3727 are well determined as luminosity class V and actually lie within 100 pc. From this subsample we can determine the distribution in MV of mainsequence stars of given spectral type ...
Big Bear Valley Astronomical Society
... connected to Sirius as the constellation itself did not take on its current form until Roman times. Sirius is a hot white star that will shine brightly for a long time to come. It is also a known binary system, with a tiny white dwarf star, coloquially known as 'the Pup', circling the brighter prima ...
... connected to Sirius as the constellation itself did not take on its current form until Roman times. Sirius is a hot white star that will shine brightly for a long time to come. It is also a known binary system, with a tiny white dwarf star, coloquially known as 'the Pup', circling the brighter prima ...
Spectral Classification: The First Step in Quantitative Spectral Analysis
... • The spectral type is obtained solely through comparison with standards • Theory & external sources of information are not used in the determination of the spectral type If these two principles are followed, the spectral type can serve as the beginning point for further spectral analysis. ...
... • The spectral type is obtained solely through comparison with standards • Theory & external sources of information are not used in the determination of the spectral type If these two principles are followed, the spectral type can serve as the beginning point for further spectral analysis. ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... 1 parsec is the distance to a star that would show 1 arcsec of parallax. (206 265 AU) ...
... 1 parsec is the distance to a star that would show 1 arcsec of parallax. (206 265 AU) ...
Stellar Classification - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... – R: Formerly a class on its own representing the carbon star equivalent of Class K stars – N: Formerly a class on its own representing the carbon star equivalent of Class M stars • S: Similar to Class M stars, but with zirconium oxide replacing the regular titanium oxide. ...
... – R: Formerly a class on its own representing the carbon star equivalent of Class K stars – N: Formerly a class on its own representing the carbon star equivalent of Class M stars • S: Similar to Class M stars, but with zirconium oxide replacing the regular titanium oxide. ...
ted_2012_power_of_design
... steps on the moon, achieving what President John F. Kennedy called “the most hazardous and dangerous and greatest adventure on which man has ever embarked.” ...
... steps on the moon, achieving what President John F. Kennedy called “the most hazardous and dangerous and greatest adventure on which man has ever embarked.” ...
What is a star?
... • Stars have different sizes, ranging from 1/100 the size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple star systems. ...
... • Stars have different sizes, ranging from 1/100 the size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple star systems. ...
Star - Astrophysics
... These are moderate mass stars (e.g. Sirius’ companion Sirius B with M = 1.05M), but with very high temperatures ( ~30000 K) and very low luminosities (~3 x 10−3L) – hence their position in the H-R diagram. These values imply radii ~7 x 10−3R ~5000km and therefore a density 3 x 109kg m−3. They are ...
... These are moderate mass stars (e.g. Sirius’ companion Sirius B with M = 1.05M), but with very high temperatures ( ~30000 K) and very low luminosities (~3 x 10−3L) – hence their position in the H-R diagram. These values imply radii ~7 x 10−3R ~5000km and therefore a density 3 x 109kg m−3. They are ...
QDSpaperFred1.tex
... between the infrared excess of space colonies and naturally occurring dust or debris. There are two approaches to this discrimination: the temperature range of the source and the age of the star. The temperature of the dust is determined by the distance from the star and the size and composition of ...
... between the infrared excess of space colonies and naturally occurring dust or debris. There are two approaches to this discrimination: the temperature range of the source and the age of the star. The temperature of the dust is determined by the distance from the star and the size and composition of ...
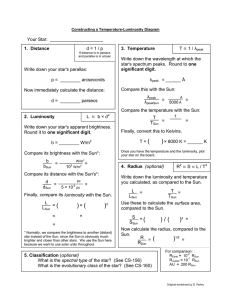
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...